YMatrix supports accessing data in HDFS through PXF (Platform Extension Framework). With PXF, YMatrix can parallelize reads of structured or semi-structured data from HDFS, eliminating redundancy and latency caused by data migration, enabling an "instant connect and use" analytics experience.
This section includes usage instructions for two access methods: Direct HDFS Access via PXF and HDFS Access via PXF with Ranger.
If PXF is not installed, refer to the PXF Installation section for installation guidance.
This section details how to configure and use PXF in YMatrix to access HDFS.
| Software | Version Information |
|---|---|
| YMatrix | MatrixDB 6.2.2+enterprise |
| Hadoop | Hadoop 3.2.4 |
| PXF | pxf-matrixdb4-6.3.0-1.el7.x86_64 |
(1)Create Directories in Hadoop (Execute on Hadoop Master Node)
First, create directories in HDFS to store data files. These directories serve as data exchange locations between YMatrix and the Hadoop cluster.
/ymatrix directory under the HDFS root. This directory stores all database-related data files. Use the following command:hdfs dfs -mkdir /ymatrix/ymatrix, create a subdirectory named pxf_examples. This subdirectory holds PXF example data. Run the following command:hdfs dfs -mkdir /ymatrix/pxf_examples
/ymatrix was created. Use the ls command:hdfs dfs -ls //ymatrix directory to confirm creation of pxf_examples.hdfs dfs -ls /ymatrix/
echo 'Prague,Jan,101,4875.33
Rome,Mar,87,1557.39
Bangalore,May,317,8936.99
Beijing,Jul,411,11600.67' > pxf_hdfs_simple.txt
/ymatrix/pxf_examples directory in HDFS.hdfs dfs -put pxf_hdfs_simple.txt /ymatrix/pxf_examples/hdfs dfs -cat /ymatrix/pxf_examples/pxf_hdfs_simple.txthdfs dfs -chown command to assign ownership of the file to the mxadmin user:hdfs dfs -chown -R mxadmin:mxadmin /ymatrix/pxf_examples/pxf_hdfs_simple.txt(2)Configure Environment Variables for mxadmin User (Add on All YMatrix Nodes)
To ensure effective interaction between YMatrix and the Hadoop cluster, configure environment variables on all YMatrix nodes.
.bashrc or the environment configuration file on each YMatrix node:export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/modules/hadoop-3.2.4
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/opt/modules/hadoop-3.2.4/etc/hadoop
export PXF_CONF=/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$PATH(3)Grant mxadmin User Access to Hadoop Cluster (Modify on All Hadoop Nodes)
To allow the mxadmin user to access the Hadoop cluster, update the core-site.xml configuration file on all Hadoop nodes.
core-site.xml file and add the following properties:<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.mxadmin.groups</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.mxadmin.hosts</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>(4)Create single_hdfs Directory (Add on All YMatrix Machines)
Create a new directory on the YMatrix master node to hold Hadoop cluster configuration files.
mkdir /usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/(5)Copy Configuration Files from Hadoop to PXF Directory (Transfer from Hadoop Master to YMatrix Master)
Copy Hadoop configuration files to the PXF directory on the YMatrix master node.
scp command:scp $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/core-site.xml 192.168.50.95:/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/
scp $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/hdfs-site.xml 192.168.50.95:/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/
scp $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/yarn-site.xml 192.168.50.95:/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/(6)Create pxf-site.xml File (Create on YMatrix Master Node)
Create the PXF configuration file pxf-site.xml on the YMatrix master node to ensure proper connection between PXF and the Hadoop cluster.
vi /usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/pxf-site.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
</configuration>(7)Update core-site.xml's fs.defaultFS to Active NameNode IP and Synchronize PXF Configuration (Execute on YMatrix Master Node)
Set the core-site.xml property in the fs.defaultFS file so YMatrix can correctly connect to the Hadoop NameNode.
