Quick Start
Cluster Deployment
Data Model
Data Writing
Data Query
SQL Reference
Maintenance and Monitoring
Tool Guide
Troubleshooting
FAQ
The database is the place where data is stored. After completing data table modeling and storage selection, you must write data to the table. Data writing faces the following challenges:
The biggest feature of time series data is that it has a large amount of data, which includes three aspects in the actual scenario:
In summary, with the huge number of equipment, acquisition indicators and high frequency acquisition density, the amount of data generated is huge, which is a huge challenge to the database throughput. MatrixDB has developed the MatrixGate high-speed writing tool. Through the implementation of data access in parallel by segment nodes, it can reach a write speed of 50 million data points/second.
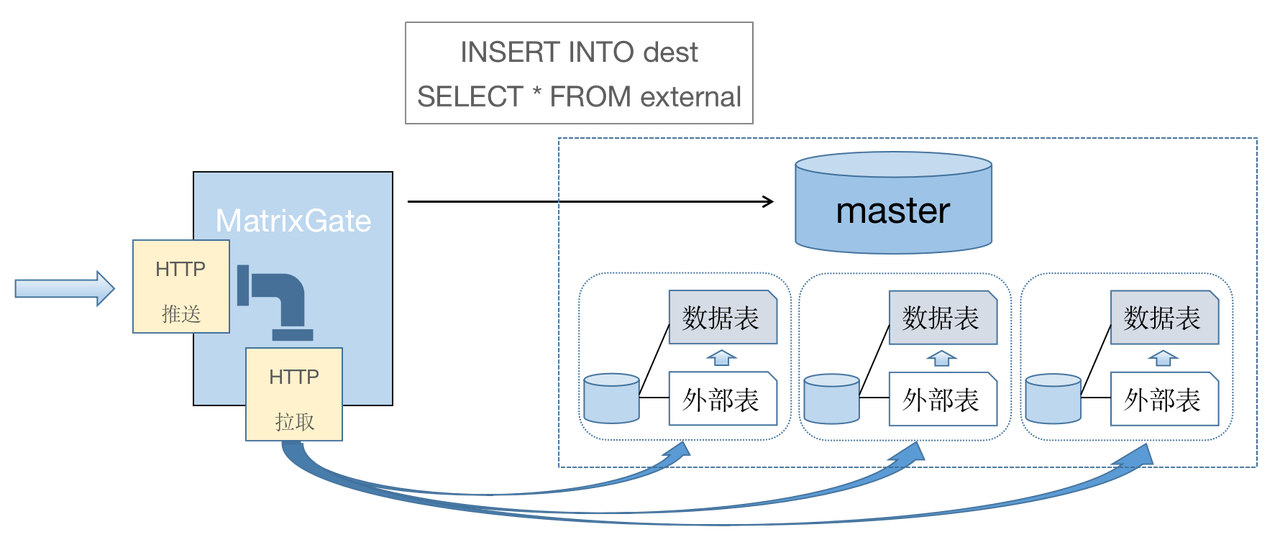
In actual scenarios, the problems faced by data writing are not only large data volume and diverse sources, but also some complex exceptions, such as:
In some scenarios, the device's acquisition indicators at a certain moment will not be sent back in one go, but will be returned in batches. The data returned multiple times need to be merged together, rather than stored in multiple records.
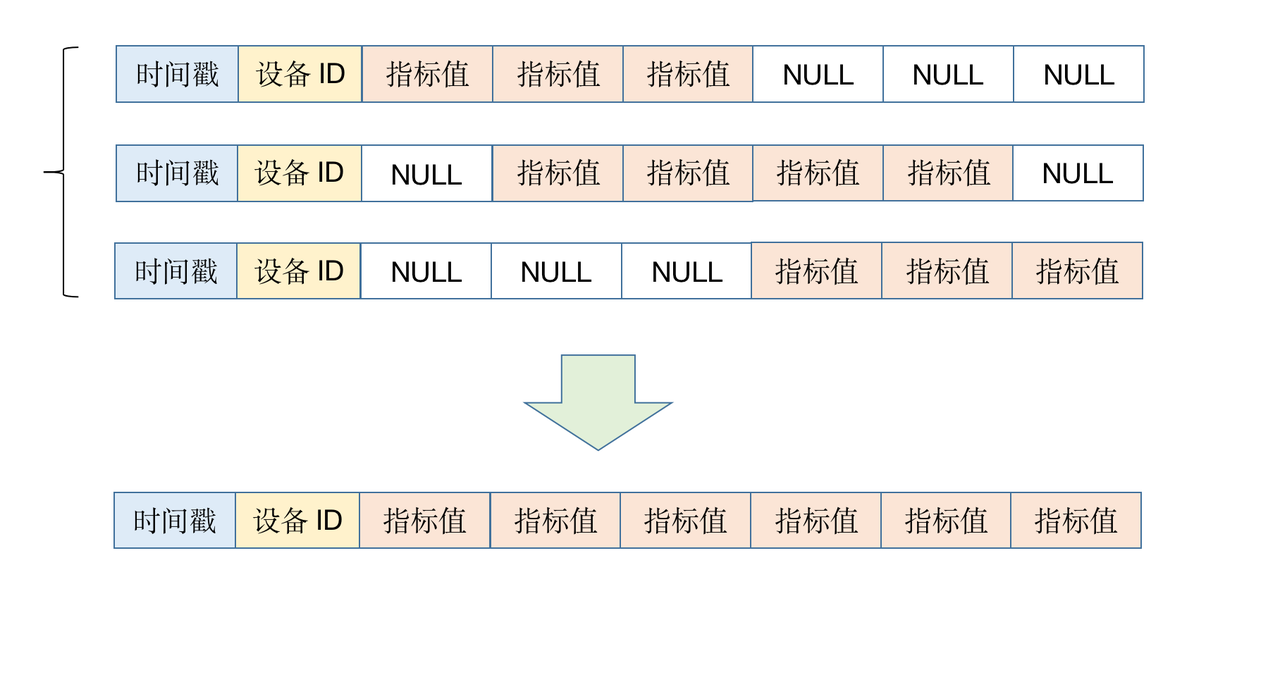
Out-of-order and delayed reporting are also supported through upsert.
