YMatrix Architecture
YMatrix adopts a Share-nothing parallel architecture. Its core characteristic is that each node operates independently, without sharing memory or storage, and nodes collaborate only through network communication. This architecture is widely used in distributed databases, big data systems, and high-concurrency web services.
Basic Architecture
A complete YMatrix production cluster includes:
- 1 Master node
- 1 Standby Master node
- N Data nodes (each running multiple primary and mirror instances)
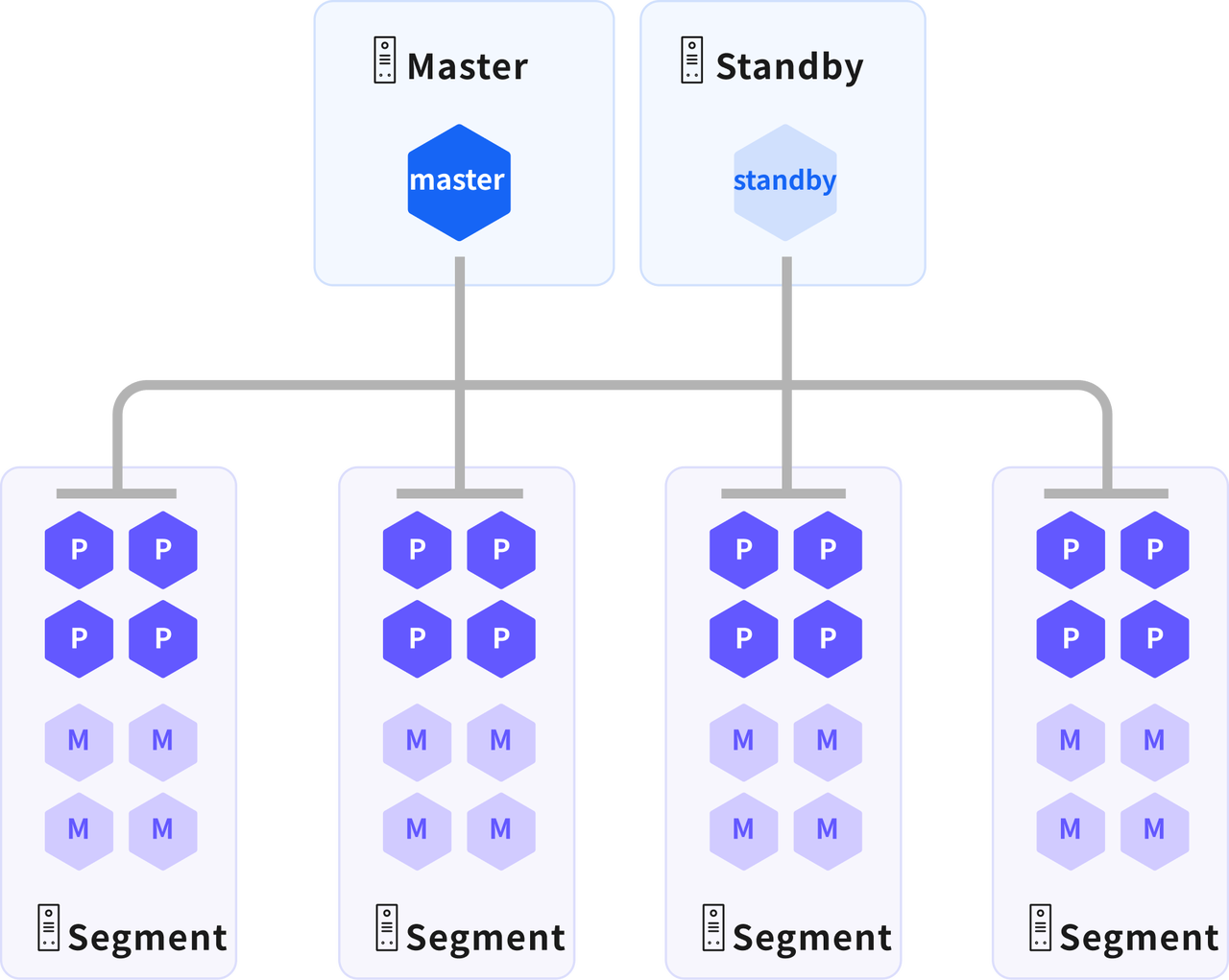
Master Node
- Client session management: Acts as the entry point for applications to access the database, responsible for receiving and managing client connection requests.
- SQL parsing and query planning: Parses SQL statements submitted by clients and generates distributed execution plans (Query Plans).
