Quick onboard
Deployment
Data Modeling
Connecting
Migration
Query
Operations and Maintenance
Common Maintenance
Partition
Backup and Restore
Expansion
Mirroring
Resource Management
Security
Monitoring
Performance Tuning
Troubleshooting
Reference Guide
Tool guide
Data type
Storage Engine
Executor
Stream
DR (Disaster Recovery)
Configuration
Index
Extension
SQL Reference
This article introduces the configuration of YMatrix data panels, the addition of node_exporter panels, the deployment of MatrixGate monitoring panels, and the deployment of etcd monitoring panels.
Notes!
Please ensure that Prometheus and Grafana monitoring are installed on the cluster. If they are not installed, please refer to Grafana Installation and Management and Prometheus Installation and Management for installation and configuration.
Click the Settings button on the Grafana main interface and select Data Sources:
Then click Add data source:

Select Prometheus in the database category:
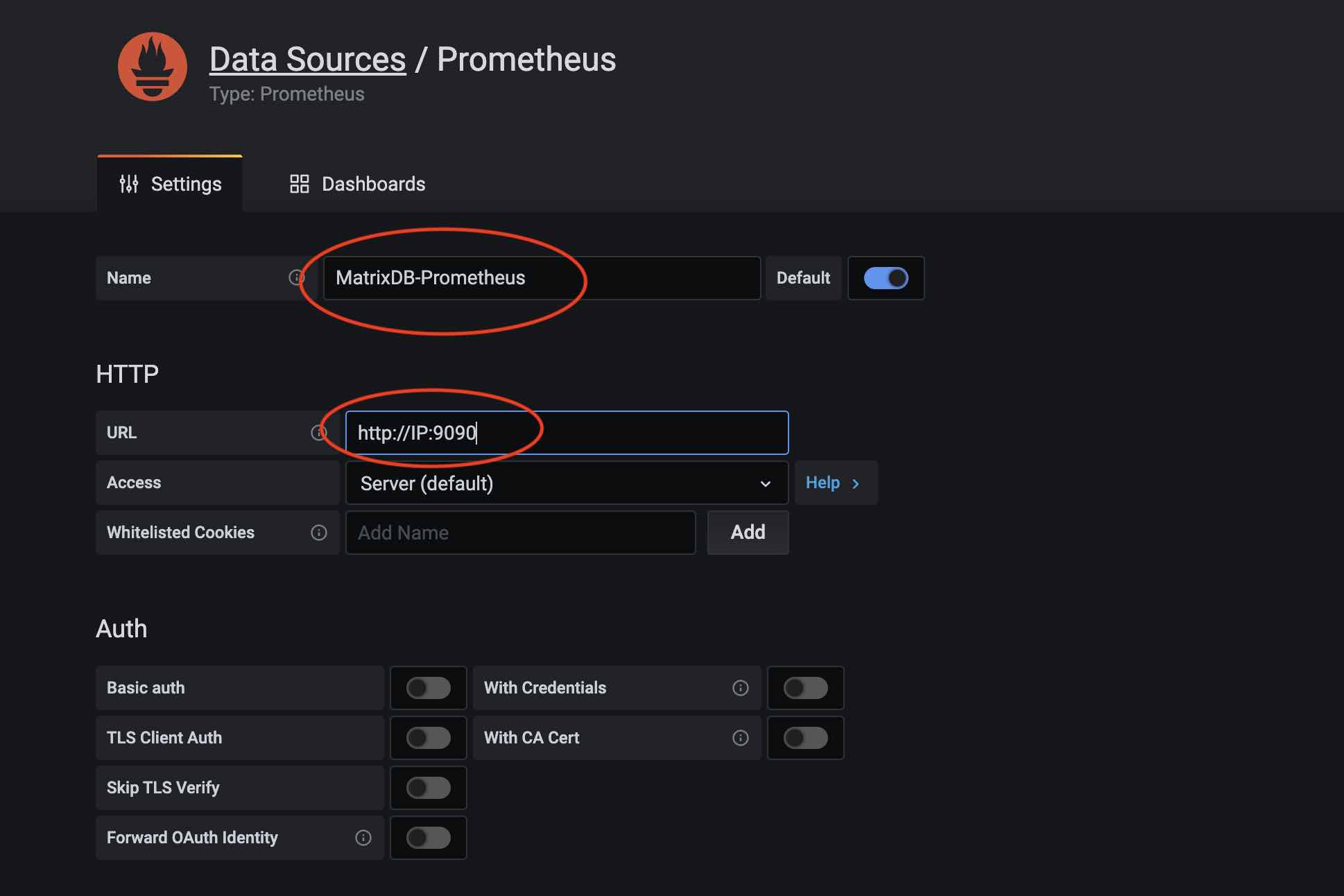
Name the data source, e.g., MatrixDB-Prometheus; then enter the Prometheus IP and port in the URL:
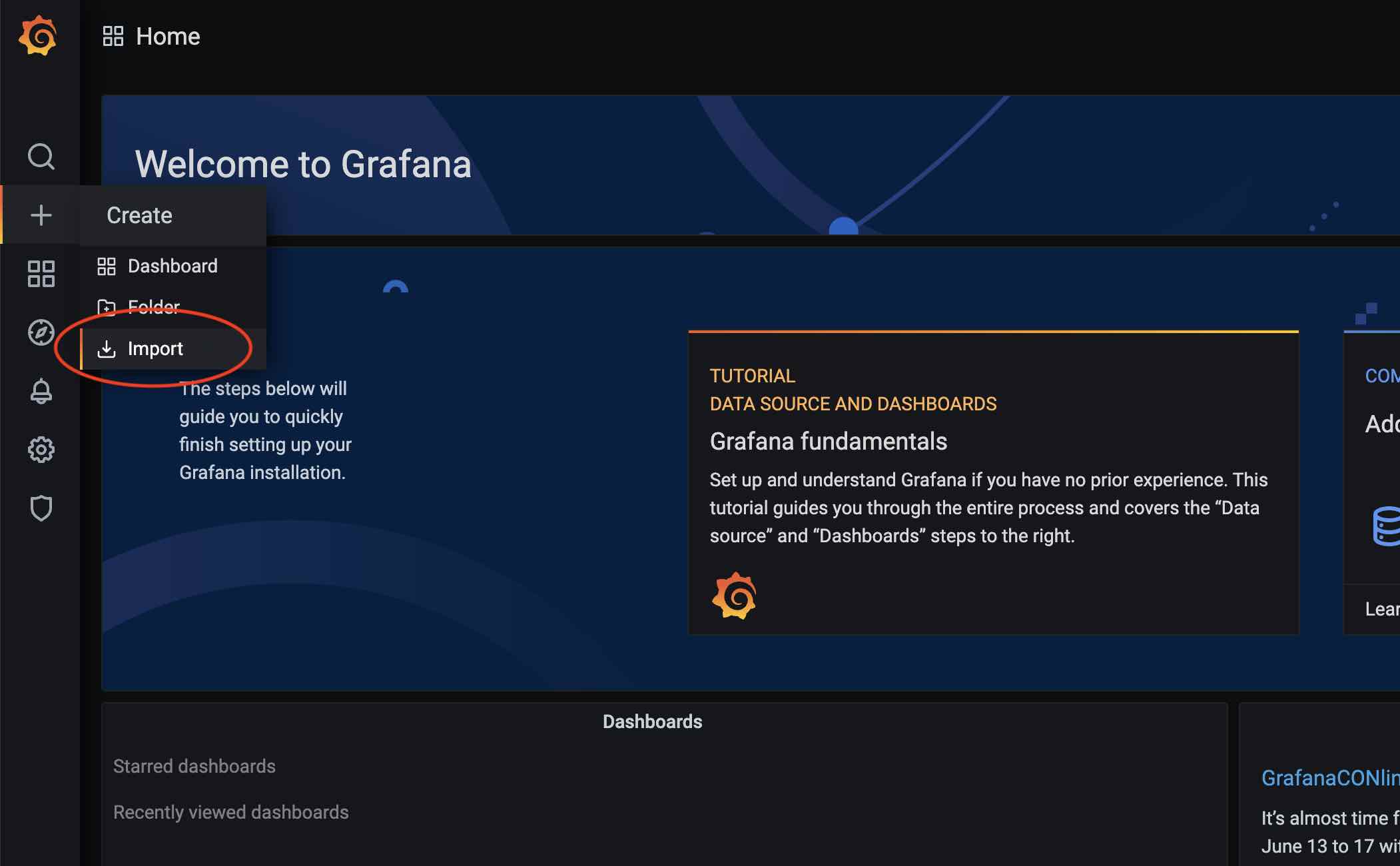
After adding the data source, load the Dashboard. Click the plus button on the Grafana main panel, then select Import:
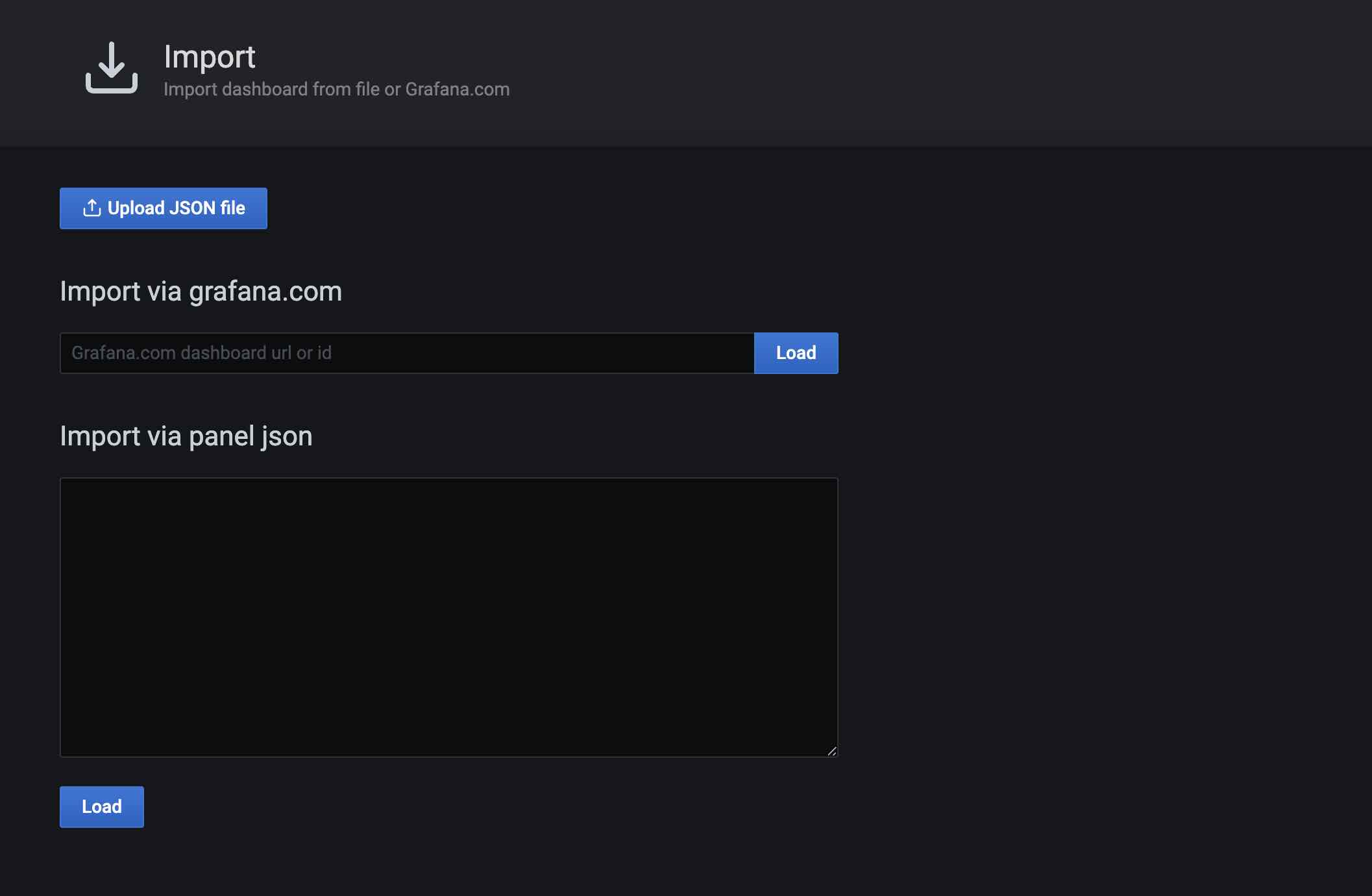
There are several ways to import: official URL or ID, paste JSON into the text box, or load from a file.
Here, we choose to load from a file. The Ymatrix Prometheus Dashboard is located in the installation directory at $GPHOME/share/doc/postgresql/extension/PrometheusDashboard.json. Load this file:
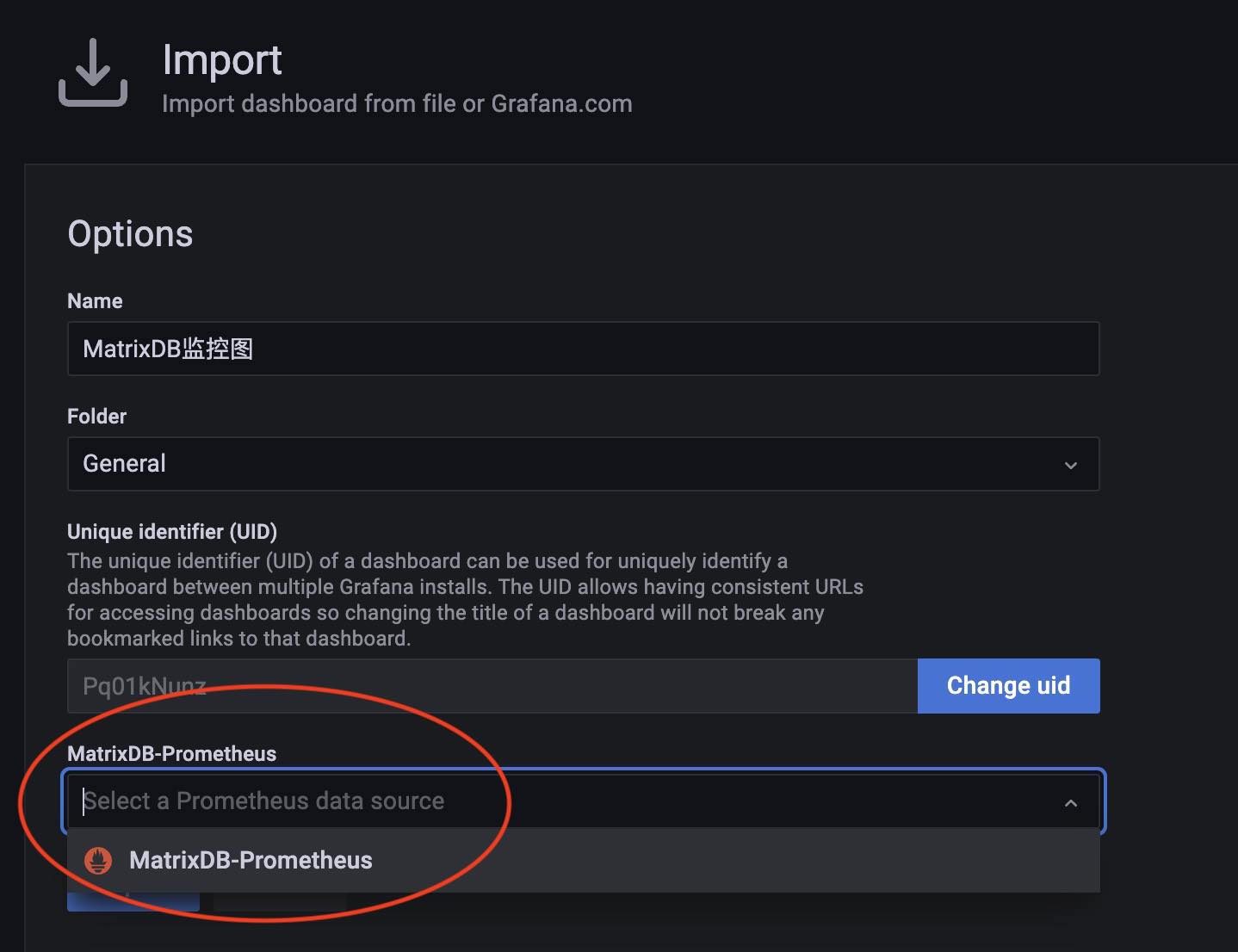
When loading the file, you need to select the Prometheus data source; here, select the source you just created.
Then, you can see the newly loaded dashboard in the dashboard list.
For a detailed explanation of dashboard monitoring parameters, please refer to YMatrix Monitoring Parameter Interpretation
This section describes how to deploy the node_exporter Dashboard.
Loading the node_exporter Dashboard: Since the corresponding Dashboard has been published on the Grafana official website, you can simply enter the ID to load it.
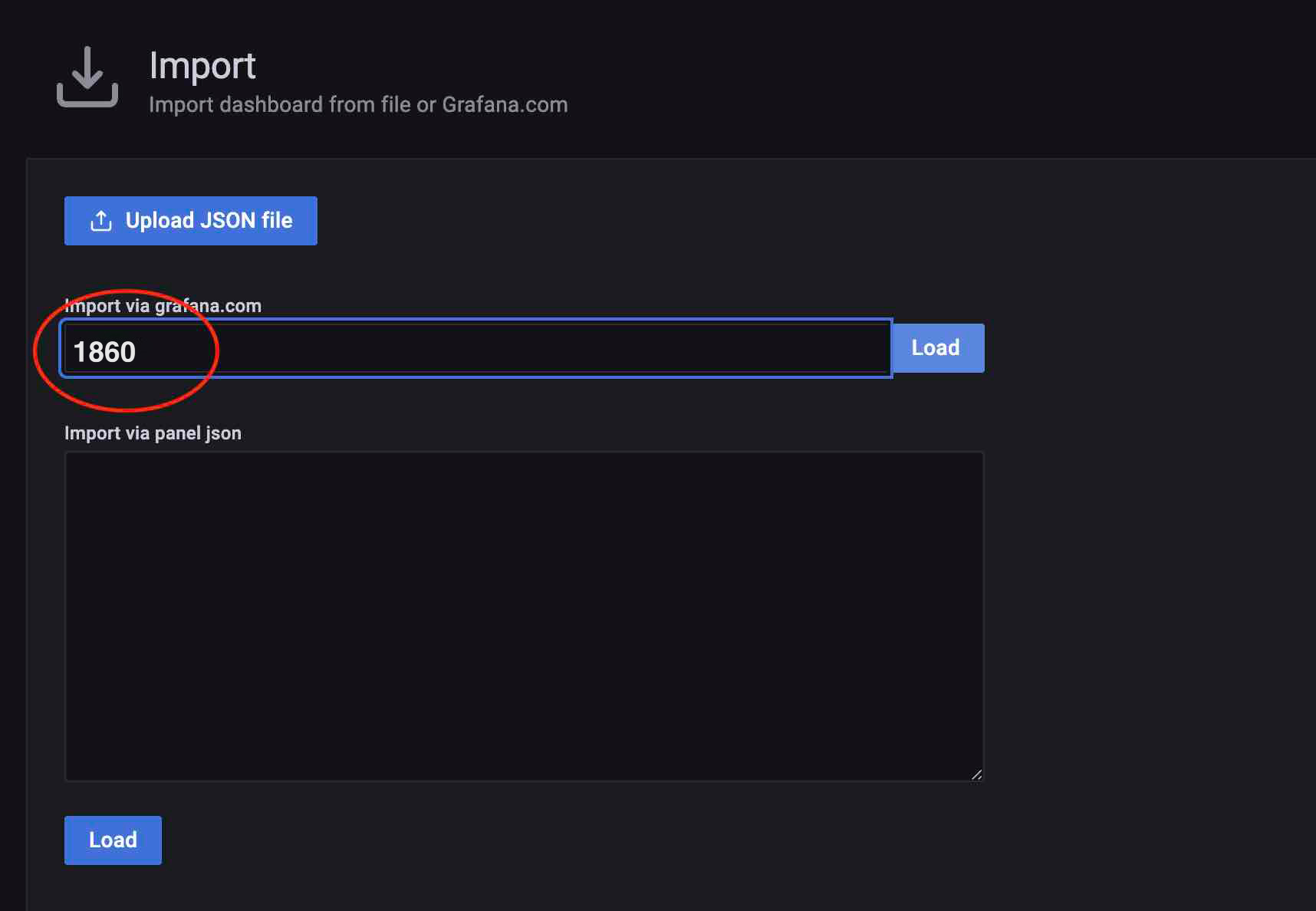
During the loading process, you need to select the data source. Choose the MatrixDB-Prometheus source you just added. If node_exporter has an independent Prometheus cluster, you need to add the data source separately.

Deploying gate exporter also requires creating the matrixmgr database and the matrixts and matrixmgr extensions.
createdb matrixmgr;psql -d matrixmgr
matrixmgr=# CREATE EXTENSION matrixts;
matrixmgr=# CREATE EXTENSION matrixmgr;mxmgr_init_gate_exporter to initialize and start:matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_init_gate_exporter();After successful completion, you will see a new schema named “gate_exporter” under the matrixmgr database. The tables and views under this schema contain gate monitoring and configuration information. Do not modify the definitions or contents of these tables and views.
This command starts gate_exporter on the Master host.
To stop the gate_exporter, execute mxmgr_remove_gate_exporter:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_remove_gate_exporter();To restart it, execute mxmgr_deploy_gate_exporter:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_deploy_gate_exporter();Like loading the YMatrix monitoring panel, the MatrixGate panel file is located at $GPHOME/share/doc/postgresql/extension/MxgateDashboard.json. Simply load this file.
For a detailed explanation of the panel monitoring parameters, please refer to MatrixGate Monitoring Parameter Interpretation.
1. Set up Prometheus to pull etcd status
Edit the configuration file.
$ cd prometheus-*
sudo vi prometheus.ymlAt the end of the file, add the following content:
- job_name: “etcd”
static_configs:
- targets: [“172.31.33.128:4679”, “172.31.45.253:4679”, “172.31.35.134:4679”]The targets field is an array that needs to be replaced with the address of each etcd node in the cluster.
This information can be found in the /etc/matrixdb6/physical_cluster.toml file on the Master host.
$ cat physical_cluster.toml
cluster_id = ‘79LhQxjuwmXgSWZCjcdigF’
supervisord_grpc_port = 4617
deployer_port = 4627
etcd_endpoints = [‘http://10.0.159.1:4679’, ‘http://10.0.172.185:4679’, ‘http://10.0.170.90:4679’, ‘http://10.0.146.2:4679’, 'http://10.0.146.195:4679', ‘http://10.0.150.110:4679’, ‘http://10.0.169.149:4679’]Note! If your host does not have the
/etc/matrixdb6/physical_cluster.tomlfile and you cannot find the etcd process, it means that your cluster is not deployed using the 6.x architecture and does not involve monitoring etcd.
