YMatrix provides a native graphical monitoring tool based on Grafana. This document describes the steps to deploy and manage the monitoring components. YMatrix includes a default monitoring dashboard that displays the following information. Users can also create custom dashboards in Grafana using the collected system data.
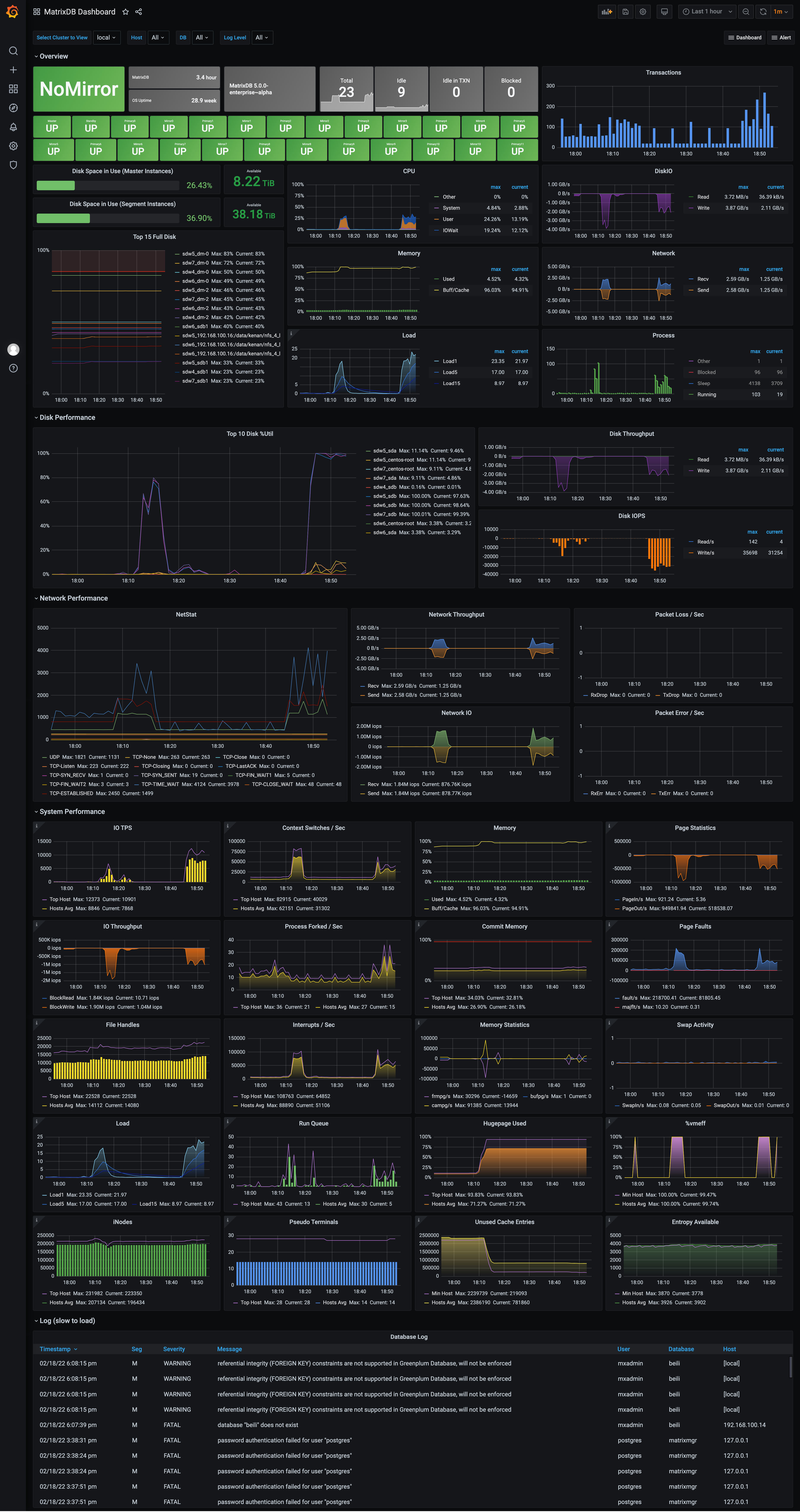
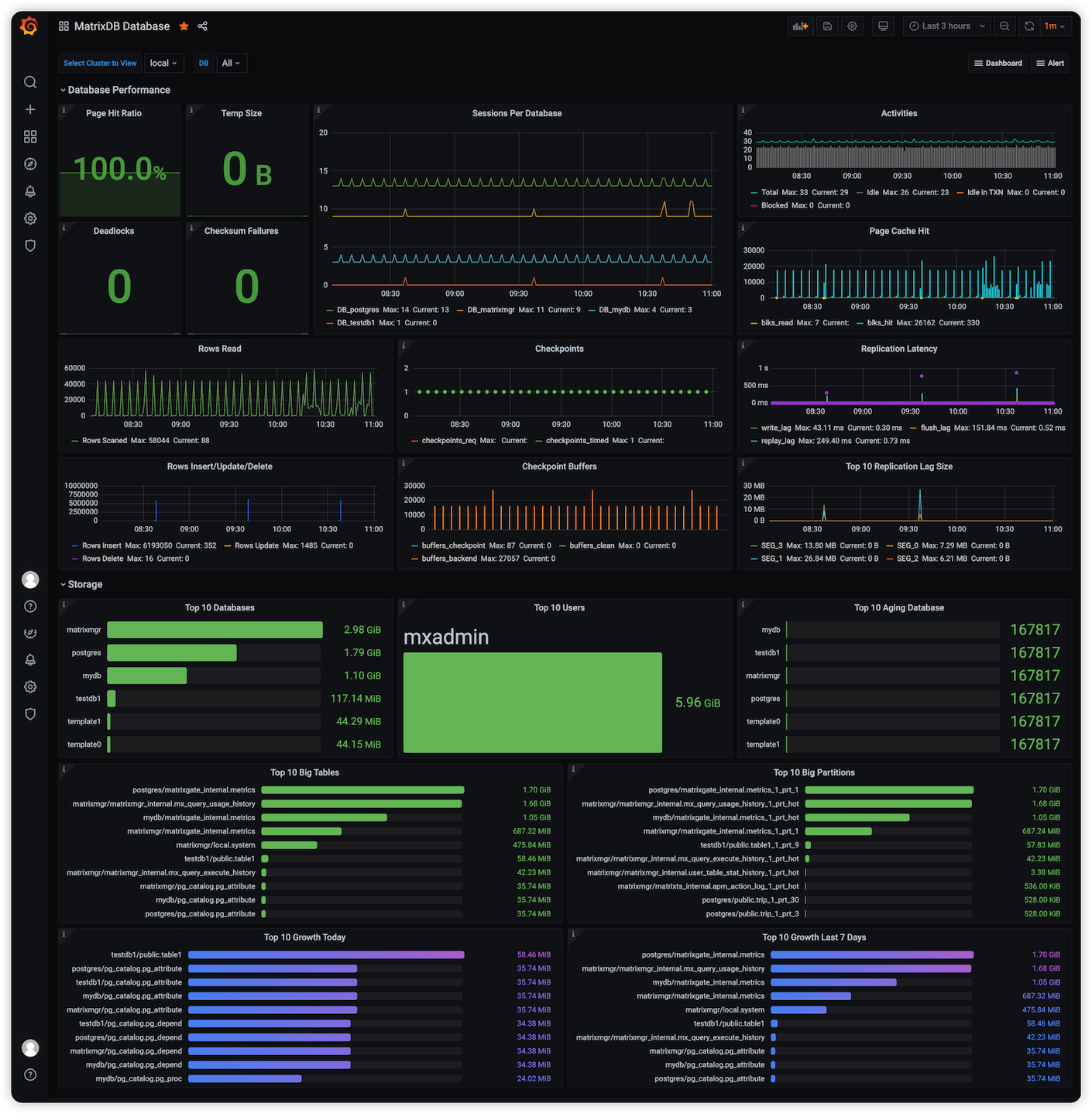
After deployment, the monitoring interface appears as shown below. Starting from version 4.4, the monitoring dashboard is split into two panels: MatrixDB Dashboard and MatrixDB Database.
MatrixDB Dashboard:
MatrixDB Database:
Monitoring components are included in the YMatrix installation package. After deploying YMatrix, complete the monitoring setup in two steps: enabling metric collection and installing and configuring Grafana.
Perform the following steps to enable metric collection for YMatrix and system resource usage. Collected data is stored in a newly created database named matrixmgr. In the examples below, the master node is named mdw.
[<普通用户>@mdw ~]$ sudo su - mxadmin[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ psql -d matrixmgr
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_init_local();Upon success, a new schema named local appears in the matrixmgr database. Tables and views under this schema contain cluster monitoring and configuration data. Do not modify the definitions or contents of these tables and views manually.
