This document describes the following aspects of the YMatrix architecture:
Global Architecture
Local Architecture
To reduce the complexity of the data ecosystem, YMatrix has designed a simple architecture with hyper-convergence genes, integrating computing, storage, and network resources into a unified system. It is based on a massively parallel processing (MPP) system and complies with the characteristics of a microkernel architecture.
This architecture is flexible and adaptable to multiple scenarios. It is not only friendly to IoT time series scenarios, but also supports traditional analytical data warehouse environments and business intelligence (BI) work.
Replacing traditional data technology stacks with hyper-converged architectures may seem like a daunting task. So why do we need to do this?
In fact, regardless of the situation, the comprehensive use of hyper-converged architectures can benefit many enterprises by providing a unified data foundation for complex IT systems, including smart connected vehicles, industrial Internet, smart manufacturing, smart cities, energy, finance, and pharmaceuticals.
Compared to complex data technology stacks like the Hadoop ecosystem, the YMatrix architecture offers the following advantages:
Hyper-convergence
High availability
Rich toolchain ecosystem
Supports standard SQL
Full support for ACID transactions
Compared to databases with other architectures, YMatrix's hyper-convergence is reflected in the integration of multiple data types and data operations, enabling high-performance support for multiple data types + multiple scenarios within a single database. In terms of YMatrix's internal architecture, it has microkernel characteristics. Building upon common foundational components, it provides different storage and execution engine combinations tailored to diverse business scenario requirements, thereby enabling distinct microkernels to achieve targeted improvements in write, storage, and query performance.
The diagram below describes the composition and functions of the hyper-converged architecture within YMatrix:
_1696644131.png)
The following sections provide a detailed overview of the components of the YMatrix hyper-converged architecture.
YMatrix's high-level database architecture is based on the classic MPP (massively parallel processing) database technology architecture with some enhancements.
The diagram below describes the core components that make up a YMatrix database system and how they work together:
_1693302582.png)
The following sections provide a detailed introduction to the various components of the YMatrix database system and their functions.
YMatrix uses its proprietary ALOHA (Advanced Least Operation High Availability) technology to ensure high availability of the cluster. When a single point of failure occurs in the cluster, the corresponding standby instance will switch roles and replace the failed instance to provide services, thereby ensuring uninterrupted cluster services.
| Faulty node instance | Impact | Time |
| Mirror | When Mirror fails, it does not affect users' queries of data in the corresponding Primary, but the faulty Mirror must be manually restored | Seconds in a network-connected environment |
| Standby | When the Standby node fails, it does not affect users' queries of cluster data, but the failed Standby node must be manually restored | |
| Primary | When the Primary node fails, users cannot query the corresponding data and must wait for the system to automatically promote the corresponding Mirror to Primary before querying again | |
| Master | When the Master fails, the cluster becomes unavailable, and users cannot query the corresponding data. They must wait for the system to automatically promote the corresponding Standby to Master before querying again. |
Notes!
For detailed steps on fault recovery, see Fault Recovery.
ALOHA services use a highly available architecture based on ETCD clusters. This architecture solves the problem of automatic failover, which essentially means implementing an automatic master node election mechanism and maintaining strong data consistency.
This mechanism includes the following steps:
Notes!
ETCD clusters will have more disk operations during storage state, so ideally, several separate physical machines should be used to deploy ETCD clusters, which can fully guarantee the performance of ETCD. However, in actual applications, the number of physical machines may not be enough to support ETCD independent deployment, so odd ETCD instances will be randomly deployed on some or all physical machines in the data cluster to save the status data of nodes and instances.