2. Start Prometheus
./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.ymlNote!
Usually, we want Prometheus to run in the background as a system service, which requires configuring it as a systemd service.
3. Configure Grafana's etcd dashboard
Note!
You need to install Grafana 8.2.5 or higher.
First, log in to the Grafana page. The default address is as follows:
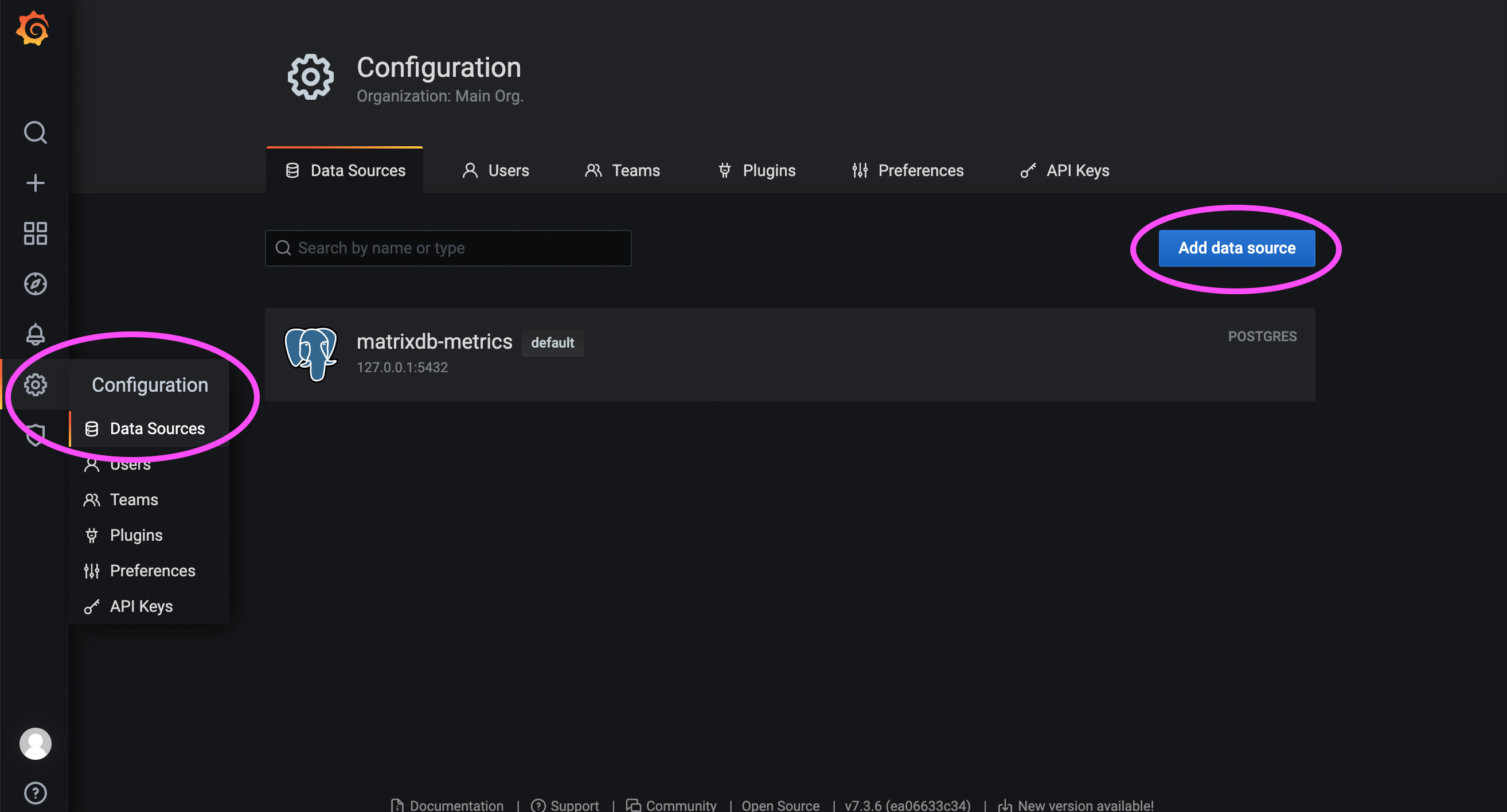
http://<IP address or domain name of the installation node>:3000a. Configure the data source (DataSource)
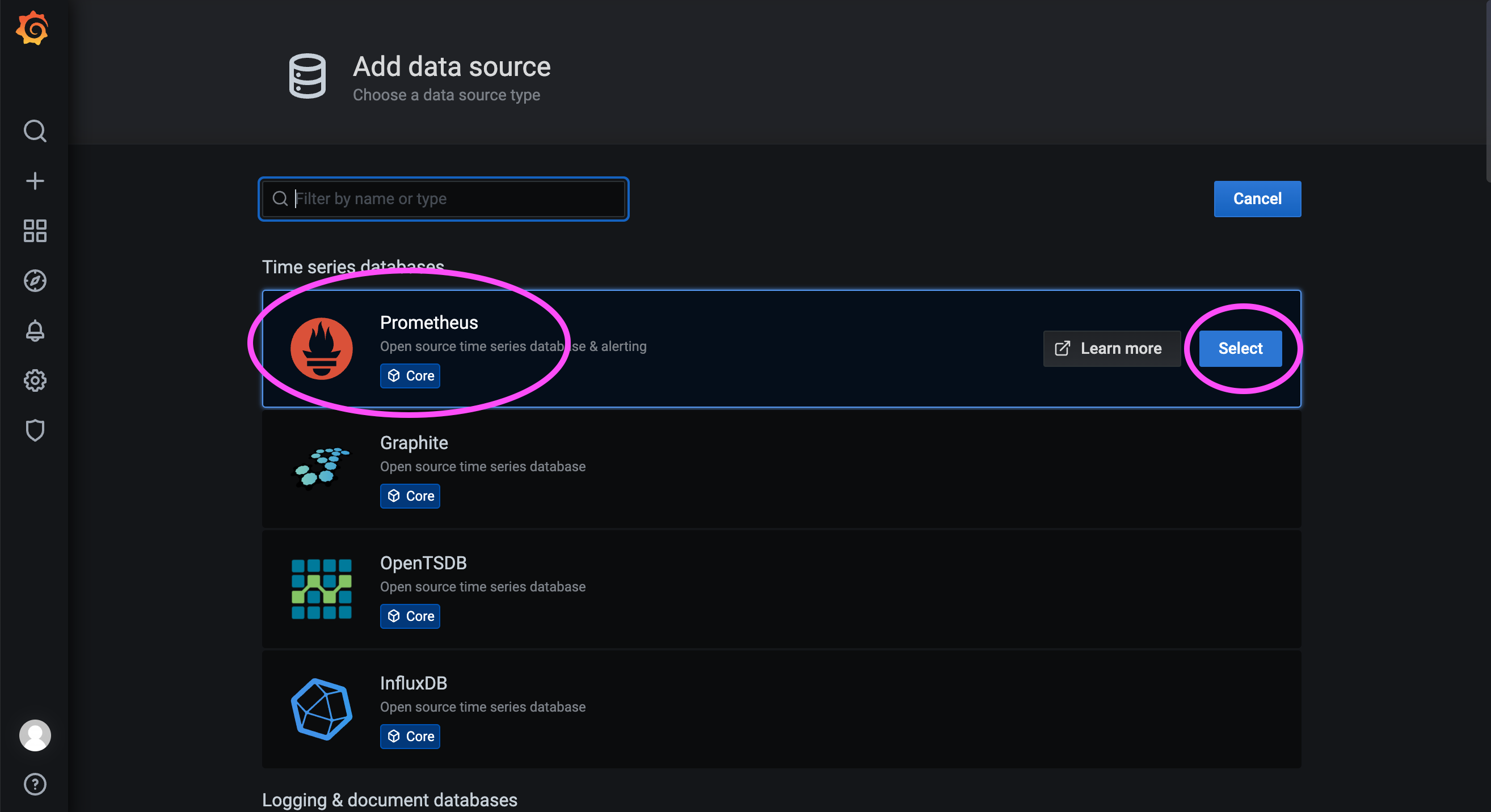

172.31.23.21:9090 is the service port of the Prometheus deployed in the previous step.
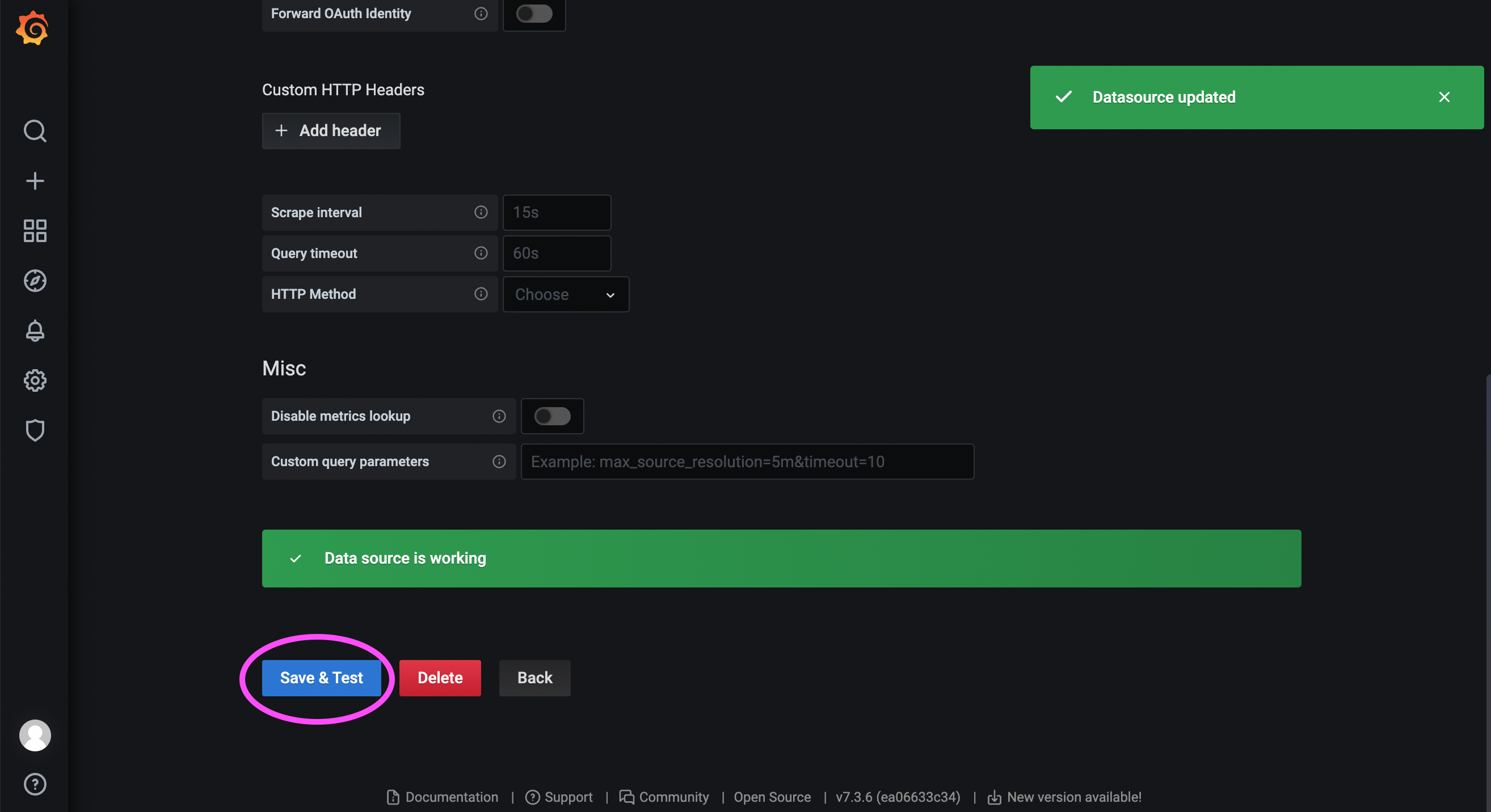
b. Import Dashboard
Access the Grafana community: https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/?search=Etcd+Cluster+Overview
The above link allows you to search for dashboards provided by the community:
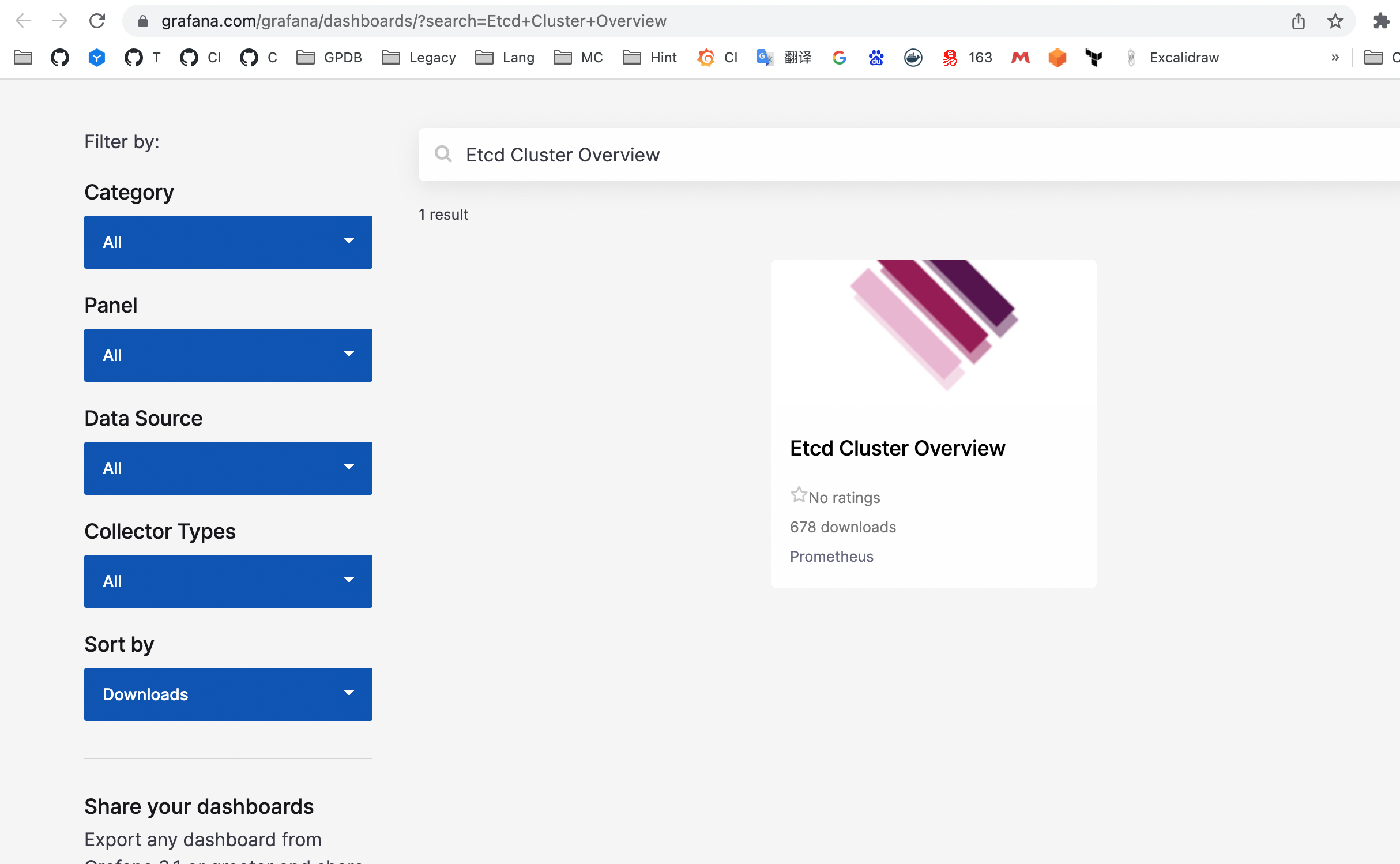
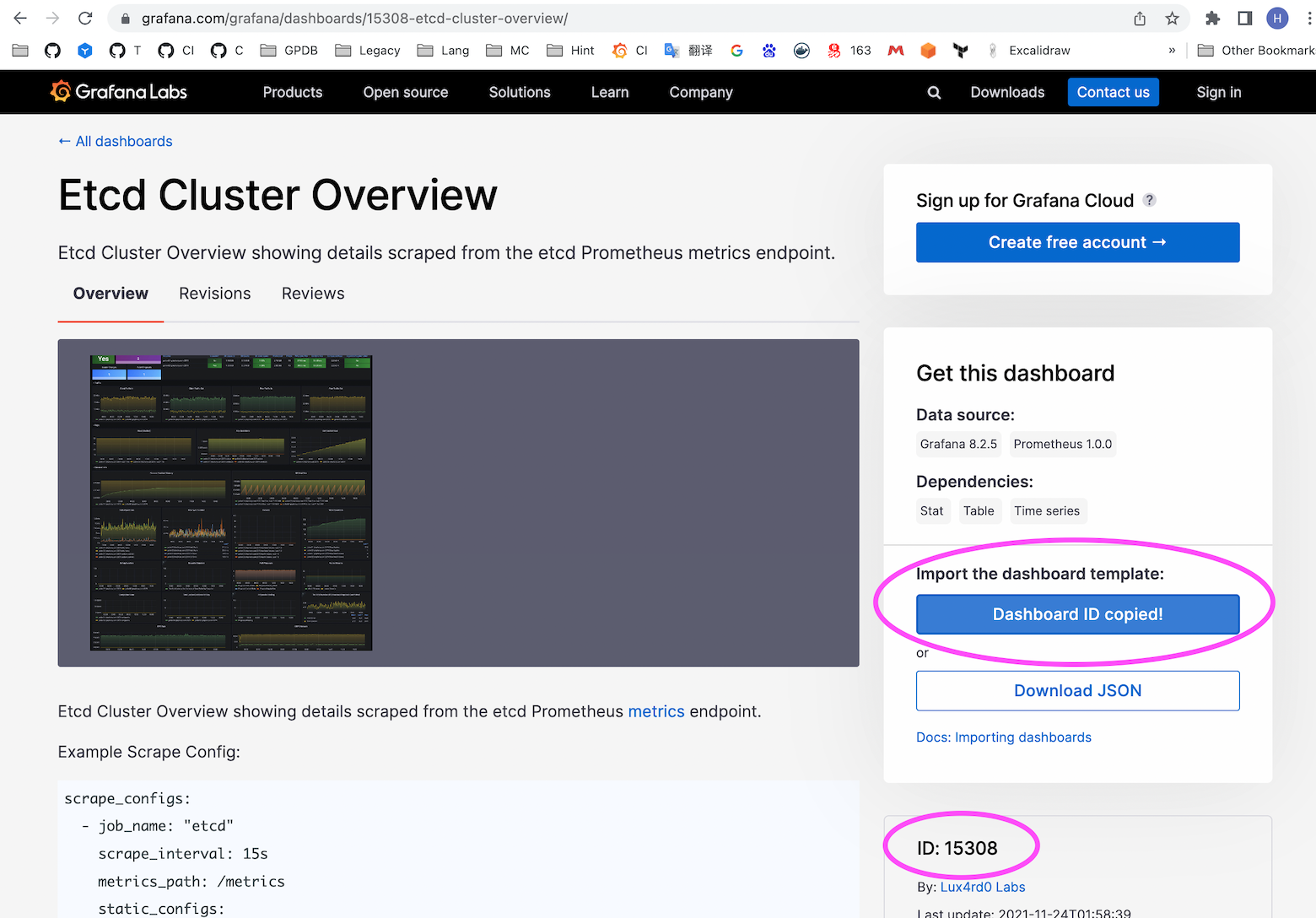
Click to enter and obtain the ID of the Dashboard:
Notes!
