YMatrix is a highly available distributed database system that supports fault recovery when nodes fail. High availability relies on redundant deployment: the Master node must have a Standby node as backup; for data nodes (Segments), each Primary node must have a corresponding Mirror node.
The following diagram illustrates a typical high-availability deployment:
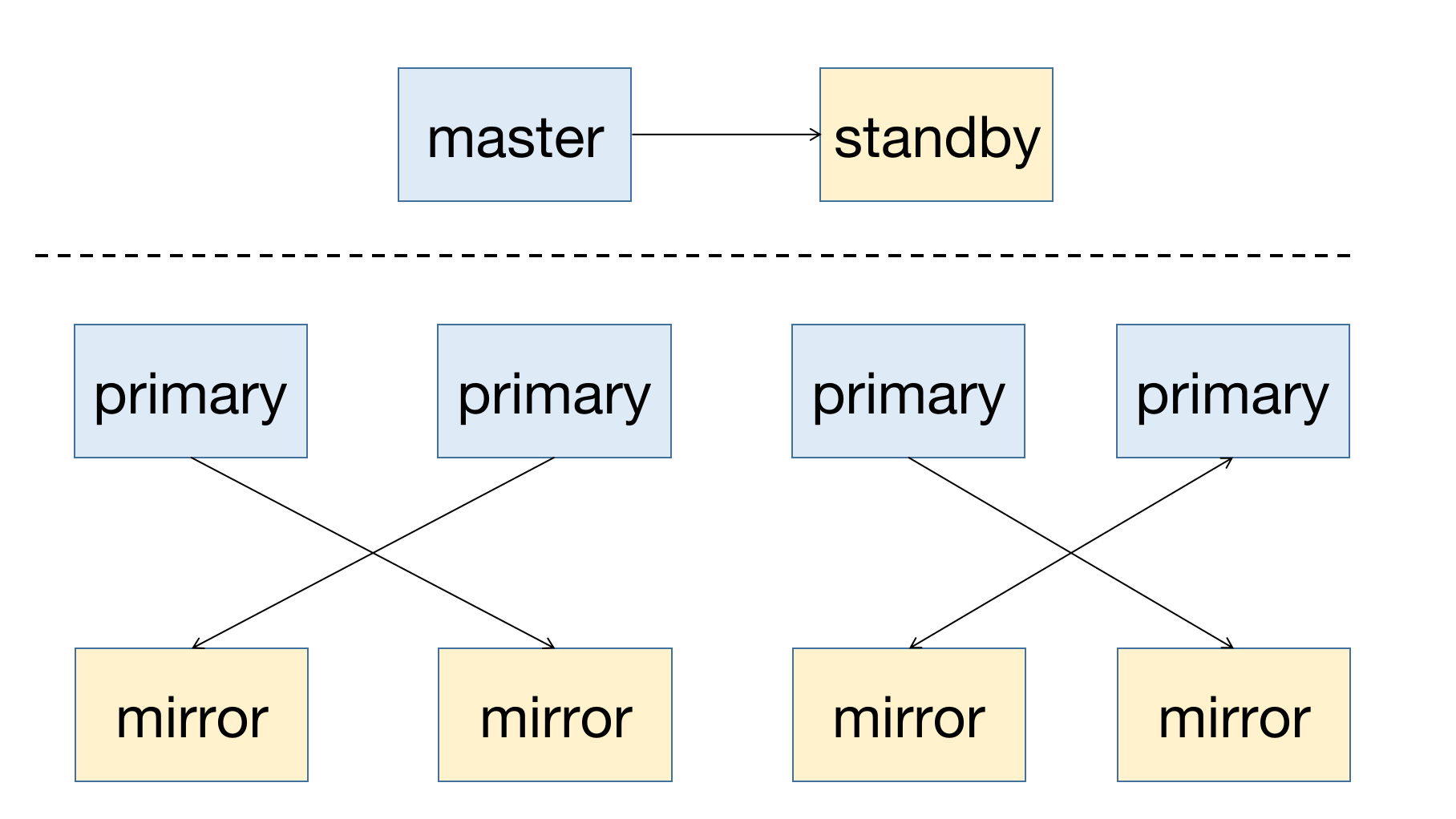
When a node fails in the cluster, you can check the node status via the graphical interface (MatrixUI). In this example, the Master is mdw, the Standby is smdw, and the Segments are sdw1 and sdw2, each with its own Mirror.
