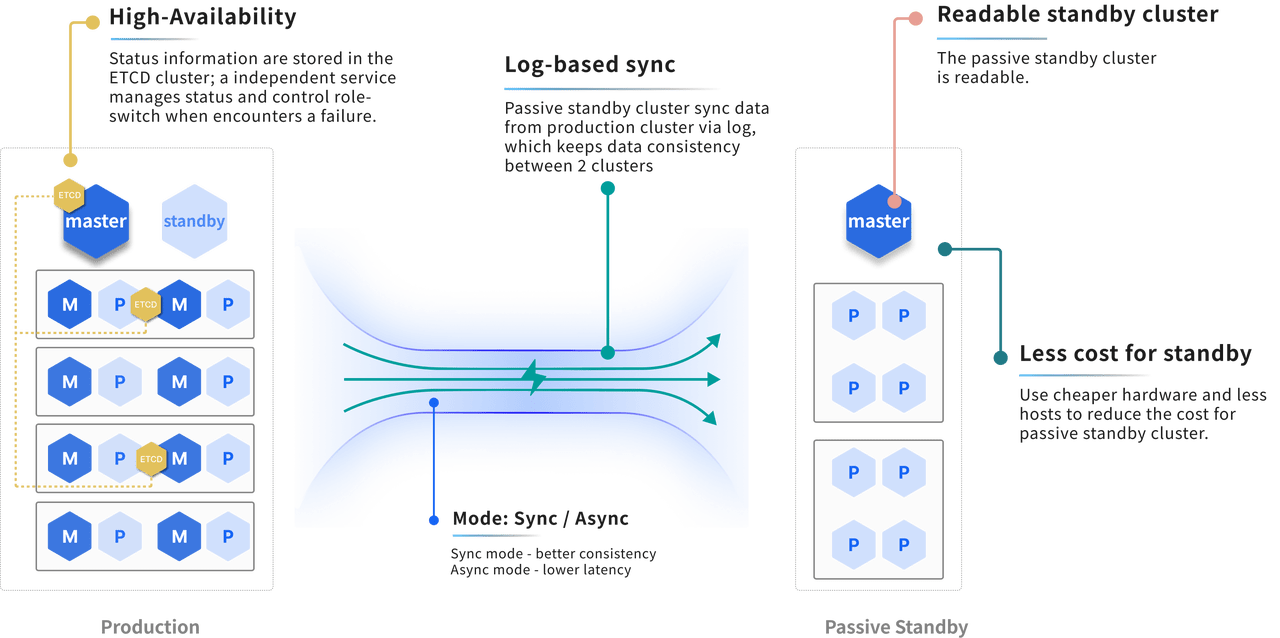
YMatrix Architecture
YMatrix adopts a Share-nothing parallel architecture. Its core feature is that each node operates independently, does not share memory or storage, and nodes only cooperate through network communication. This architecture is widely used in distributed databases, big data systems and high concurrent Web services.
Infrastructure
A complete YMatrix production cluster includes:
- Master Node x 1
- Alternate master node x 1
- Data Node x N (multiple master instances and mirror instances run on each data node)
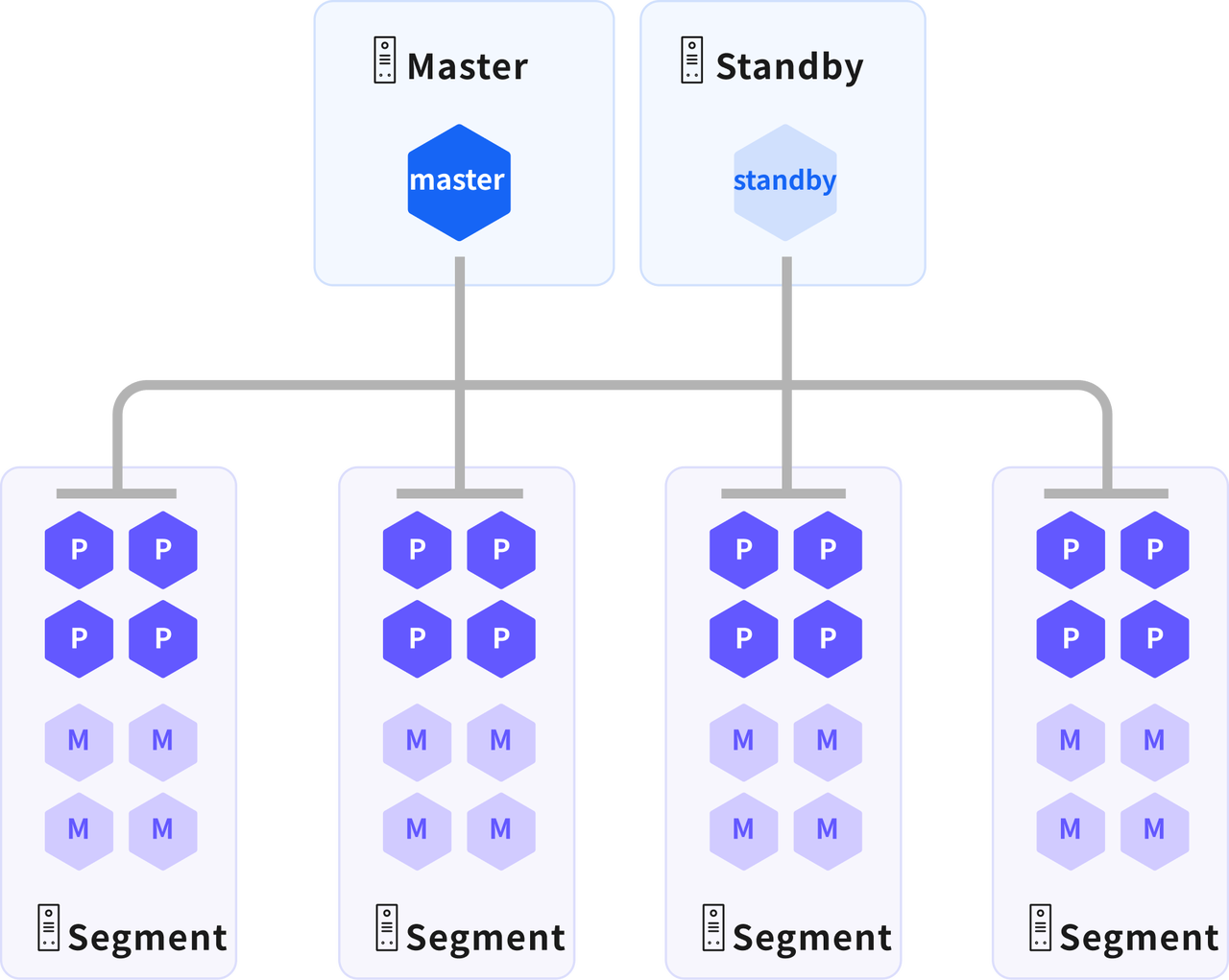
Master node
- Establish a session connection with the management client: As the entrance to the application to access the database, it is responsible for receiving and managing the client's connection requests
- Parses SQL statements and generates a query plan: parse the SQL statements submitted by the client and generate a distributed execution plan (Query Plan)
- Distribute query plan and monitor execution: Distribute the generated query plan to all data nodes (segments) for execution, and monitor the query execution process at the same time
- Collect results and return to the client: summarize the results after execution of each data node, and finally return them to the client
- Storage data dictionary: does not store business data, only system metadata (data dictionary), including the definitions of all data elements and attribute collections
Alternate master node
- Data backup and consistency guarantee: Data and functions that keep the backup master nodes completely consistent with the master nodes
- Automatic fault switching: When a master node fails, the backup master node will be automatically promoted to a new master node to ensure cluster service continuity
- Distributed Isolation Deployment: The standby master and master must be deployed on different physical hosts
Data Node
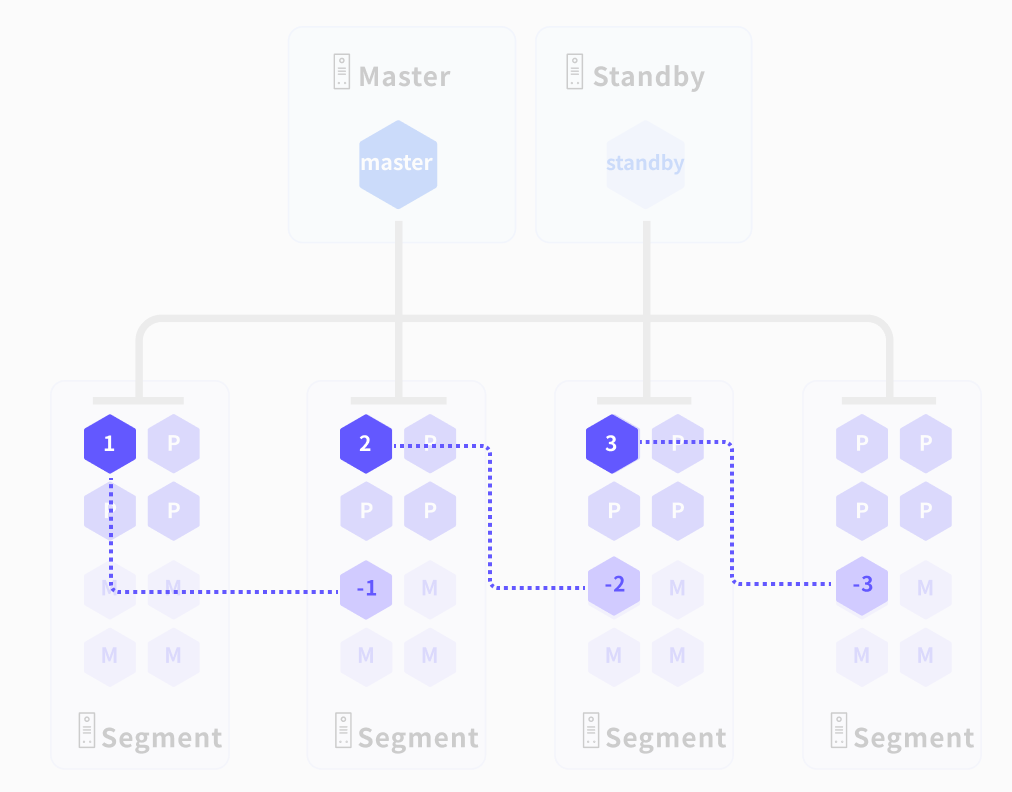
The data node is the core unit of YMatrix for data storage and computing. Data in the data table will be distributed to each primary instance according to the configuration, and each primary instance independently holds data shards that do not coincide with other primary instances. When executing a query, the master node generates a query plan and distributes it to all master instances for parallel execution, improving query response speed through parallel calculation
Main instance (Primary)
There can be multiple independent master instances on a node
- Data storage: The data of the data table will be distributed to each master instance according to the configuration. Each master instance independently holds data fragments that do not coincide with other master instances.
- Distributed Query Execution: Responsible for executing query plans issued by the master node, and improve query response speed through parallel computing
- Data processing core: It is the key to data nodes achieving high performance. A large number of master instances with the same capabilities can evenly distribute data and workloads, so that all master instances can work for one task at the same time and complete it synchronously.
Mirror instance (Mirror)
There can be multiple independent mirror instances on a node
- Keep data consistent with primary instance: The image instance maintains data and functionality exactly consistent with the primary instance.