The schematic diagram is as follows:
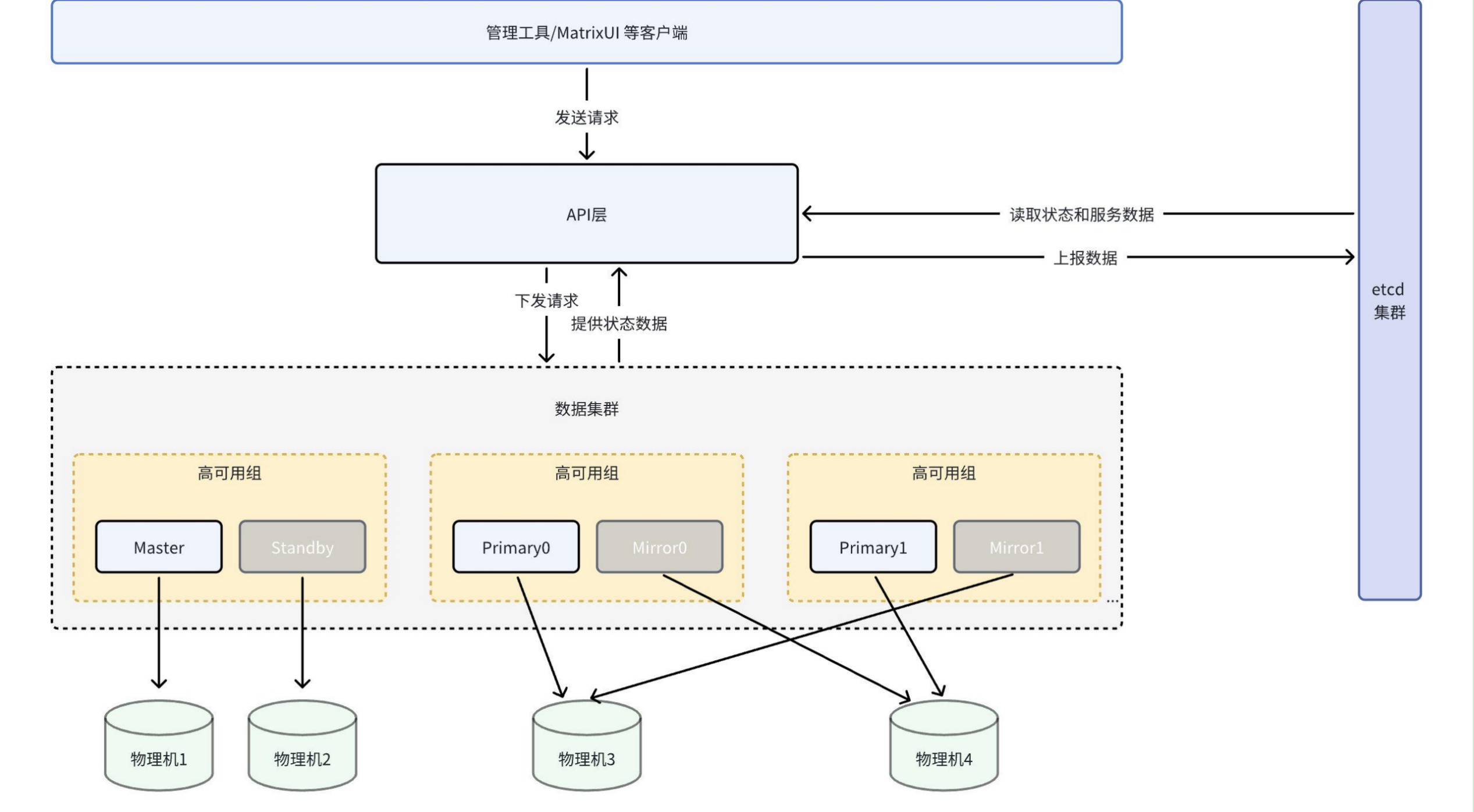
You can see:
ETCD is a distributed key-value storage cluster used to store and retrieve data in a distributed system. ETCD uses Raft consistency algorithm to ensure data consistency and reliability. It is designed to be highly available with strong failure recovery capabilities. ETCD provides a simple RESTful API interface, allowing applications to easily access and manipulate key-value pairs stored there.
Important concepts: