| Operating System | Supported CPU Architecture |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu 20.04 | amd64 |
The server installation process includes 5 steps: viewing the basic server information, installation preparation, database DEB package installation, database deployment and post-installation settings.
Before performing the installation operation, check the basic server information first. It is rarely a good habit to understand that a server helps you better plan and deploy a cluster.
| Step | Commands | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | free -h | View operating system memory information |
| 2 | df -h | View disk space |
| 3 | lscpu | View CPU quantity |
| 4 | lsb_release -a | View operating system version |
| 5 | uname -a | Out all kernel information in the following order (where the detection results of -p and -i are omitted if they are agnostic): kernel name; host name on network node; kernel issue number; kernel version; host hardware architecture name; processor type (not portable); hardware platform (not portable); operating system name |
| 6 | tail -11 /proc/cpuinfo | View CPU information |
Notes!
2 Installation preparation and 3 Database DEB package installation commands must be performed on all nodes.
By default, you have completed the configuration of the software list in the /etc/apt/sources.list configuration file. Next, you need to update the software list under the root user or with root permissions.
# sudo apt updateAPT (Advanced Package Tool) is an advanced package tool. Its main functions are related to obtaining and installing software packages. You can download software packages, install software packages, analyze software package dependencies, update software lists, etc.
Set the regional language settings under root user or using root permissions.
# sudo apt install -y locales && sudo locale-gen "en_US.UTF-8" && sudo update-locale LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"Make sure that there are persistent host names on all nodes. If they do not exist, please use the following command to set the host name. For example, you can set it in the master node like this:
# hostnamectl set-hostname mdwThe two child nodes also set corresponding host names:
# hostnamectl set-hostname sdw1# hostnamectl set-hostname sdw2Ensure that all nodes in the cluster can access each other through hostname and IP. First install the vim tool.
# sudo apt install vimAdd a record in /etc/hosts and map the host name to a local network card address. For example, the /etc/hosts of the three nodes contain something like this:
# sudo vim /etc/hosts
192.168.100.10 mdw
192.168.100.11 sdw1
192.168.100.12 sdw2After entering, press esc to exit, and then enter :wq to save.
Notes!
The DEB package download link can be obtained from the official email.
Copy the upcoming DEB packages installed to all nodes from locally.
~ scp <local path> <username>@<Server IP address>: <server path>Install the YMatrix DEB package under the root user or with root permissions.
# sudo apt install -y /path/to/matrixdb5_5.0.0+enterprise-1_amd64.debNotes!
During the actual installation process, please replace the file name with the latest downloaded DEB package name,/path/to/with the correct path, and./if it is the current path.
After the installation is successful, the supervisor and MXUI processes will be automatically started. These background processes are used to provide graphic operation interfaces and process management services.
If you have the requirement to configure ports, modify the /etc/matrixdb5/defaults.conf file for configuration after installing the DEB package. This operation is only done on the Master.
# vim /etc/matrixdb5/defaults.confOn all nodes, use the root user or sudo permissions to execute the following command to install the Python package that YMatrix depends on. Note that source greenplum_path.sh must be executed so that the correct version of the dependency package can be installed.
# sudo apt install -y \
gcc \
python3-dev \
python3-pip \
python3-psutil \
python3-pygresql \
python3-testresources
# sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3 50The graphic deployment provided by YMatrix is still used here. Remote graphic deployment requires server ports 8240 and 4617 to be accessible. After the installation is complete, these ports of all nodes will be opened by default. The graphic UI service is provided by the MXUI process.
Notes!
You cannot deploy YMatrix using a graphic interface, please refer to Command Line Deployment.
Use your browser to access the following graphic installation wizard URL, which is the IP of the mdw server:
http://<IP>:8240/On the first page of the installation wizard, you need to fill in the super user password and use the sudo more /etc/matrixdb5/auth.conf command to view it.

Select "Multi-node deployment" on the second page and click Next.
Next, start the four steps of multi-machine deployment.
The first step is to add a node and click the "Add Node" button.
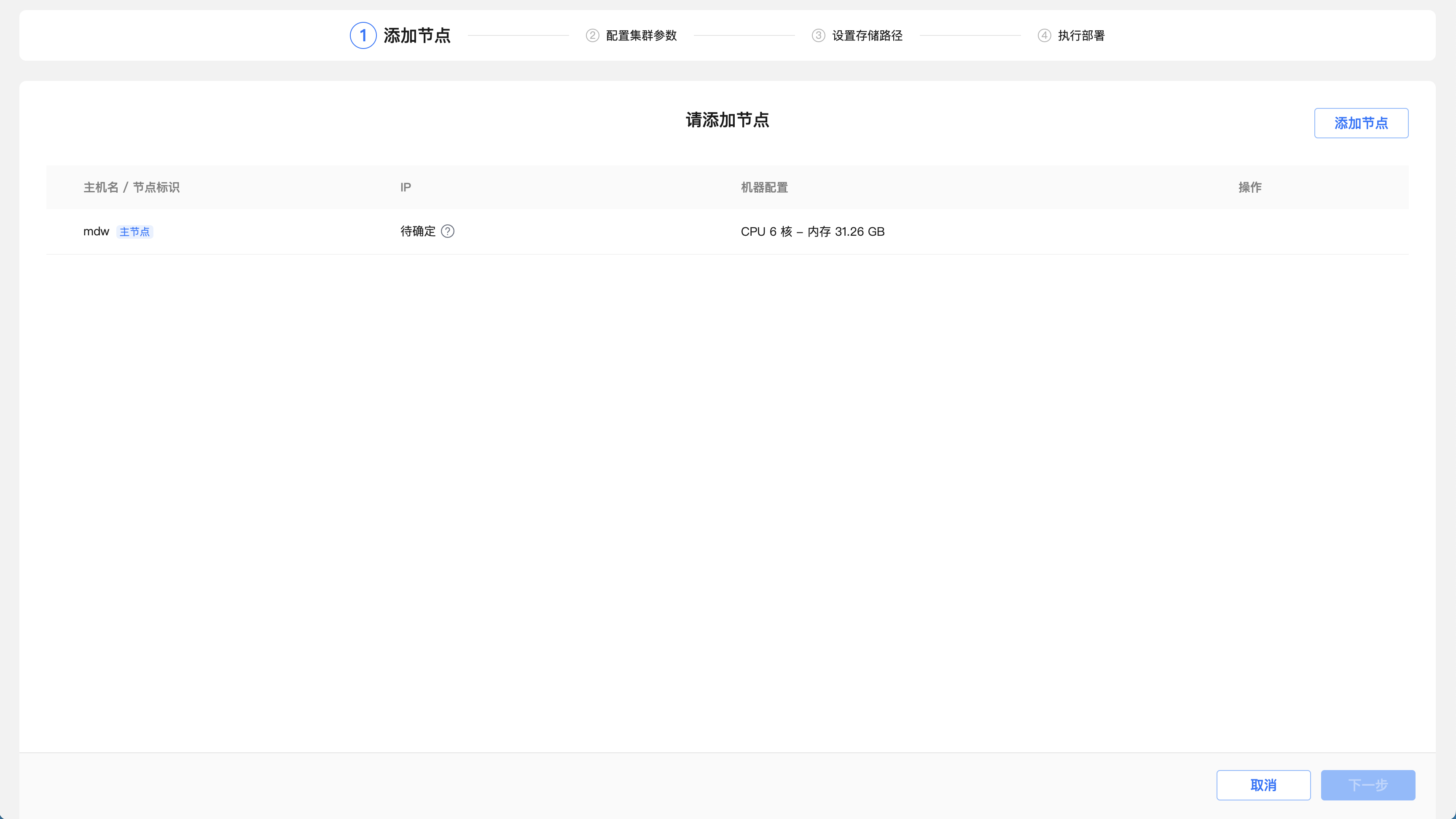
Enter the IP addresses or hostname or FQDN of sdw1 and sdw2 in the text box, click "OK", and click "Next".
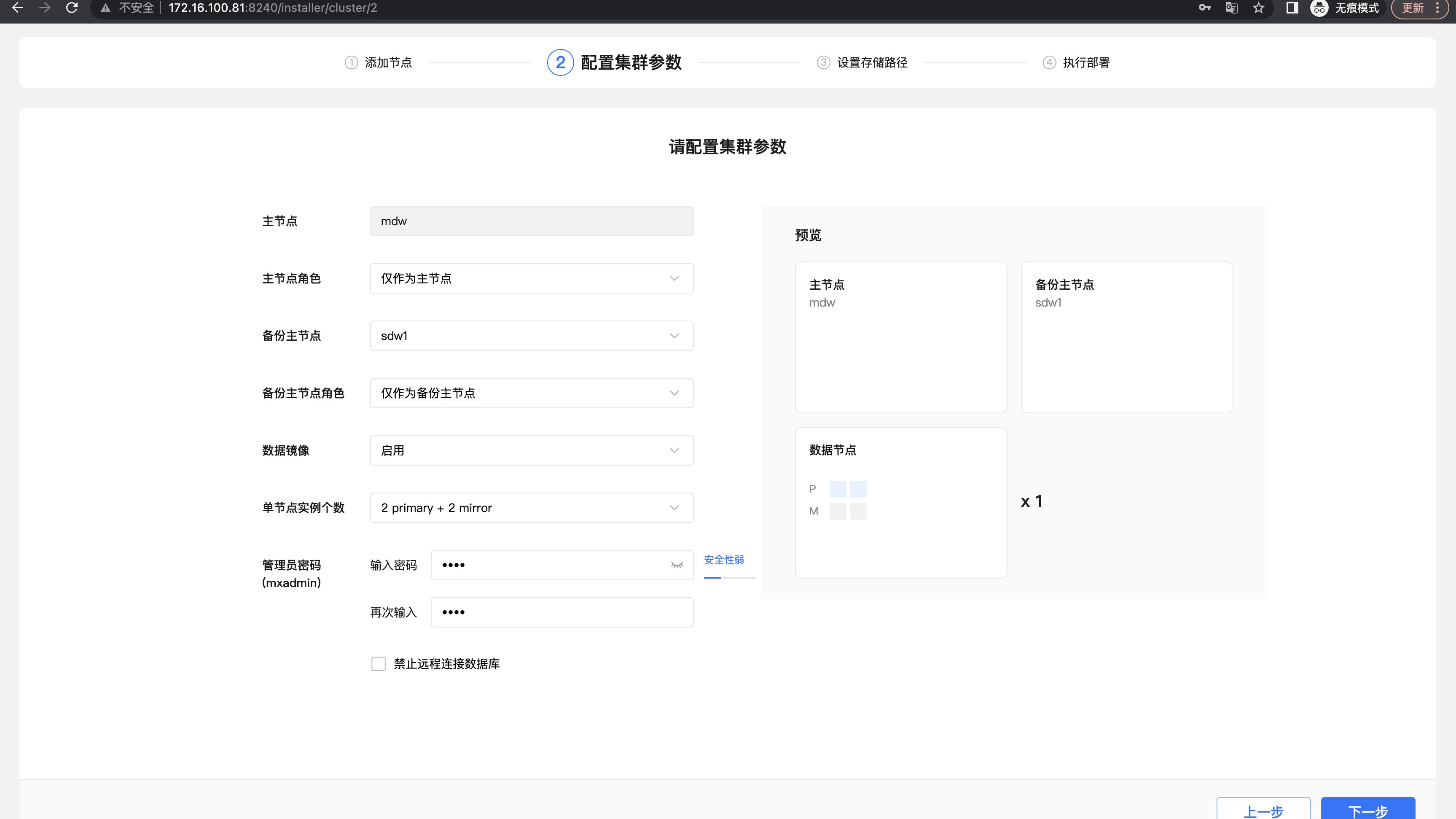
The second step is to configure cluster parameters. "Data mirroring" determines whether the cluster data node contains backup images. It is recommended to enable it in the production environment so that the cluster is highly available. The system automatically recommends the largest space of disks and the number of segments matching the system resources, which can be adjusted according to the specific usage scenario. The configured cluster structure can be viewed through the schematic diagram. After confirming, click "Next".
The third step is to set the storage path.

Step 4: Execute deployment. This step will list the configuration parameters for the previous operation. After confirming that it is correct, click "Execute deployment".
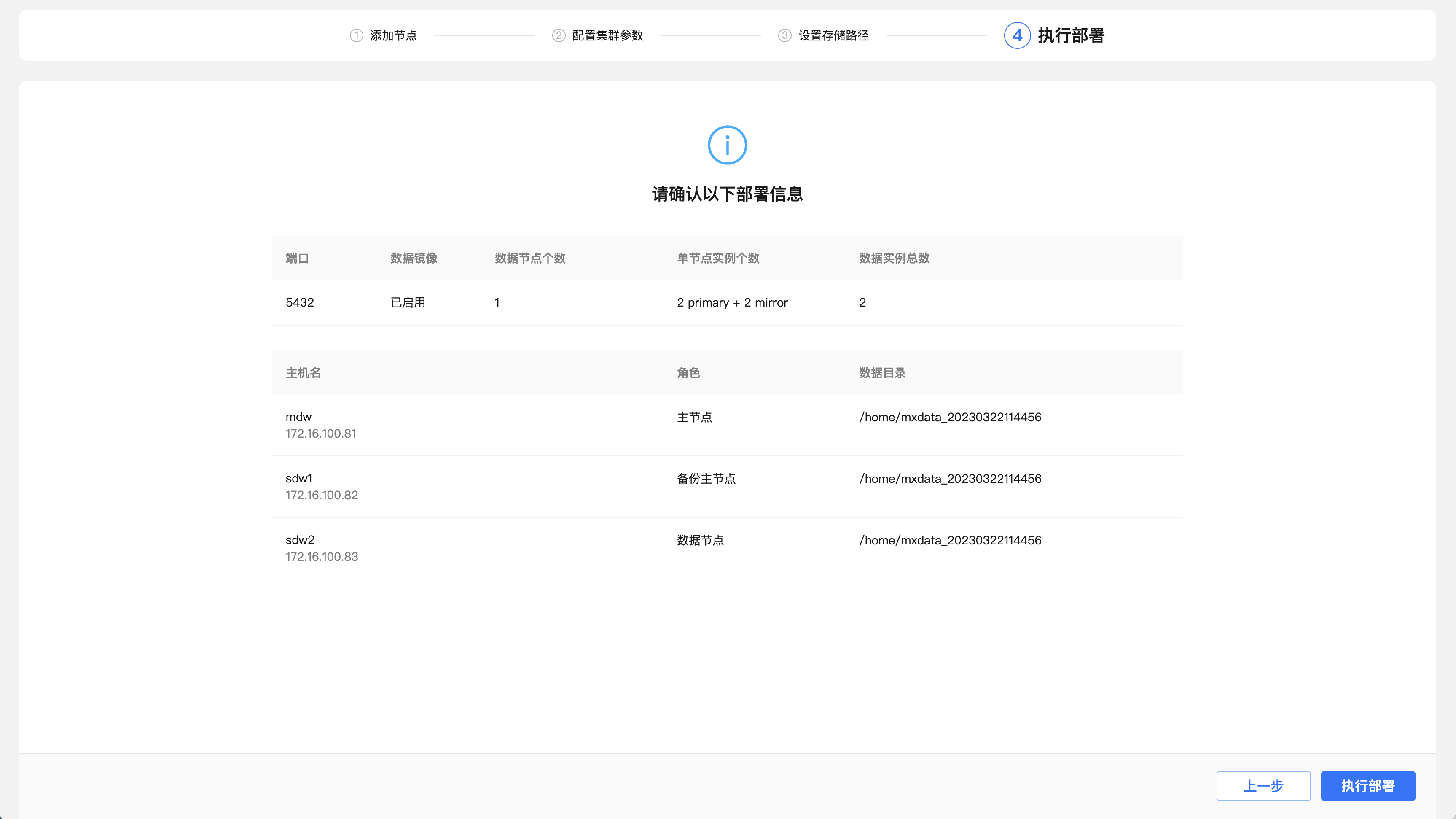
The system will then automatically deploy the cluster and list detailed steps and execution progress. After all the steps are successfully executed, it means that the deployment is completed.
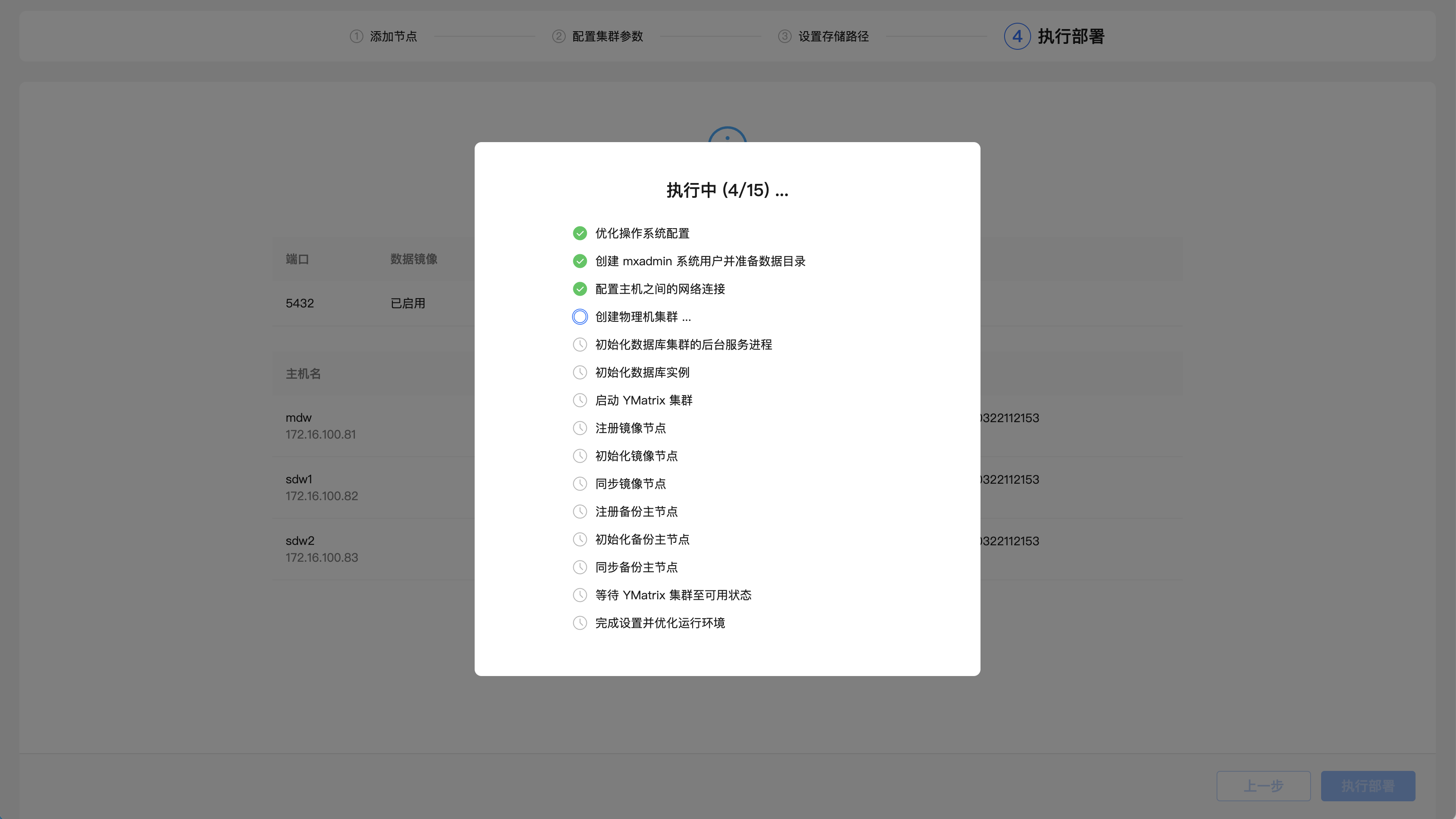
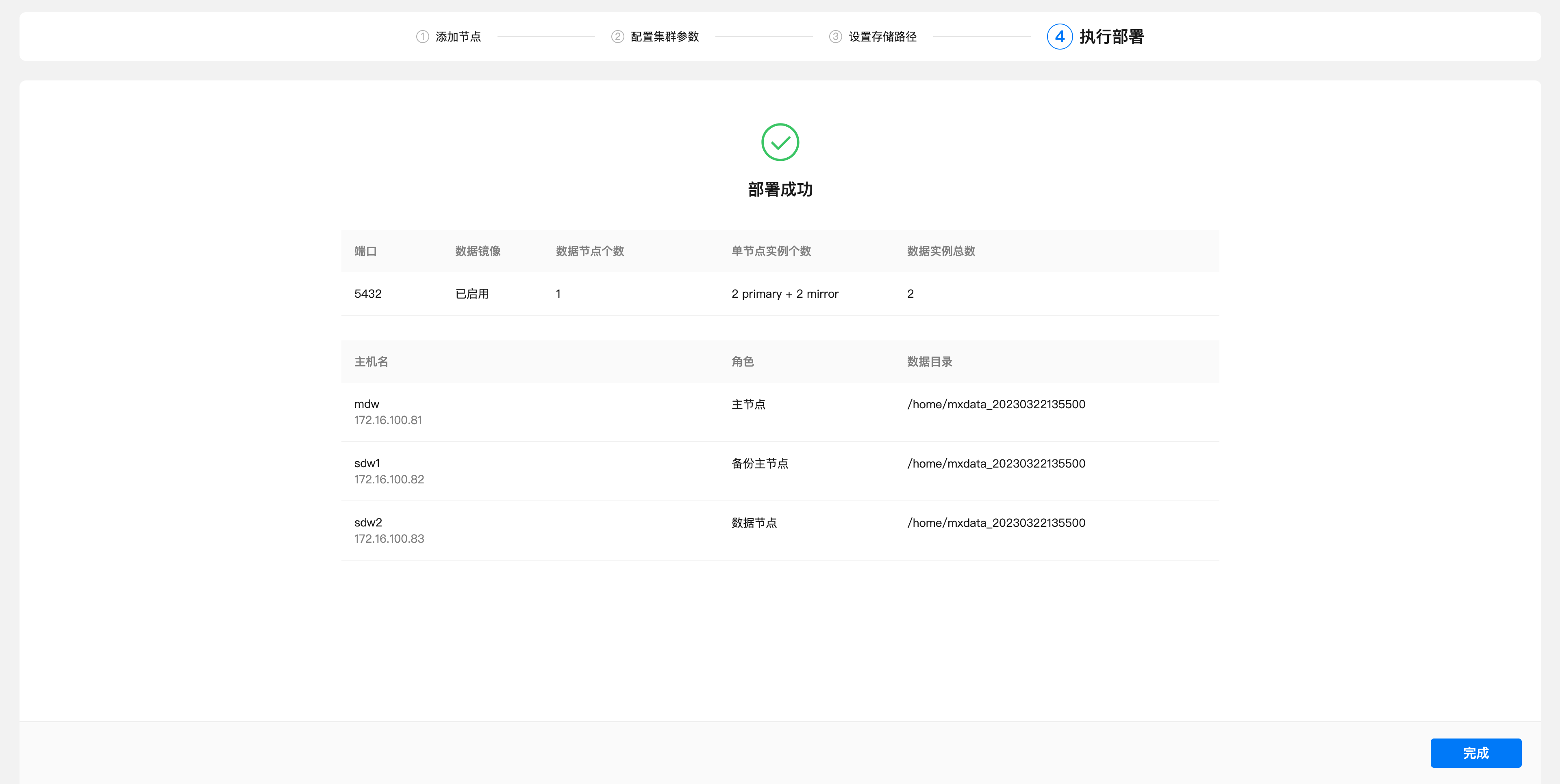
Complete the deployment.
On all nodes, modify the sysstat file, change ENABLED="false" to ENABLED="true", then click esc, enter :wq to save and exit.
# sudo vi /etc/default/sysstatRestart the service.
# sudo service sysstat restartYMatrix default installation supports remote connections. If "Allow remote connection to database" is not checked during the installation process, please manually modify the $MASTER_DATA_DIRECTORY/pg_hba.conf file to add a line like this, indicating that users from any IP who access all databases are allowed to connect through password authentication. The IP range or database name can be limited according to actual needs to be used to reduce security risks:
# host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5After completing these modifications, you need to execute the following command to reload the pg_hba.conf configuration file:
# mxstop -uThe start, stop, restart and status viewing of YMatrix can be completed by the following commands:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| mxstop -a | Stop the cluster. (In this mode, if there is a session link, closing the database will be stuck) |
| mxstop -af | Quickly shut down the cluster |
| mxstop -arf | Restart the cluster. Wait for the currently executing SQL statement to end (in this mode, if there is a session link, closing the database will be stuck) |
| mxstate -s | View cluster status |