Deployment principles:
This deployment avoids single-host failure causing system unavailability and balances cluster load.
Below describes the automatic operation and maintenance mechanism of YMatrix clusters and solutions for various node failure scenarios.
YMatrix supports Cluster Service for automated operations. This service includes two key features: automatic failover and automatic failback (powered by the mxrecover tool). Together, they enable complete node recovery workflows.
Automatic failover refers to the mechanism where, upon detecting a node failure through etcd cluster health checks, the system automatically switches roles between primary and standby nodes. The etcd cluster is the core component of YMatrix Cluster Service, managing the state of all nodes. When any node fails, the database system automatically performs failover without manual intervention.
After failover completes, only the new Primary/Master remains active—there is no healthy Mirror/Standby. If another failure occurs, recovery will not be possible. Therefore, use the mxrecover tool to create a new healthy Mirror/Standby for the promoted Primary/Master.
The mxrecover tool provides the following functions:
Note!
For detailed usage ofmxrecover, refer to mxrecover.
When the system detects a Mirror/Standby node failure, the node status in the graphical interface changes to down.
Note!
A Mirror failure does not affect cluster availability, so the system does not automatically reactivate it.
Use themxrecovertool to reactivate the Mirror—see below.
If the downtime was short and the amount of data on the failed node is small, consider incremental recovery first. Running mxrecover without parameters or with only -c triggers incremental recovery mode. If incremental recovery fails, perform full data replication to reactivate the node using the mxrecover -F command.
When a Primary node fails, the system automatically promotes its Mirror to Primary.
After the system promotes a Mirror/Standby, run mxrecover to generate a new Mirror/Standby for the current Primary/Master and synchronize data incrementally or fully to restore the failed node. Simply running mxrecover reactivates the failed Mirror/Standby with incremental recovery. As mentioned above, use mxrecover -F to force full recovery if needed.
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxrecoverAlthough mxrecover creates a new Mirror for the promoted Primary, it may result in uneven distribution—one host now runs two Primary nodes (e.g., both on sdw2). This causes unbalanced resource usage, placing heavier load on sdw2.
To redistribute roles, run:
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxrecover -rAfter executing mxrecover -r, verify the updated configuration in the cluster management page of the graphical interface.
Master failover occurs under two conditions:
Below details the impact of Master failover on various components and recommended actions for each scenario.
This indicates that after Master failure, failover has occurred and Standby now manages the cluster.
In this case, access the graphical interface on the Standby node. The default address is http://<standbyIP>:8240.
You can log in using either the mxadmin database password or the /etc/matrixdb5/auth.conf superuser password on the Standby node.
All functions remain fully usable after login. Red on the left indicates a failed node; yellow indicates a completed failover.
This means the entire cluster is unavailable. You may still access the MatrixUI via the Master node to view status, but database query functionality will be limited.
Note!
If your cluster did not initially configure a Standby but later added one using themxinitstandbytool, the behavior matches that of a pre-configured Standby.
Note!
Always configure a Standby in production environments.
Failover has occurred—the Standby now manages the cluster.
Two scenarios apply:
MatrixGate resides on the Master host, which has failed and rendered the cluster unusable.
In this case, the MatrixGate process is considered dead or network-isolated along with the host.
MatrixGate automatically redirects monitoring data insertion to the Standby. Monitoring continues uninterrupted—no manual intervention needed.
To view Grafana dashboards, manually update the data source to point to the Standby’s address.