fs.defaultFS configuration:<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://<namenode_ip>:9000</value>
</property>pxf cluster sync(8)Query Using PXF Plugin in YMatrix Database (Execute on YMatrix Master Node)
create extension pxf_fdw;CREATE SERVER single_hdfs FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER hdfs_pxf_fdw OPTIONS ( config 'single_hdfs' );CREATE USER MAPPING FOR mxadmin SERVER single_hdfs;CREATE FOREIGN TABLE pxf_hdfs_table (location text, month text, num_orders int, total_sales float8)
SERVER single_hdfs OPTIONS ( resource '/ymatrix/pxf_examples/pxf_hdfs_simple.txt', format 'text', delimiter ',' );SELECT * FROM pxf_hdfs_table;(1)Create Directory (Execute on Hadoop Master Node)
Create a new HDFS directory to store written data.
hdfs dfs -mkdir /ymatrix/pxf_dir_examples(2)Create External Table (Execute on YMatrix Master Node)
Create a foreign table in YMatrix pointing to the new HDFS directory.
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE pxf_hdfsdir_table (location text, month text, num_orders int, total_sales float8)
SERVER hdfs_svr OPTIONS (resource '/ymatrix/pxf_dir_examples', format 'text', delimiter ',' );(3)Write Data (Execute on YMatrix Master Node)
Insert data from existing foreign table pxf_hdfs_table into the new table pxf_hdfsdir_table.
INSERT INTO pxf_hdfsdir_table SELECT * FROM pxf_hdfs_table ;(4)Query Foreign Table to Retrieve All Data (Execute on YMatrix Master Node)
Verify successful write operation.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM pxf_hdfsdir_table;This section describes how to use PXF with Ranger to manage HDFS file access permissions.
(1)Create Directories in Hadoop (Execute on Hadoop Master Node)
Create directories in HDFS for data exchange between YMatrix and Hadoop.
Create the /ranger directory under HDFS root
Used for storing database-related data files. Run:
hdfs dfs -mkdir /rangerList root directory contents to verify /ranger exists
Use ls to list and confirm:
hdfs dfs -ls /Generate test data file
Create a local test file using:
echo "testuser,May,100,999.99" > /tmp/pxf_test_verify.txt
Upload local file to /ranger directory in HDFS
Use hdfs dfs -put to upload:
hdfs dfs -put -f /tmp/pxf_test_verify.txt /ranger/View uploaded file content to confirm success
Run:
hdfs dfs -cat /ranger/pxf_test_verify.txt
(2)Configure Environment Variables for mxadmin User (Add on All YMatrix Nodes)
Ensure YMatrix can interact with Hadoop by setting environment variables on all nodes.
In .bashrc or environment file, add:
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/modules/hadoop-3.2.4
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/opt/modules/hadoop-3.2.4/etc/hadoop
export PXF_CONF=/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$PATH(3)Grant mxadmin User Access in Hadoop Cluster (Modify on All Hadoop Nodes)
Allow mxadmin user access by updating core-site.xml on all Hadoop nodes.
Edit core-site.xml and add:
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.mxadmin.groups</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.proxyuser.mxadmin.hosts</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>(4)Create single_hdfs Directory (Add on All YMatrix Machines)
Create a directory on the YMatrix master node for Hadoop configuration files.
Command:
mkdir /usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/(5)Copy Configuration Files from Hadoop to PXF Folder (Transfer from Hadoop Master to YMatrix Master)
Copy Hadoop configs to the PXF directory on YMatrix master.
Use scp:
scp $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/core-site.xml 192.168.50.95:/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/
scp $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/hdfs-site.xml 192.168.50.95:/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/
scp $HADOOP_CONF_DIR/yarn-site.xml 192.168.50.95:/usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/(6)Create pxf-site.xml File (Create on YMatrix Master Node)
Create the PXF config file pxf-site.xml to ensure correct connectivity.
vi /usr/local/pxf-matrixdb4/servers/single_hdfs/pxf-site.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
</configuration>(7)Update core-site.xml's fs.defaultFS to Active NameNode IP and Sync PXF Config (Execute on YMatrix Master Node)
Set the core-site.xml property in fs.defaultFS for correct NameNode connection.
fs.defaultFS:<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://<namenode_ip>:9000</value>
</property>pxf cluster syncPXF interacts with HDFS using OS-level users, not database users. Therefore, Ranger's HDFS permission control is based on operating system users.