- Replace the main instance to provide services when a failure occurs: When the main instance fails (such as power failure of the machine, instance failure, etc.), the mirror instance will be automatically promoted to the main instance, and it will replace it to provide data storage and computing services to ensure that the cluster service is not interrupted. In production environments, the main instance and the mirror instance are usually distributed on different hosts to avoid the impact of single node failures.
Query execution
The query generates an execution plan through the optimizer, and then reads the corresponding data through the calculation engine and storage engine, and performs calculations to finally obtain the query result.
Optimizer
YMatrix provides 2 optimizers:
- PQO (Postgres Query Optimizer): An optimizer based on PostgreSQL native optimizer, suitable for transaction (TP) scenarios and most analytical (AP) scenarios.
- ORCA: It is an optimizer based on the Cascades framework. It can generate more reasonable plans when processing large and complex queries, reduce system resource usage, and improve query performance.
Storage Engine
YMatrix provides 2 storage engines:
- HEAP: A classic line storage engine inherited from PostgreSQL, suitable for transaction (TP) scenarios, and has good performance in writing, updating, and deleting.
- MARS3: YMatrix's self-developed high-performance ranks and sequence hybrid storage engine has excellent performance in analysis (AP) and timing scenarios, and can improve the compression ratio.
Computing Engine
YMatrix provides a vectorized execution engine that has been fully vectorized. In the case of large data volume, query speed can be greatly improved.
High availability
YMatrix ensures high availability of the cluster through the mirroring mechanism, and also provides the off-site disaster recovery function to ensure that services can be provided through backup clusters under extreme conditions.