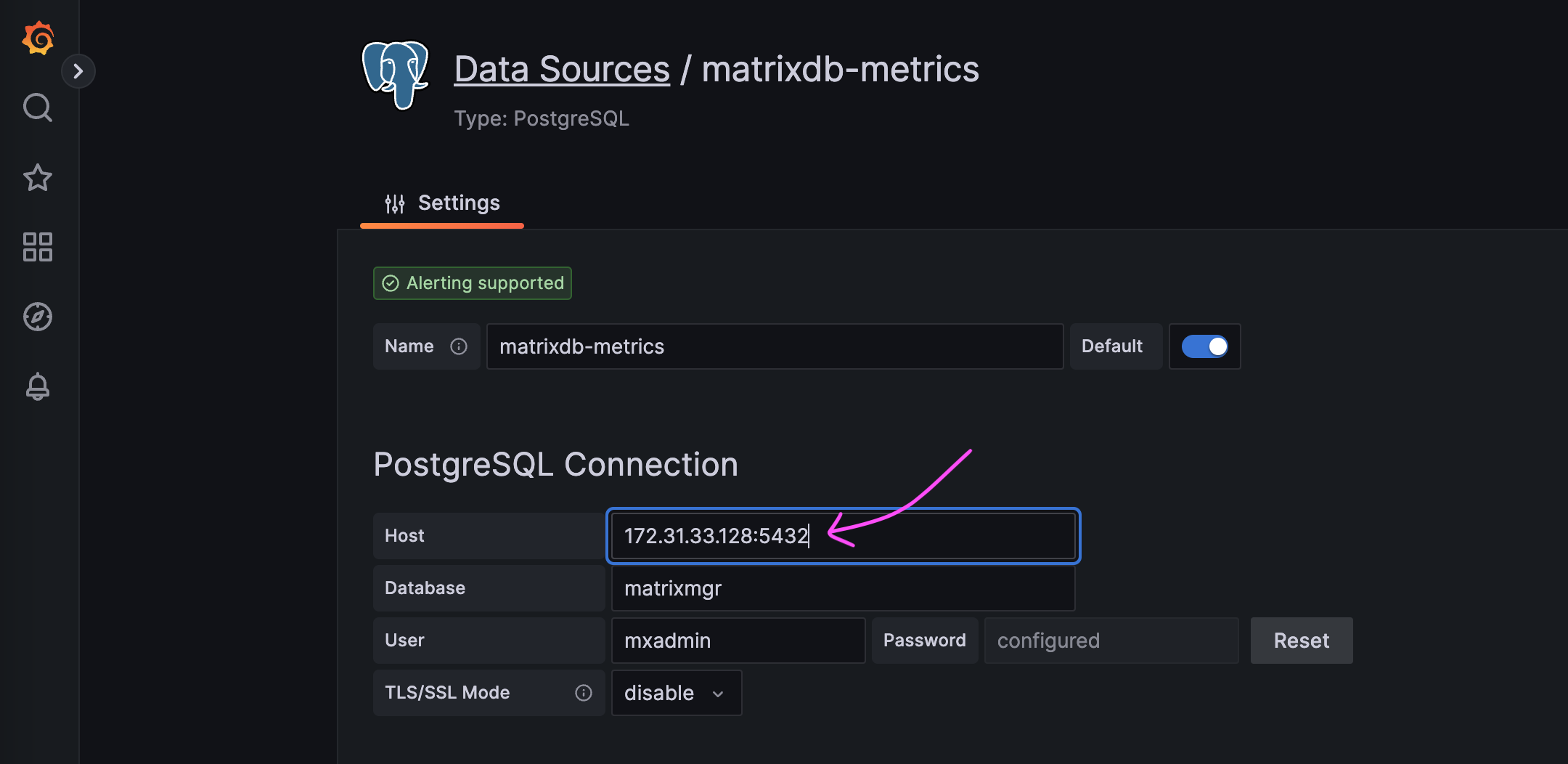
In this case, the MatrixGate instance used for monitoring has failed, so no new monitoring data will be generated.