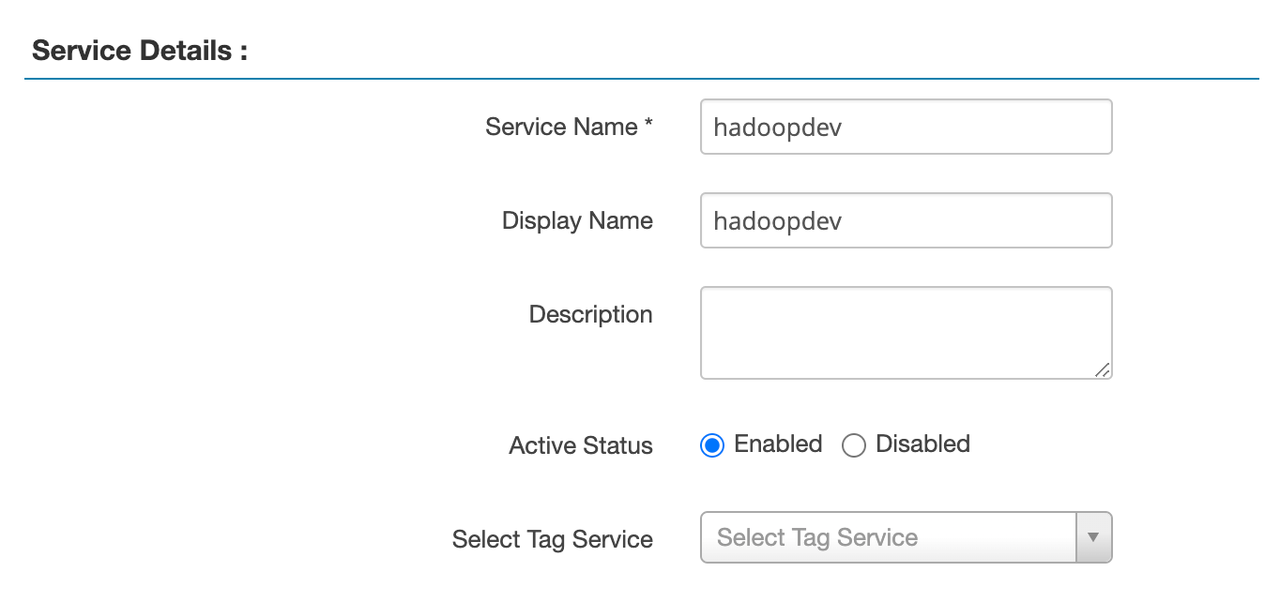
core-site.xml)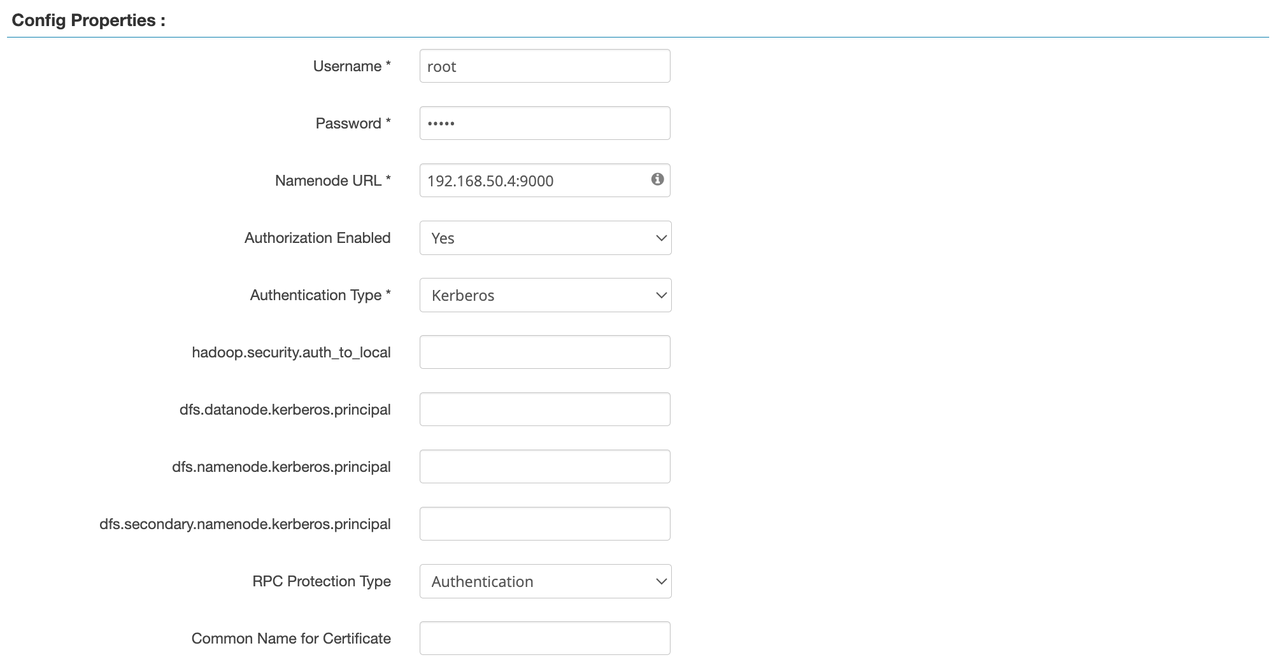
In Ranger, Kerberos vs Simple authentication:
Kerberos: Uses tickets and encryption; high security, suitable for production environments, especially across multiple systems.
