Quick onboard
Deployment
Data Modeling
Connection
Migration
Query
Operations and Maintenance
Common Maintenance
Partition
Backup and Restore
Expansion
Monitoring
Performance Tuning
Troubleshooting
Reference Guide
Tool guide
Data type
Storage Engine
Executor
Stream
DR (Disaster Recovery)
Configuration
Index
Extension
SQL Reference
In YMatrix 6.0.0, this feature is only used as an experimental feature.
To meet the needs of different customers and business scenarios, YMatrix 6.X will support Disaster Recovery (DR) capabilities to solve high-availability needs of business data for customers.
DR clusters are Disaster Recovery, which is used to build disaster recovery clusters to ensure business continue in the event of a disaster.
DR clusters are usually an auxiliary environment independent of the primary production environment for storing backup data, running backup systems, and providing disaster recovery services.
The main goal of a DR cluster is to back up the full data and configuration information of the primary cluster in real time so that business can be restored quickly and reliably in the event of a disaster or failure. Once a major system fails, the DR cluster will take over the service, allowing the business to resume normal operation in a shorter time, while trying to avoid data loss and shorten the time for business interruptions.
The main implementation functions of DR cluster are as follows
| Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Backup and Replication | Data from the primary cluster is backed up regularly or in real time to the DR cluster to ensure data security and integrity. Backup data can be transmitted and stored through data replication, offline backup, snapshot, incremental backup and redundant arrays. |
| Disaster Recovery | DR clusters need to formulate detailed disaster recovery plans, including emergency response when a disaster occurs, data recovery process, system startup sequence, network reconnection and other steps. This helps ensure that recovery operations can be performed quickly and organized in the event of a disaster. |
| Redundant and High Availability | DR clusters are often designed with redundant and high availability, including multiple backup servers, storage devices, and network connections to ensure seamless switching to the backup system in the event of a primary cluster failure and provide reliable services. |
| Monitoring and testing | DR clusters require regular monitoring and testing to ensure the integrity of backup data, the availability of backup systems, and the feasibility of the recovery process. This helps to promptly identify and resolve potential issues and improves the reliability and availability of DR clusters. |
| Limits | Description |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive Project | In addition to the functions of YMatrix software, it also covers many factors such as infrastructure, security specifications, network equipment, investment costs, usage costs, and DR goals (RTO, RPO). It is necessary to standardize general technical indicators, and all parties have good cooperation. |
In YMatrix, DR clusters form a complete city/off-site disaster recovery framework (or processes) through some internal processes.
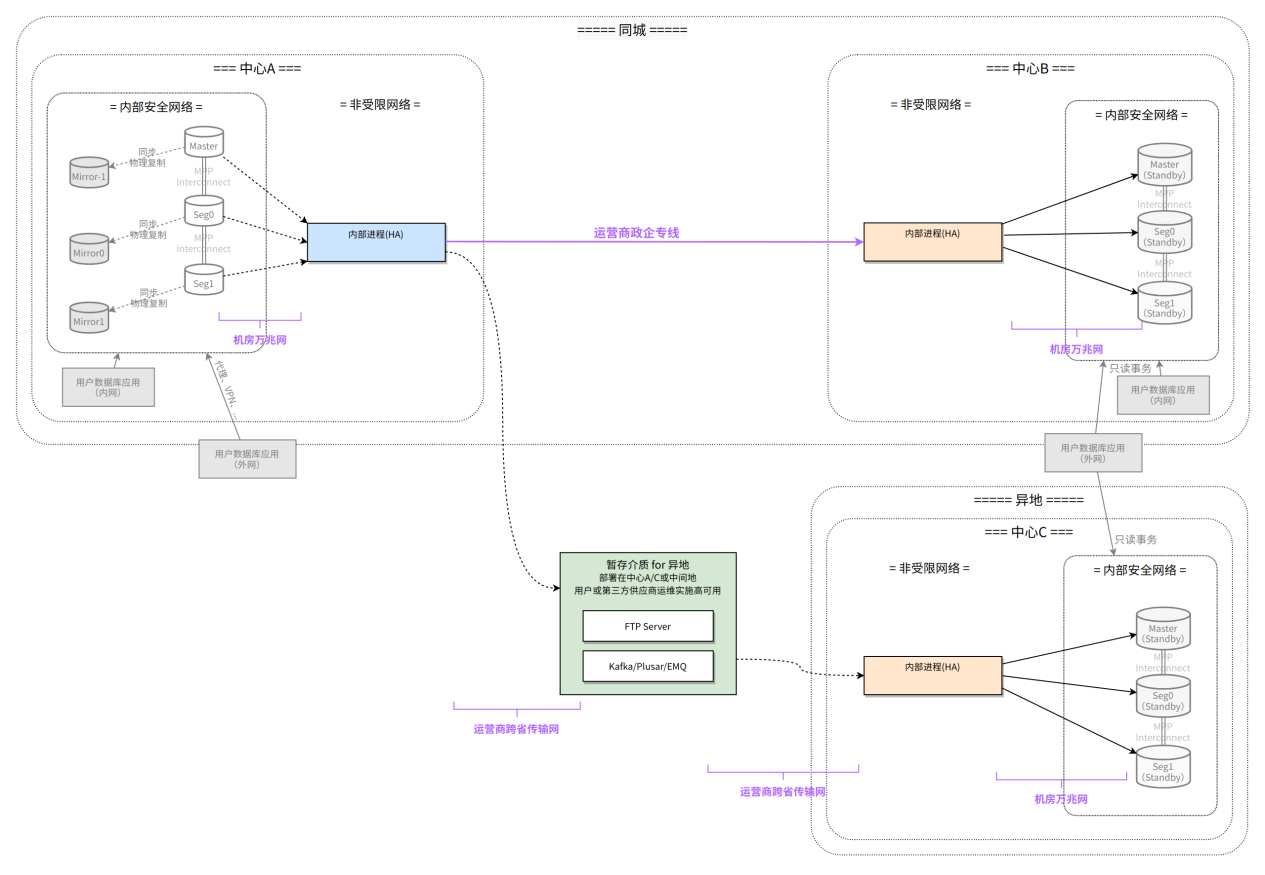
We build two independent auxiliary environments for the main production environment center A, the same-city backup center B and the off-site backup center C. Each auxiliary environment has complete redundant data.- City backup center B Due to the close distance, you can consider using the operator's government-enterprise dedicated line to the production environment center A (the data transmission method here is only an illustration. In actual use, you can choose one of the three methods: direct connection/stage storage medium/object storage) to ensure a faster data backup speed. However, direct connections have certain limitations, that is, if Center B fails, redundant data will be backlogged in cluster A, affecting performance and even blocking source cluster transactions, causing source cluster to fail to work.
Off-site backup center C Due to the long distance, it may be preferred to transmit redundant data through temporary storage media. This solution can ensure that when a problem occurs in Center C, Center A will not be degraded or more affected by data transmission.
Each DR cluster-related internal process is highly available on its own.
Both disaster recovery clusters B and C can only read data, but cannot write data. If cluster A is not available, manual intervention is required, and B or C should be selected as the new primary cluster.