The Dashboard corresponding to this ID may be subject to change. The current ID is 15308. Users should refer to their own search results.
As shown in the figure below, we will import Dashboard ID 15308.
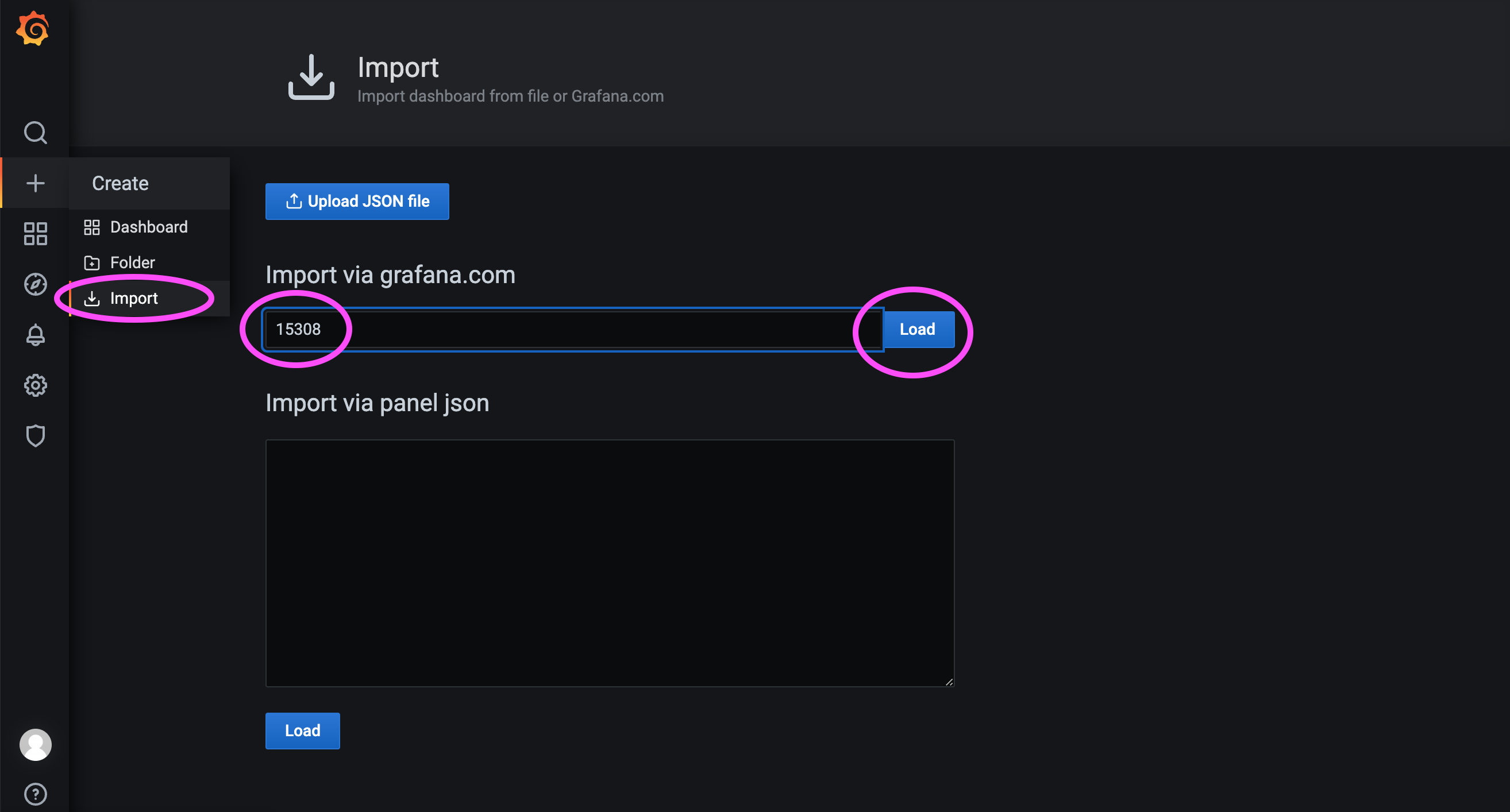
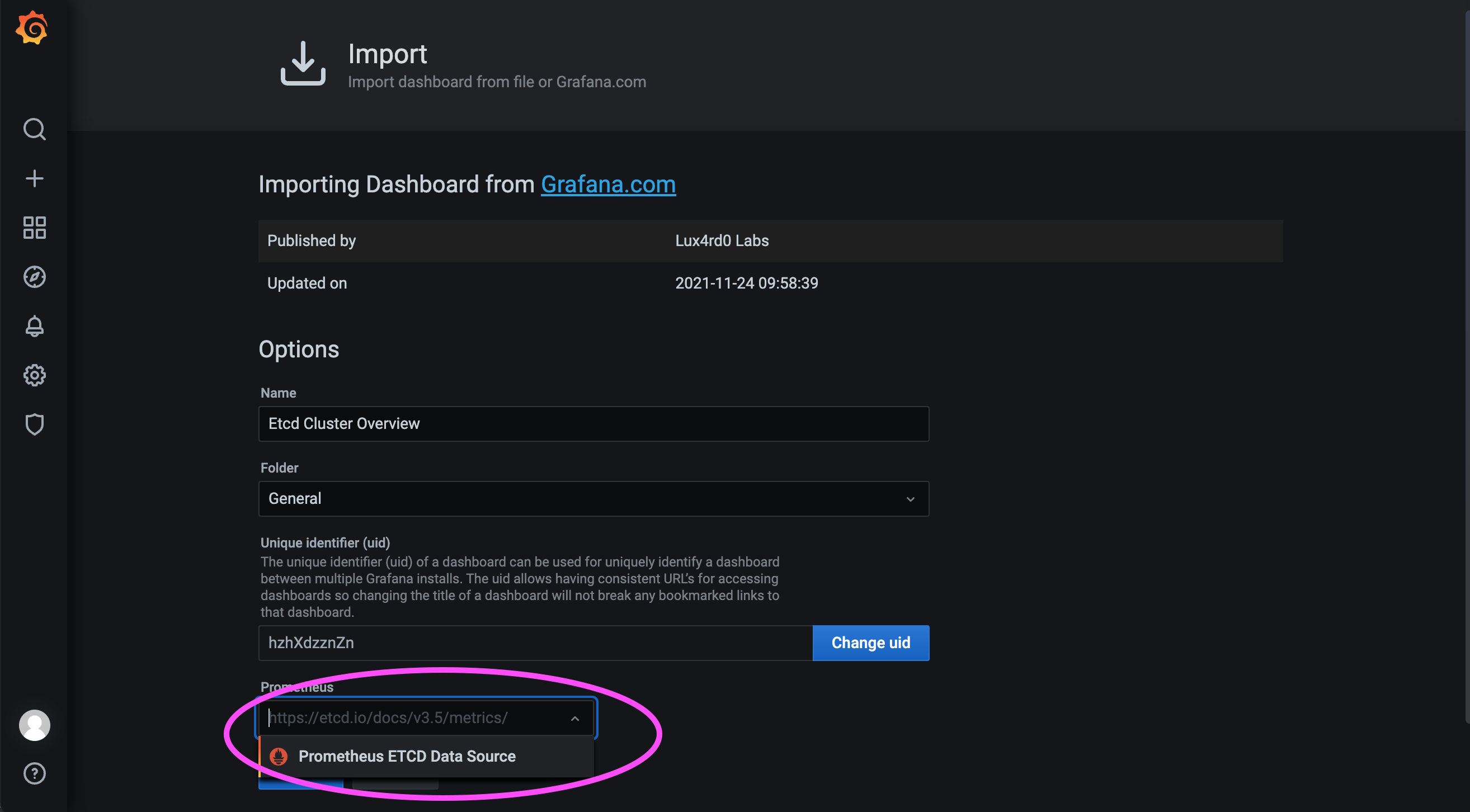
As shown in the figure below, select the data source name we just configured, and finally load the Dashboard.