Simple: Username/password-based; lower security, ideal for development or testing.
Save the service configuration.
Note!
After creating the service, restart the Hadoop Ranger Plugin for changes to take effect.
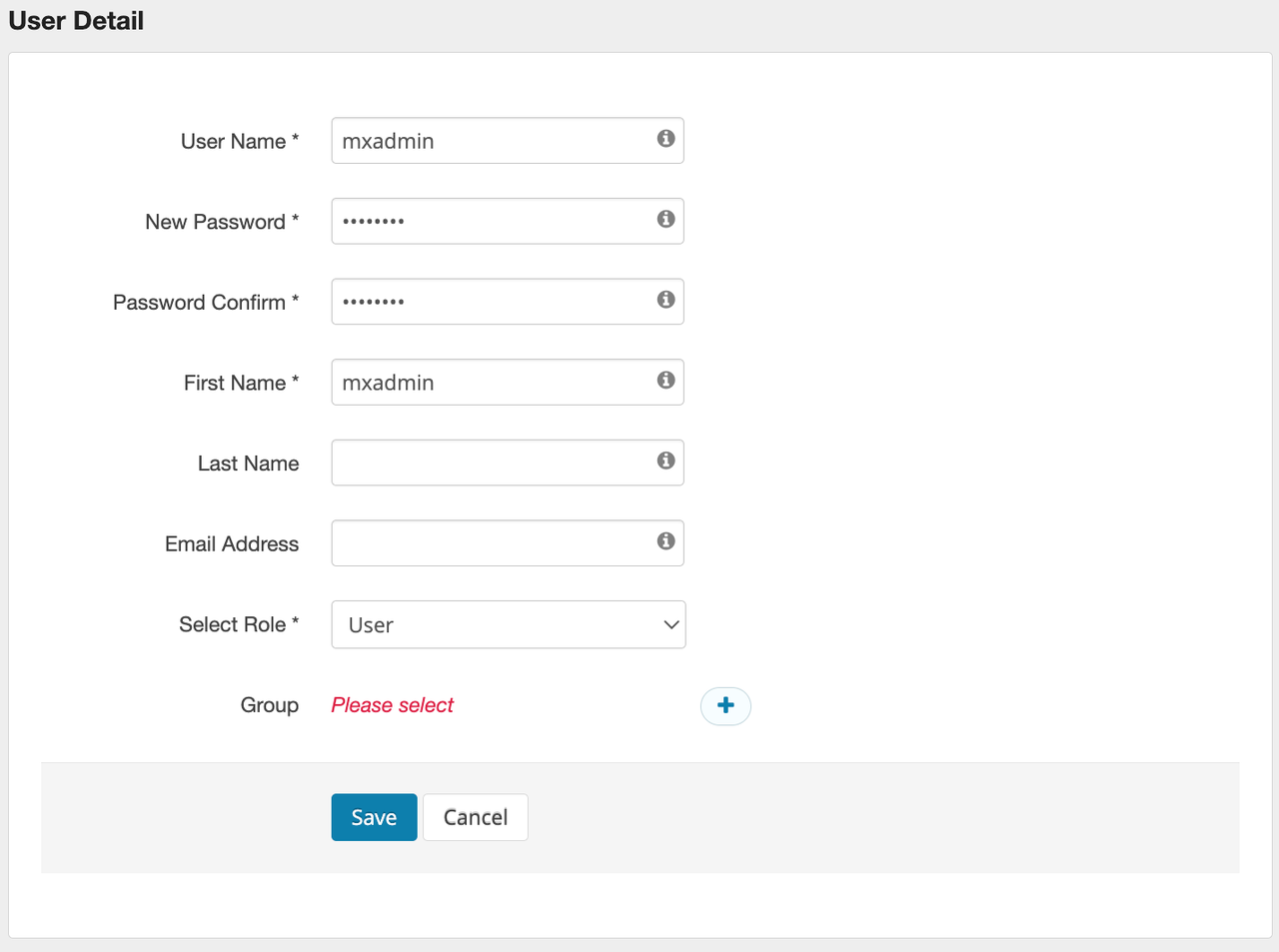