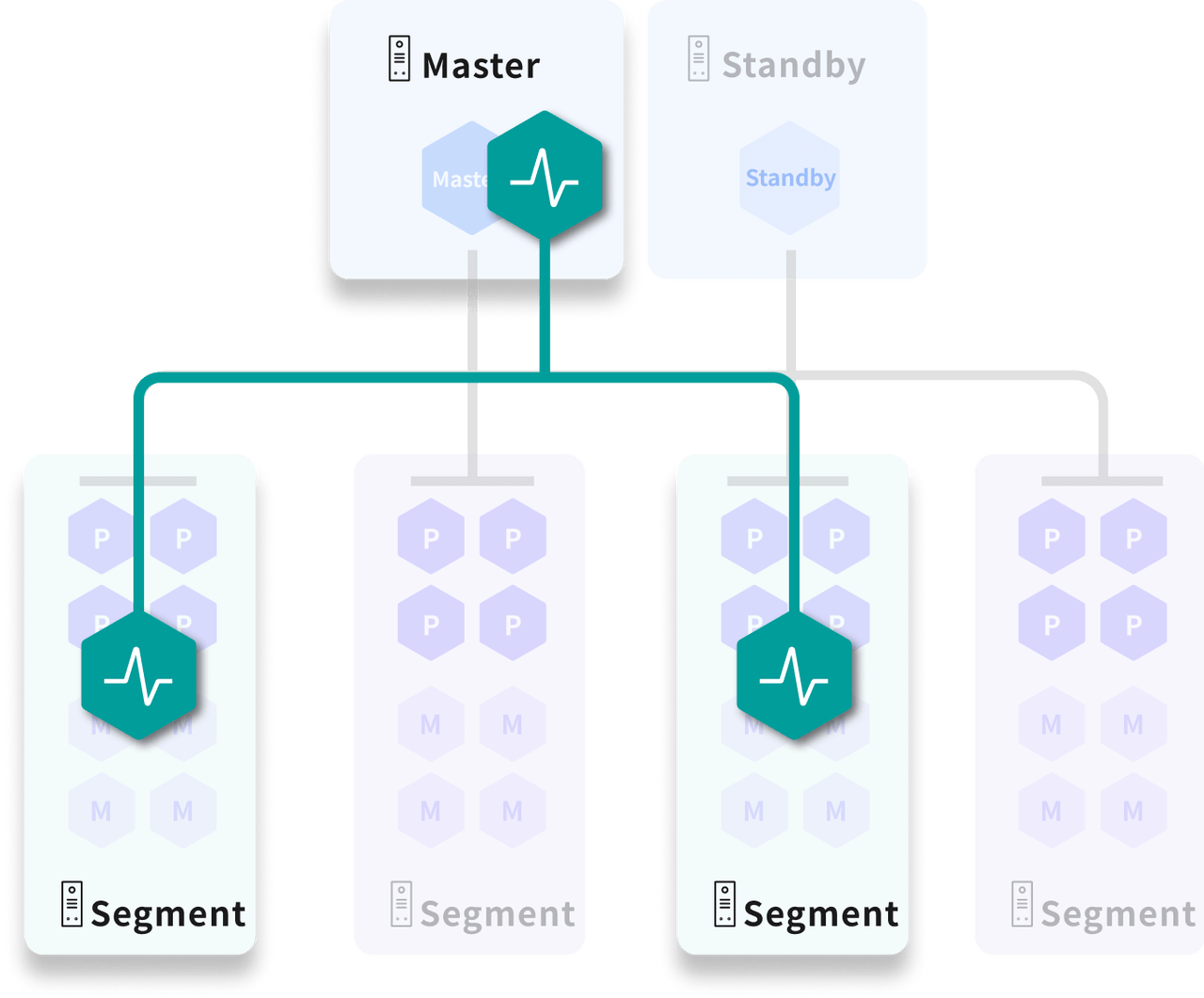
Mirroring mechanism
After enabling the mirroring function, each primary instance will correspond to a mirror instance, and the mirror instance will maintain exactly the same data and functions as the primary instance. In a production environment, we keep the primary instance and the corresponding mirrored primary instance distributed on different hosts.
- When the cluster works normally, the mirrored instance does not participate in the calculation and only remains exactly consistent with the main instance data.
- When the main instance fails, or if the machine where the main instance is located fails, the corresponding mirror instance will replace the failed main instance to provide services, thus ensuring that the data service is not interrupted.
Status Management
ALOHA (Advanced Least Operation High Availability) is a newly designed cluster state management service.
In the YMatrix cluster, odd nodes will be randomly selected to build a distributed ETCD cluster to save the status of nodes and instances; when a failure (node downtime/instance failure, etc.), the system can schedule according to the status of the cluster to realize automatic switching between main and standby, automatic fault transfer, etc., to ensure the high availability of the cluster.
Disaster preparations in other places
YMatrix provides off-site disaster recovery cluster deployment solutions. Once a failure occurs on the main cluster side, you can switch to the backup cluster and the backup cluster provides normal services. At this time, the use of the cluster is consistent with the normal use of the YMatrix database cluster.