- Plan distribution and execution monitoring: Distributes the generated query plan to all data segments for execution and monitors the execution process.
- Result aggregation and return: Aggregates results from all data segments and returns the final result to the client.
- Metadata storage: Does not store business data; stores only system metadata (data dictionary), including definitions and attributes of all data elements.
Standby Master Node
- Data backup and consistency: Maintains identical data and functionality with the master node.
- Automatic failover: When the master node fails, the standby master is automatically promoted to become the new master, ensuring service continuity.
- Isolated deployment: The standby master must be deployed on a different physical host than the master node.
Data Node
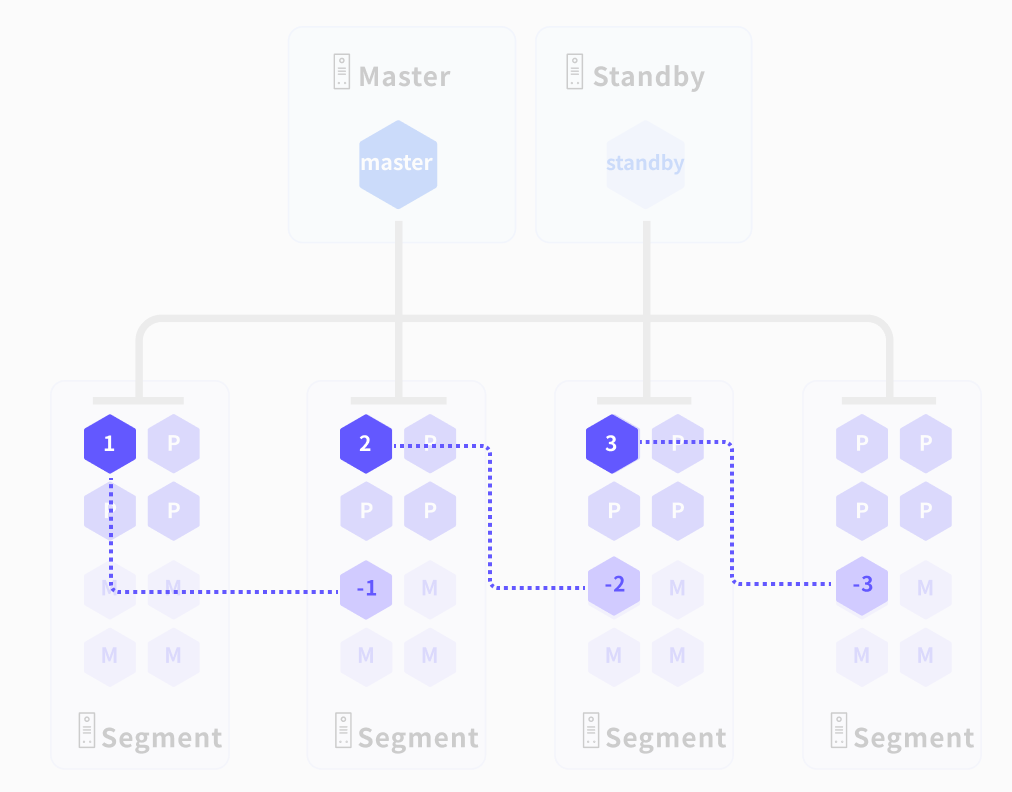
Data nodes are the core units for data storage and computation in YMatrix. Table data is distributed across primary instances according to configuration. Each primary instance holds a unique data shard with no overlap. During query execution, the master generates a query plan and distributes it to all primary instances for parallel processing, improving query response speed through parallel computing.
Primary Instance
Multiple independent primary instances can exist on a single node.
- Data storage: Table data is distributed across primary instances based on configuration. Each primary instance holds a non-overlapping data shard.
- Distributed query execution: Executes query plans dispatched by the master node, leveraging parallel computing to accelerate query responses.
- Core of data processing: Key to achieving high performance. Data and workload are evenly distributed across multiple homogeneous primary instances, enabling them to work simultaneously on a single task and complete it in sync.
Mirror Instance
Multiple independent mirror instances can exist on a single node.
- Data consistency with primary: Maintains identical data and functionality with its corresponding primary instance.
- Failover support: When a primary instance fails (e.g., due to machine power loss or instance crash), the mirror instance is automatically promoted to take over data storage and computation, ensuring uninterrupted service. In production environments, primary and mirror instances are typically deployed on separate hosts to avoid single-point failures.
Query Execution
Queries are optimized to generate an execution plan, which is then executed by the compute and storage engines to read data, perform computations, and return results.