mxadmin User in Ranger(i)Go to “User / Groups” page
From the menu, select User / Groups, then click Add New User.
(ii)Create mxadmin user
Enter mxadmin in the User Name field and click Save.
(iii)Assign HDFS Access Permissions to mxadmin
In Ranger, go to the hadoop_hdfs service and click Add New Policy. Configure as follows:
Policy Name: test_allow_mxadmin
Resource Path: /ranger/pxf_test_verify.txt
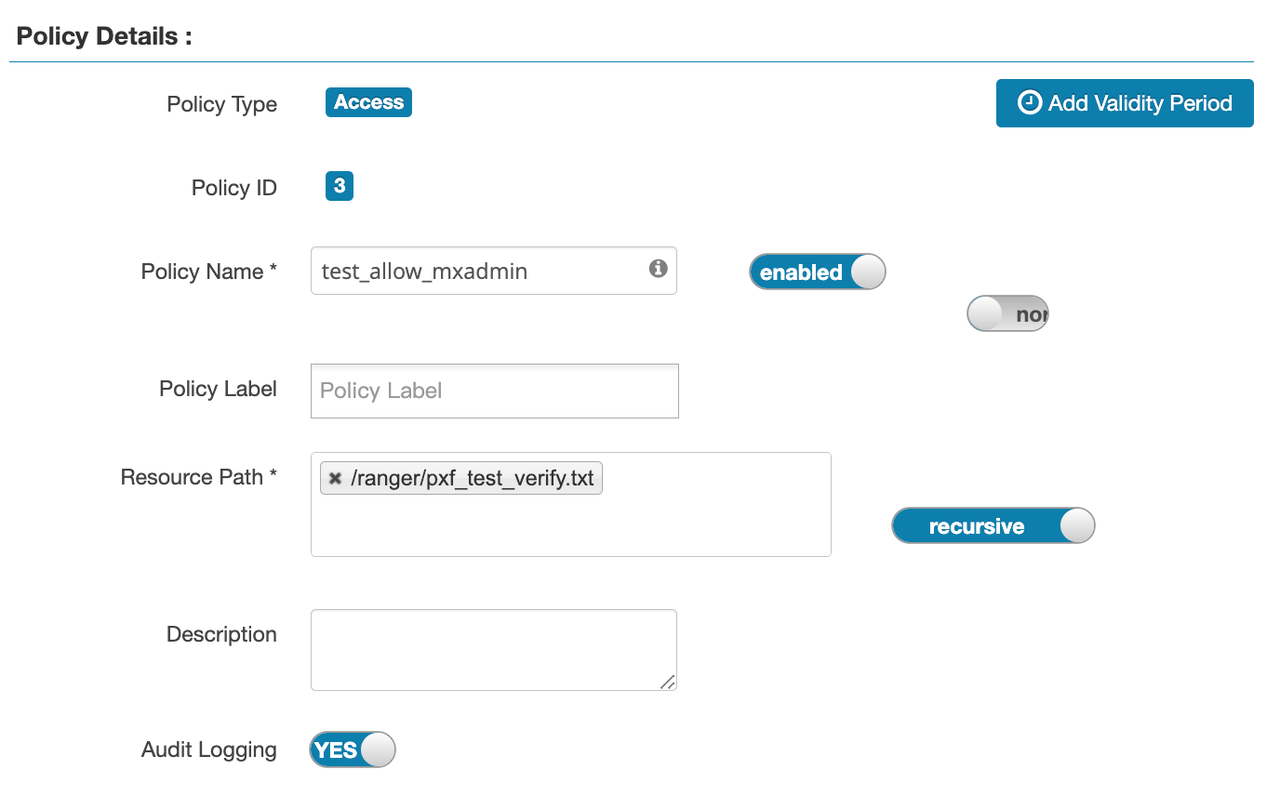
User: mxadmin
Permissions: read
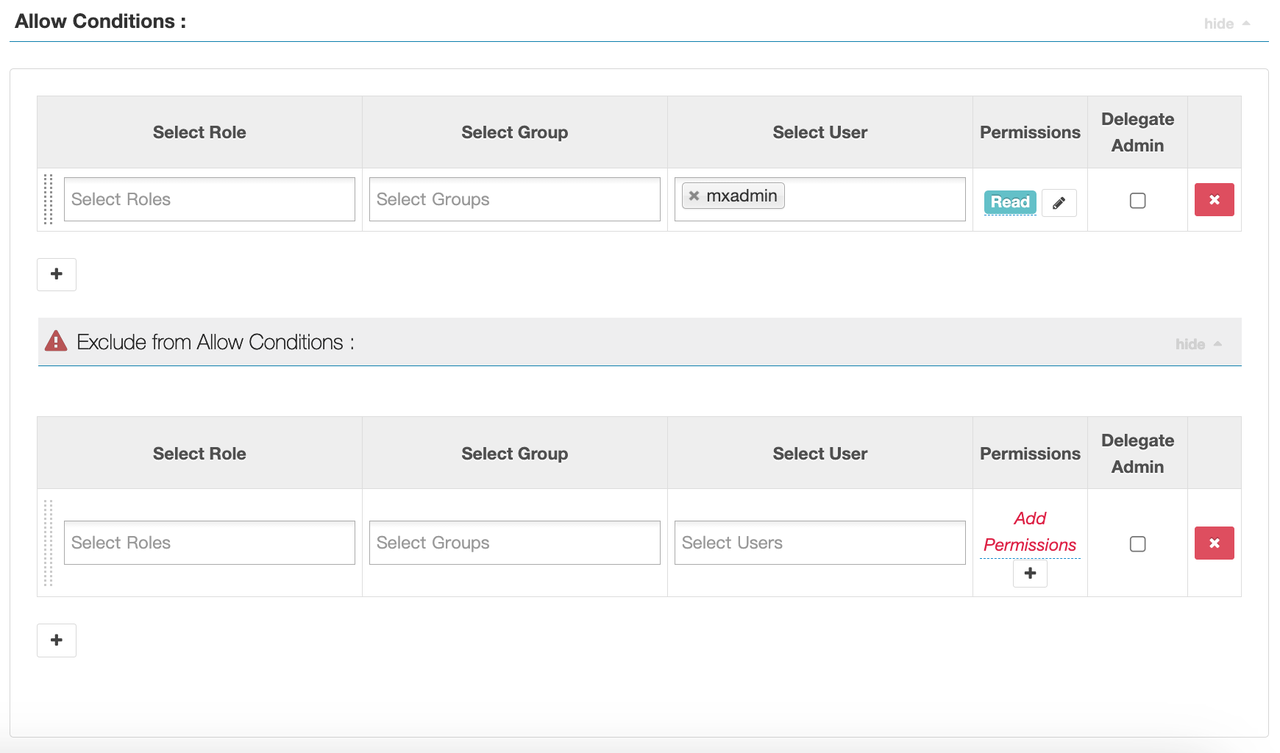
Save the policy.