Prepare a host that can access both the Master node and the internet. This can be the Master, Standby Master, or a separate machine (Linux, macOS, Windows, etc.).
Install Grafana, version 7.3 or later is recommended. The official download link is https://grafana.com/grafana/download.
Commands below use CentOS 7 as an example. For other operating systems, refer to the corresponding documentation.
Note!
YMatrix supports offline installation of Grafana. For details, see Monitoring and Alerting FAQ.
wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana-7.3.6-1.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install grafana-7.3.6-1.x86_64.rpm[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ sudo systemctl start grafana-server
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ sudo systemctl status grafana-server
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ sudo systemctl enable grafana-serverNote!
- The Grafana version provided by
yumin CentOS 7 is often outdated (6.x), sosudo yum install grafanais not recommended.- For the complete official installation guide, see https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/latest/installation/rpm
After installation, access the following URL in a browser. Port 3000 is the default Grafana port and can be changed. Log in using the default credentials (admin / admin). For security, change the password after login by clicking the user icon in the lower-left corner.
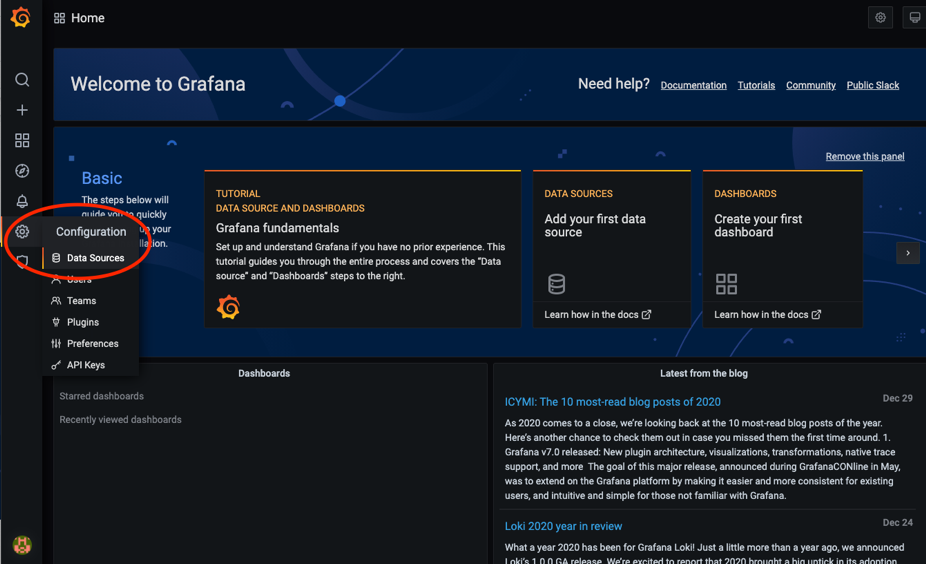
http://<IP_or_domain_of_installed_node>:3000After Grafana is installed, add the matrixmgr database in YMatrix as a data source and import the predefined monitoring dashboards.
Steps to add a data source:


Before importing the predefined dashboards, copy the dashboard.json and database.json files to your local machine. The process is: locate the files on the server, copy them, and then upload them locally. Follow these steps:
First, log in to the server and switch to the mxadmin user. Locate the dashboard.json and database.json files in the path shown below. You can use the cd command, find command, or any other method you prefer. The find command example below searches for database.json.
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ cd /opt/ymatrix/matrixdb5/share/en/doc/postgresql/extension
##or
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ find /opt/ymatrix/matrixdb5/share/en/doc/postgresql/extension -name database.jsonNext, use the scp command to copy the files to your local machine. Permission issues may arise. Consider copying the file to the /tmp/ directory first, then from /tmp/ to your local machine. The example below uses database.json.
Note!
When copying from/tmp/, ensure you switch users to avoid permission issues.
[mxadmin@mdw]$ scp mxadmin@<server_IP>:/opt/ymatrix/matrixdb5/share/en/doc/postgresql/extension/"database.json" mxadmin@<server_IP>:/tmp/
~ scp waq@<server_IP>:/tmp/"database.json" /Users/akkepler/workplace/GrafanaFinally, open the local folder or use the command line to verify the file was copied successfully. After confirmation, upload the files in the Grafana interface.
Note!
If the import fails, perform the following variable modifications.