Optimizer
YMatrix provides two optimizers:
- PQO (Postgres Query Optimizer): Based on PostgreSQL's native optimizer, suitable for transactional (TP) workloads and most analytical (AP) scenarios.
- ORCA: A Cascades-based optimizer that generates more efficient execution plans for large, complex queries, reducing resource consumption and improving query performance.
Storage Engine
YMatrix supports two storage engines:
- HEAP: A classic row-store engine inherited from PostgreSQL, ideal for transactional (TP) workloads with strong performance in insert, update, and delete operations.
- AO(Append-Optimized): AO tables are divided into AOCO (Append-Optimized Column-Oriented) and AORO (Append-Optimized Row-Oriented). They are best suited for tables or partitioned tables where data is initially bulk-loaded and subsequently updated infrequently, with new data inserted only in batch mode.
- AOCO:Columnar storage + sequential writes + column-level compression + block-level indexing + MPP parallel scanning.Ideal for large-scale analytical workloads.
- AORO:Sits between traditional Heap tables and AOCO. It is an enhanced row-store format optimized for analytical use cases. Well-suited for point queries or small-range scans.
- MARS3: A high-performance hybrid row-column storage engine developed by YMatrix, delivering excellent performance in analytical (AP) and time-series workloads, along with high compression ratios.
Compute Engine
YMatrix features a fully vectorized execution engine. In large-data scenarios, this significantly improves query speed.
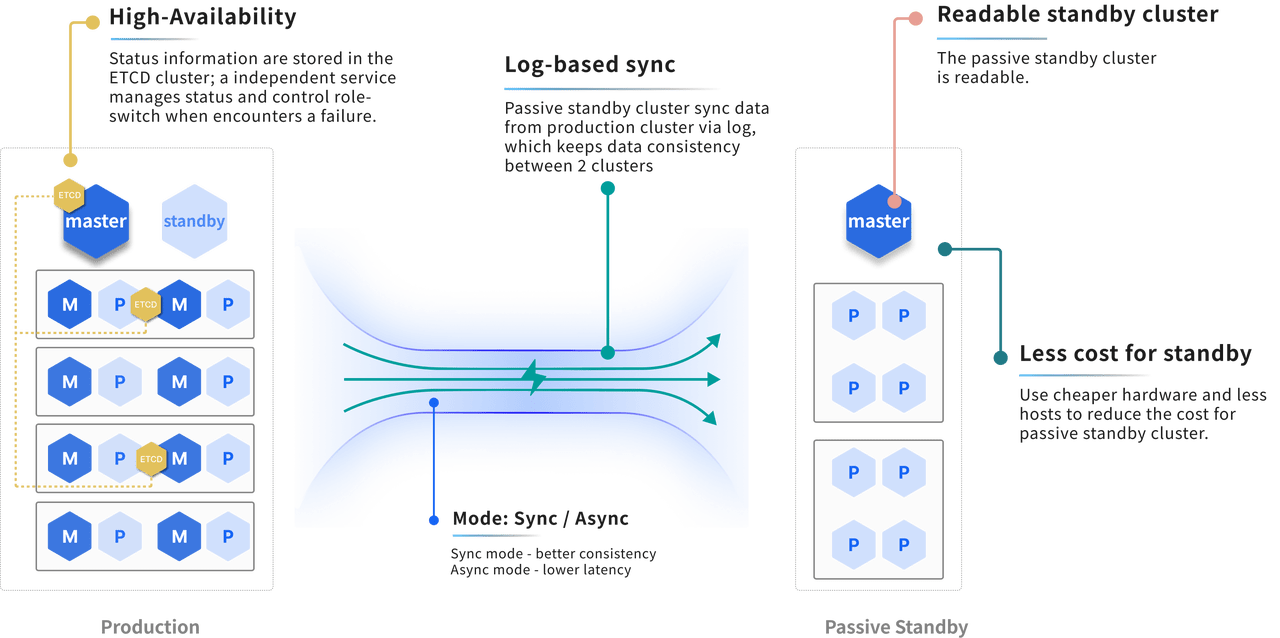
High Availability
YMatrix ensures high availability through mirroring, and also provides disaster recovery across sites to maintain service continuity under extreme conditions.
Mirroring
When mirroring is enabled, each primary instance has a corresponding mirror instance with identical data and functionality. In production, primary and mirror instances are placed on separate hosts.
- During normal operation, mirror instances do not participate in computation; they only maintain data synchronization with their primaries.