1. Create Test Database
create database mxadmin;
# Switch to mxadmin database
\c mxadmin2. Install Plugin
Enable the PXF plugin in YMatrix to access HDFS data.
Run:
create extension pxf_fdw;3. Create FDW Server
Create an external data source for the Hadoop file system.
SQL command:
CREATE SERVER single_hdfs FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER hdfs_pxf_fdw OPTIONS ( config 'single_hdfs' );4. Create FDW User Mapping
Map the YMatrix user to the FDW server.
Command:
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR mxadmin SERVER single_hdfs;5. Create FDW Foreign Table
Map the HDFS file to a YMatrix table.
Run:
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE pxf_hdfs_verify (
name text,
month text,
count int,
amount float8
)
SERVER single_hdfs
OPTIONS (
resource '/ranger/pxf_test_verify.txt',
format 'text',
delimiter ','
);6. Query External Table
SELECT * FROM pxf_hdfs_verify;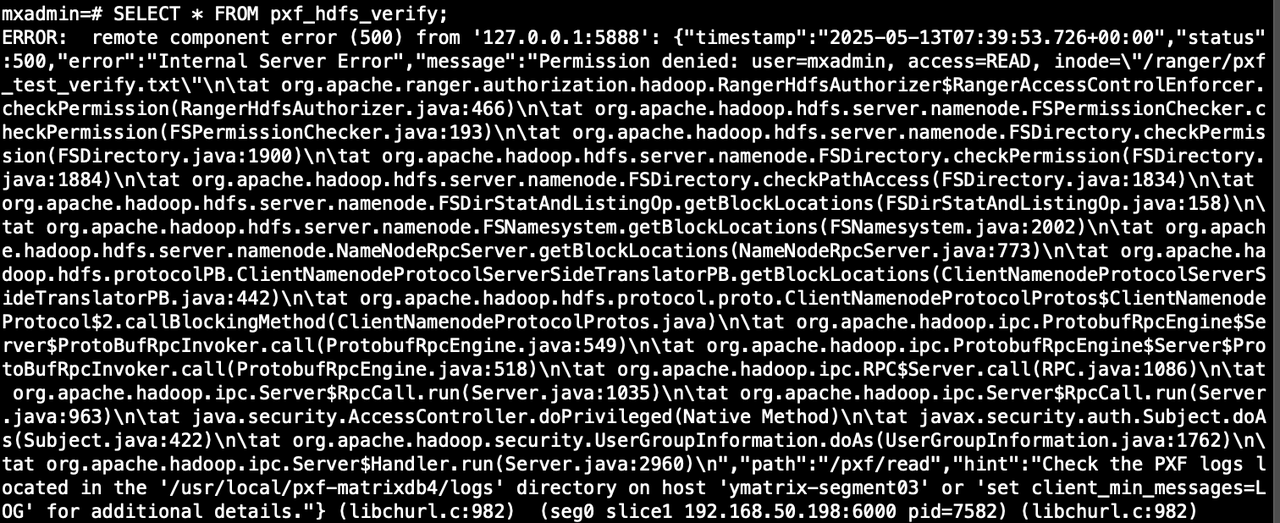
SELECT * FROM pxf_hdfs_table;