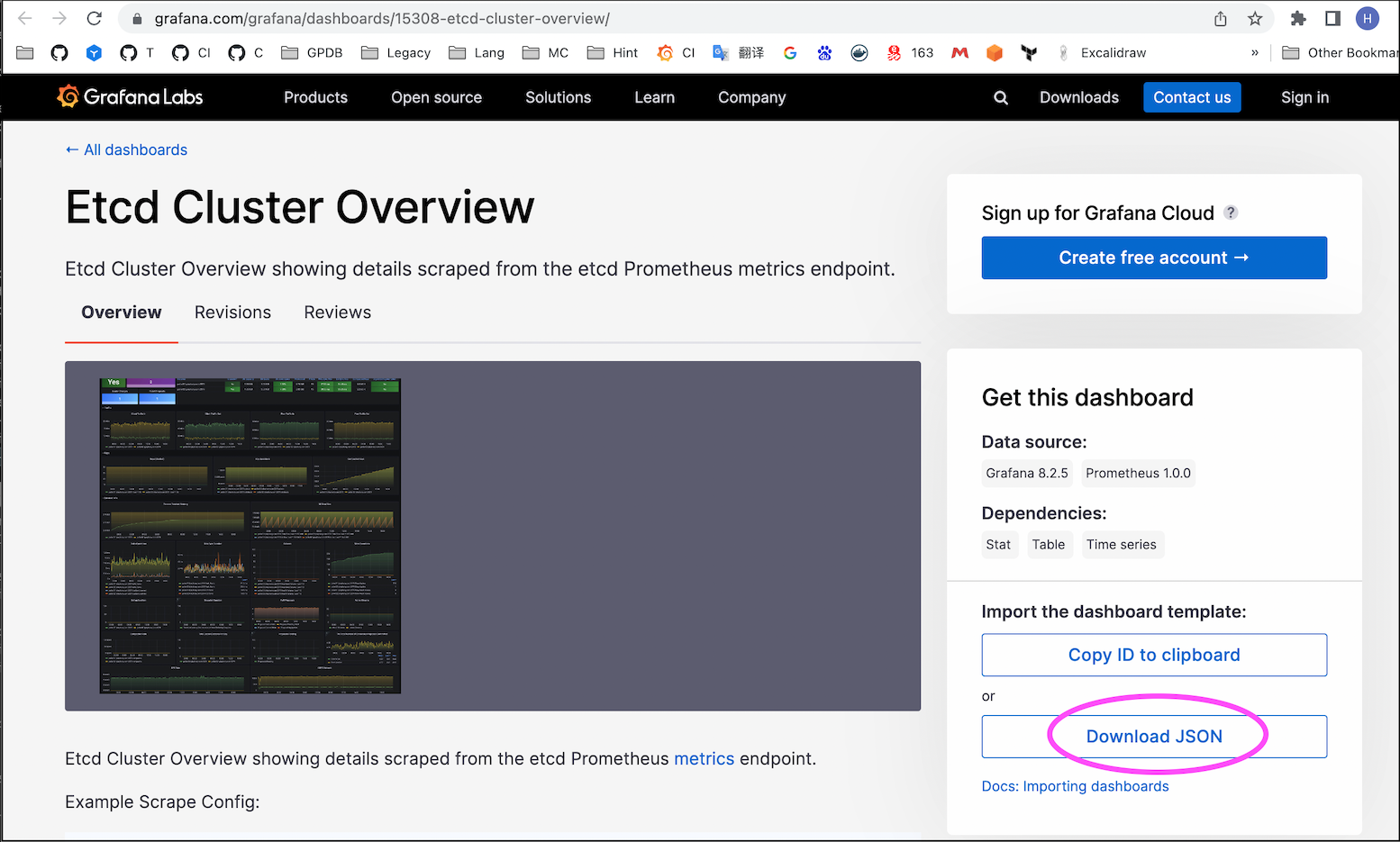
If the server is on an internal network, it may not be possible to import using ID 15308. You need to download the JSON file of the Dashboard from another computer with internet access Download Dashboard and then import it.
For more information on etcd Dashboard key features, refer to the etcd documentation .