The so-called heterofrequency reporting refers to the acquisition of different indicators of the device according to different frequencies. For example, some are collected once in 1s, and some are collected once in 2s. As shown in the figure below:
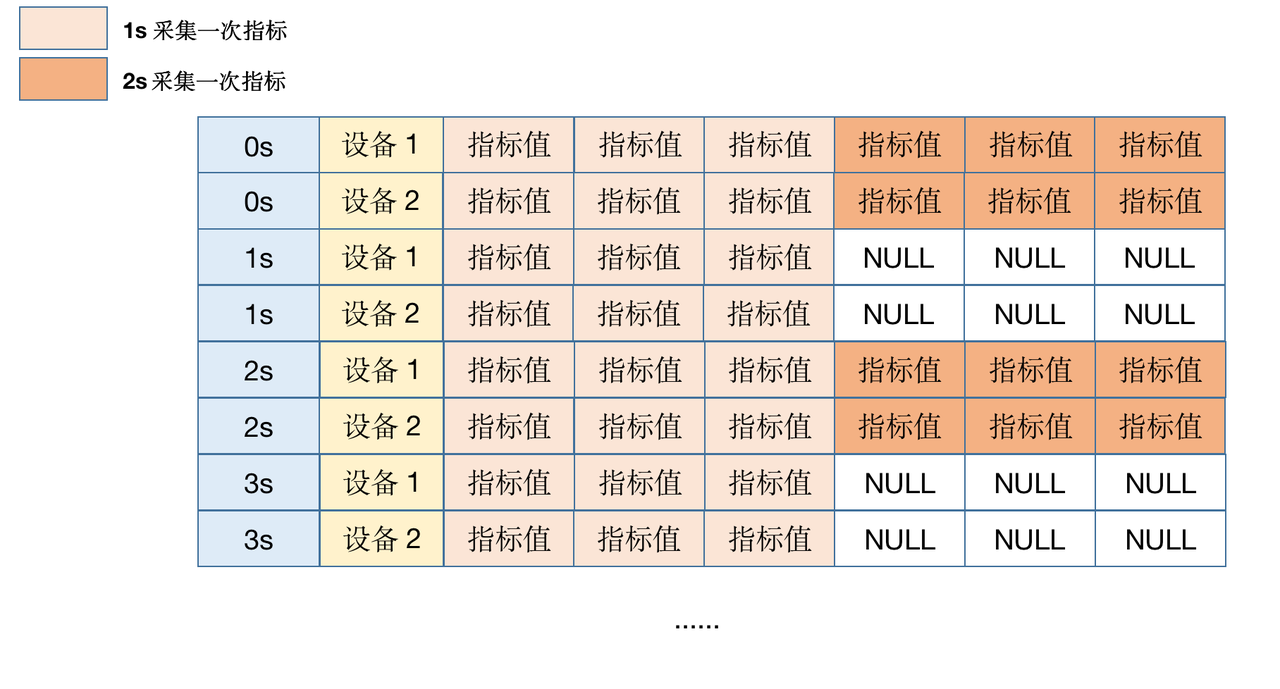
Extrafrequency reporting will cause a large number of NULLs in the index values collected for low-frequency when storing data. As long as NULL columns exist, storage space will also be occupied in MatrixDB storage. For Heap tables, the storage overhead is [Number of Columns/8] bytes; for Mars tables, the storage overhead is [Number of RowGroup/8] bytes. Therefore, the solution should be comprehensively considered based on the situation of NULL.