In dashboard.json, replace all instances of ${cluster} with local. Replace $host with the actual hostnames. For example, if your cluster consists of mdw, sdw1, and sdw2, change all $host entries in dashboard.json to 'mdw','sdw1','sdw2'. For database.json, only replace ${cluster} with local. After modification, import the files in Grafana.

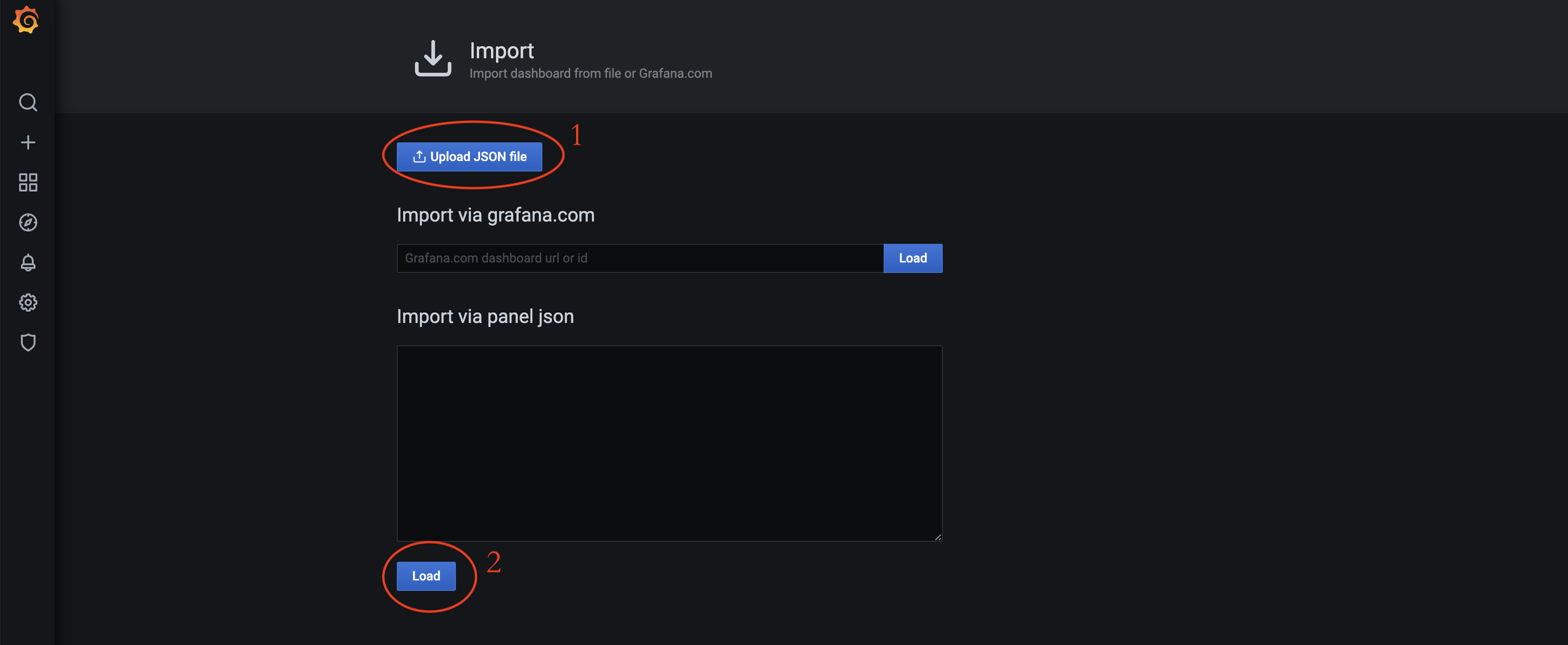
Click Upload JSON file to select and import the dashboard.json and database.json files. These files are located by default in /opt/ymatrix/matrixdb5/share/en/doc/postgresql/extension.

After enabling cluster metric collection, each host runs a collection service. Related logs are stored in the /var/log/matrixdb directory.
If you restart YMatrix or reboot the server and then restart YMatrix, the data collection service starts automatically. No manual intervention is required.
To stop the data collection service, connect to the matrixmgr database and run mxmgr_remove_all. Collected data remains preserved after stopping:
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ psql -d matrixmgr
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_remove_all('local');If the collection service is stopped manually or after reinstalling YMatrix, re-enable collection by connecting to the matrixmgr database and running mxmgr_deploy:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_deploy('local');