YMatrix is a highly available distributed database system that supports failure recovery after node downtime. The premise of high availability is redundant deployment, so the master node needs to have a standby node (Standby) as backup; for data node (Segment), Primary is the primary node, and it needs to have a corresponding mirror node (Mirror).
The deployment diagram of a highly available system is as follows:
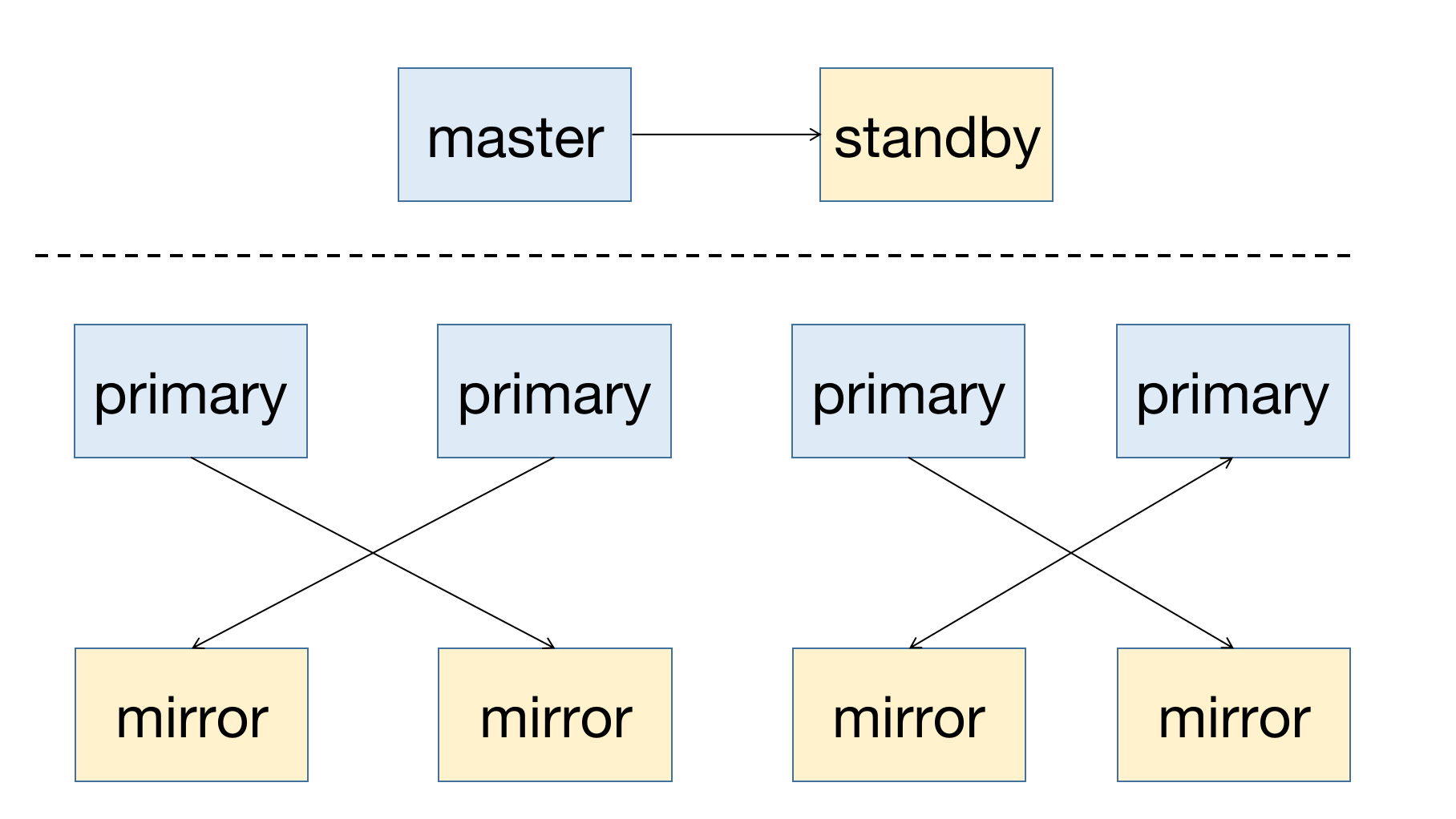
When a node in the cluster fails, you can get the node status information by viewing the graphical interface (MatrixUI). The sample cluster master is mdw, Standby is smdw, Segment is sdw 1 and sdw 2, each with a Mirror.
Deployment status:
The above deployment method is to avoid the system unavailability caused by single host failure and disperse the pressure on the cluster.
The following will briefly describe the automatic operation and maintenance principle of YMatrix cluster and the solution to the airport scene of different role nodes.
YMatrix supports Cluster Service for operation and maintenance automation. This service mainly includes two functions: Failover and Failback supported by the mxrecover tool. Using these two functions, a complete recovery process for node failures can be achieved.
Automatic fault transfer refers to the mechanism in the automatic operation and maintenance system that transfers the fault by recalling the node status diagnostic information of the etcd cluster and switching the main and backup nodes. The etcd cluster is a core component in the YMatrix cluster state service, responsible for managing the status information of all nodes. When any node in the cluster fails, the database system will automatically fail over the node without manual intervention.
After the automatic fault transfer is completed, the corresponding node only has Primary/Master and there is no healthy backup node. If a failure occurs again, it cannot be restored. Therefore, you need to use the mxrecover tool to generate healthy Mirror/Standby nodes for the new Primary/Master.
The mxrecover tool has the following functions:
Notes!
For details on the use of the mxrecover tool, see mxrecover.
When the system finds that Mirror / Standby is down, the node status of the graphical interface will change to down.
Notes!
Mirror downtime does not cause the cluster to be unavailable, so the system does not reactivate Mirror.
To activate Mirror, you need to use themxrecovertool, see below for details.
At this time, if the downtime interval is short and the data volume of the downtime node is not very large, it is recommended that you try incremental recovery first. Incremental recovery mode is used when there are no parameters after the mxrecover command or only -c. If incremental recovery fails, you need to activate the downtime node by copying the full amount of data, that is, use the mxrecover -F command.
When the system finds that Primary is down, the corresponding Mirror will be automatically raised to Primary.
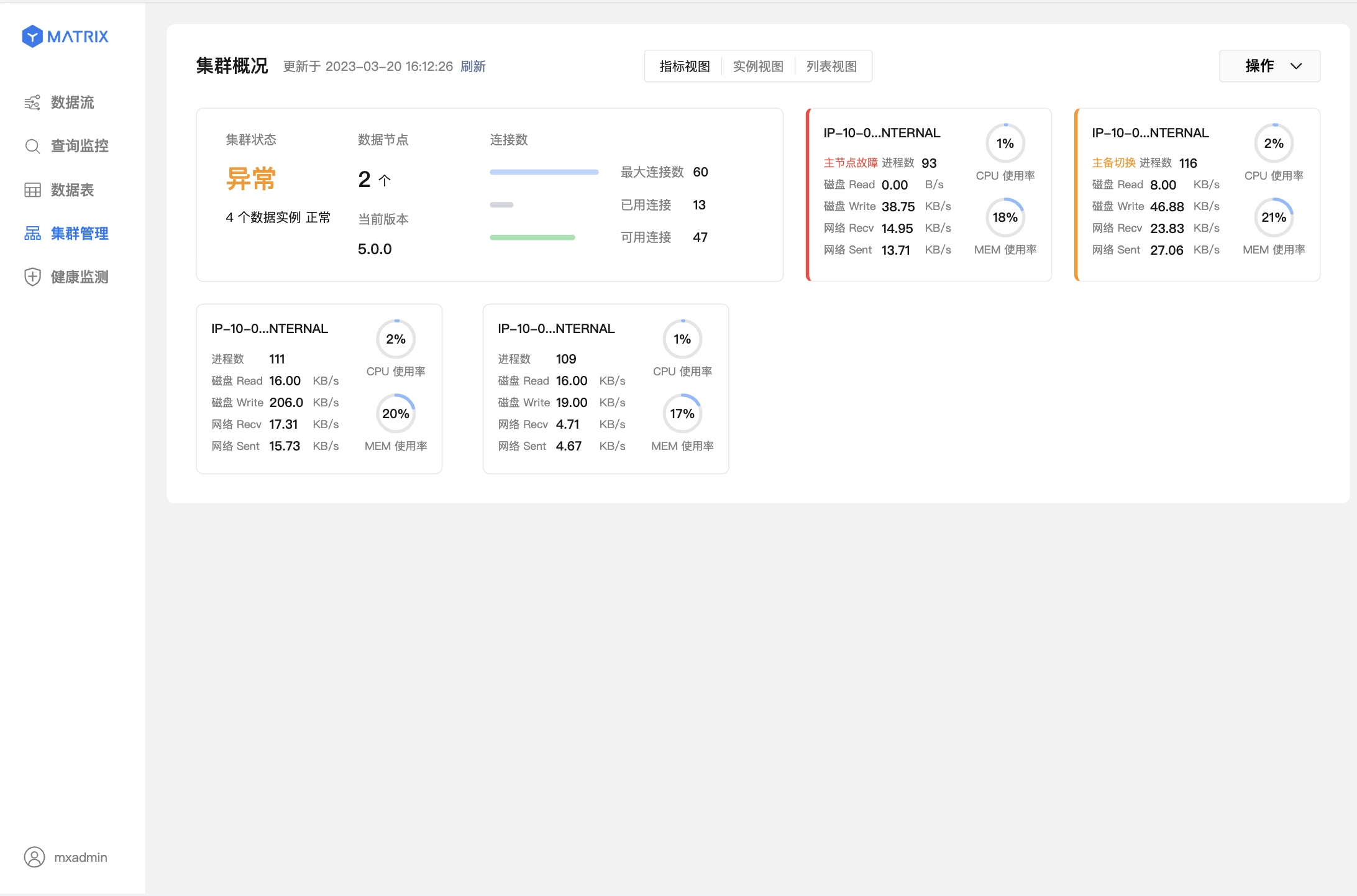
The figure below shows the master node (Master) failure and the master-support switching has been completed. The red to the left of the box indicates that this node has failed, and the yellow indicates that this node has completed failover.
The following two figures represent data node (Segment) failure and master-slave switching has been completed.
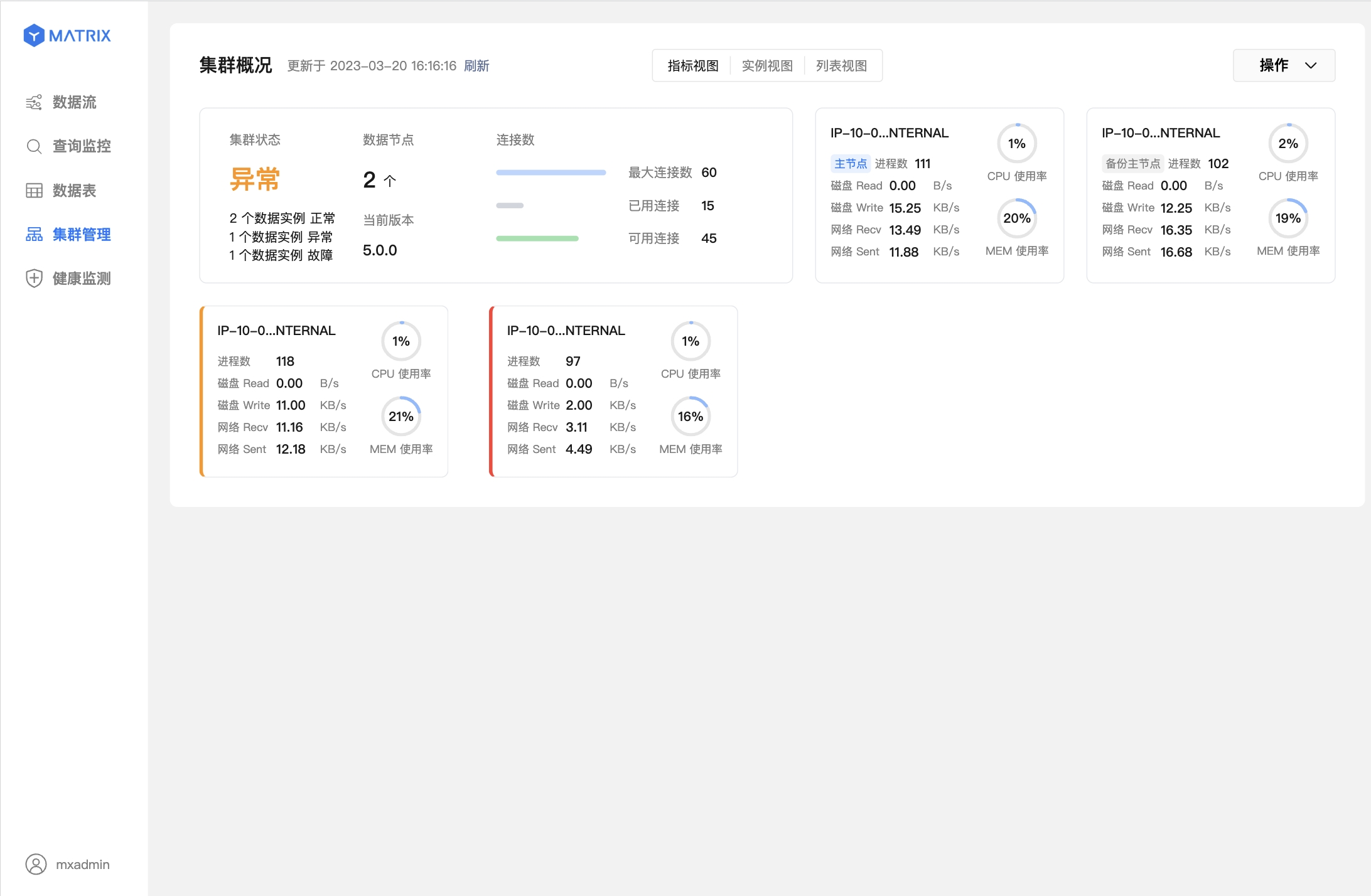
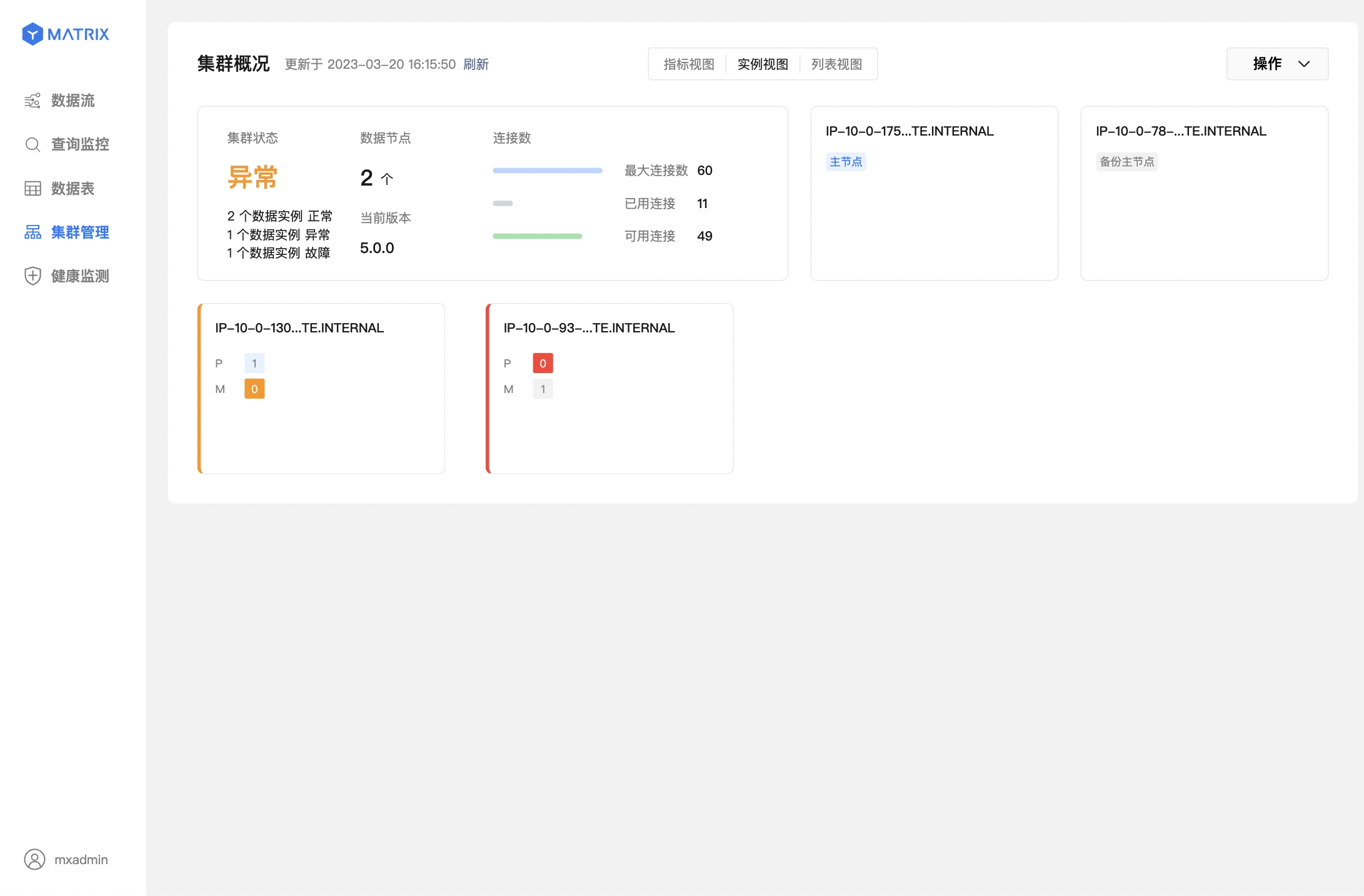
After the system automatically completes the Mirror/Standby promotion, execute mxrecover to generate the corresponding Mirror/Standby for the new Primary/Master, and synchronize the node data in full or incremental to restore the downtime node. Execute mxrecover directly to activate the downtime Mirror/Standby and restore data incrementally. As mentioned above, if full recovery is required, you need to use the mxrecover -F command to enforce it.
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxrecoverAlthough mxrecover regenerated Mirror for the new Primary node, it also brought about a new problem. The distribution relationship of the Primary node has changed, and both Primary nodes are distributed on sdw2. This will cause uneven host resource allocation, and sdw2 will also carry more loads.
The redistribution command is as follows:
[mxadmin@mdw ~]$ mxrecover -rAfter executing mxrecover -r, you can enter the cluster management page of the graphical interface to check.
Automatic failure transfer of Master occurs based on two situations:
The following will explain the impact of automatic Master failure transfer on different components and recommended operations in these two situations.
This situation shows that the failure automatically transfers after the Master crashes, and switches to Standby to manage the cluster.
At this time, the user should access the graphical interface on the Standby node according to the prompts. The default address is http://<standbyIP>:8240.
You can log in normally with the database password of mxadmin or the super password /etc/matrixdb5/auth.conf on the Standby node:

All functions can be used normally after logging in.
This situation indicates that the cluster is no longer available. At this time, you can still check the cluster status through the graphical interface of Master login, but the function of querying the database will be restricted.
Notice!
If your cluster is not configured with Standby when it is installed but has been appended with Standby through the mxinitstandby tool, it is no different from the case where Standby was configured at the beginning.
Notice! It is recommended that Standby be configured in a serious production environment.
This situation shows that the failure automatically transfers after the Master crashes, and switches to Standby to manage the cluster.
There are two types of influences here:
In this case, MatrixGate should be on the Master host, and the Master host is down, which has caused the cluster to be unavailable.
In this scenario, the MatrixGate process can be considered to have died with the host or isolated from other node networks on offline hosts.
At this time, MatrixGate will automatically switch to insert data into Standby, and the monitoring data will continue to be stored normally without manual intervention.
If you need to view the Grafana monitoring page, you need to manually modify the data source and point to the Standby address.

In this case, since the MatrixGate service that monitors deployed has died, no new monitoring data will be generated.