- If a primary instance fails or its host goes down, the mirror instance takes over seamlessly, ensuring uninterrupted service.
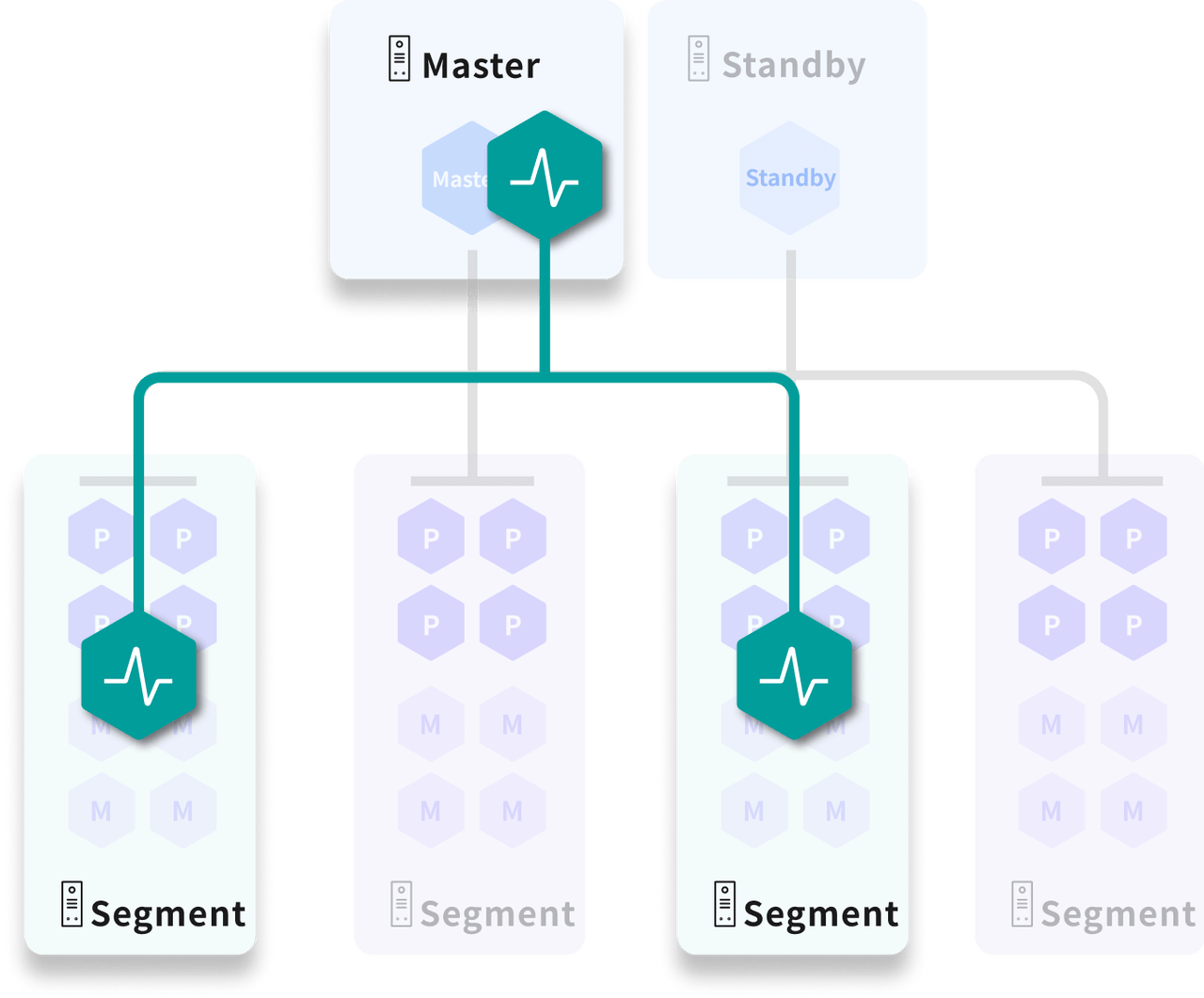
State Management
ALOHA (Advanced Least Operation High Availability) is a newly designed cluster state management service.
In a YMatrix cluster, an odd number of nodes are randomly selected to form a distributed ETCD cluster, which stores node and instance states. Upon failure (node outage, instance crash, etc.), the system uses this state information to perform automatic failover and fault migration, ensuring high availability.
Disaster Recovery Across Sites
YMatrix supports cross-site disaster recovery deployment. If the primary cluster fails, services can switch to the backup cluster, which then functions identically to a normal YMatrix database cluster.