MatrixGate, abbreviated as mxgate, is a high-performance data loading tool that comes with YMatrix. It is located in bin/mxgate in the YMatrix installation directory and currently supports loading data through the SDK or HTTP and STDIN API interfaces. The data format supports TEXT and CSV.
Using mxgate for data loading performance is much higher than that of the native INSERT statement. Because mxgate can communicate directly with the Segment, there is no Master single point bottleneck.
mxgate currently mainly supports the following functions:
The logic of MatrixGate loading data is shown in the following figure:
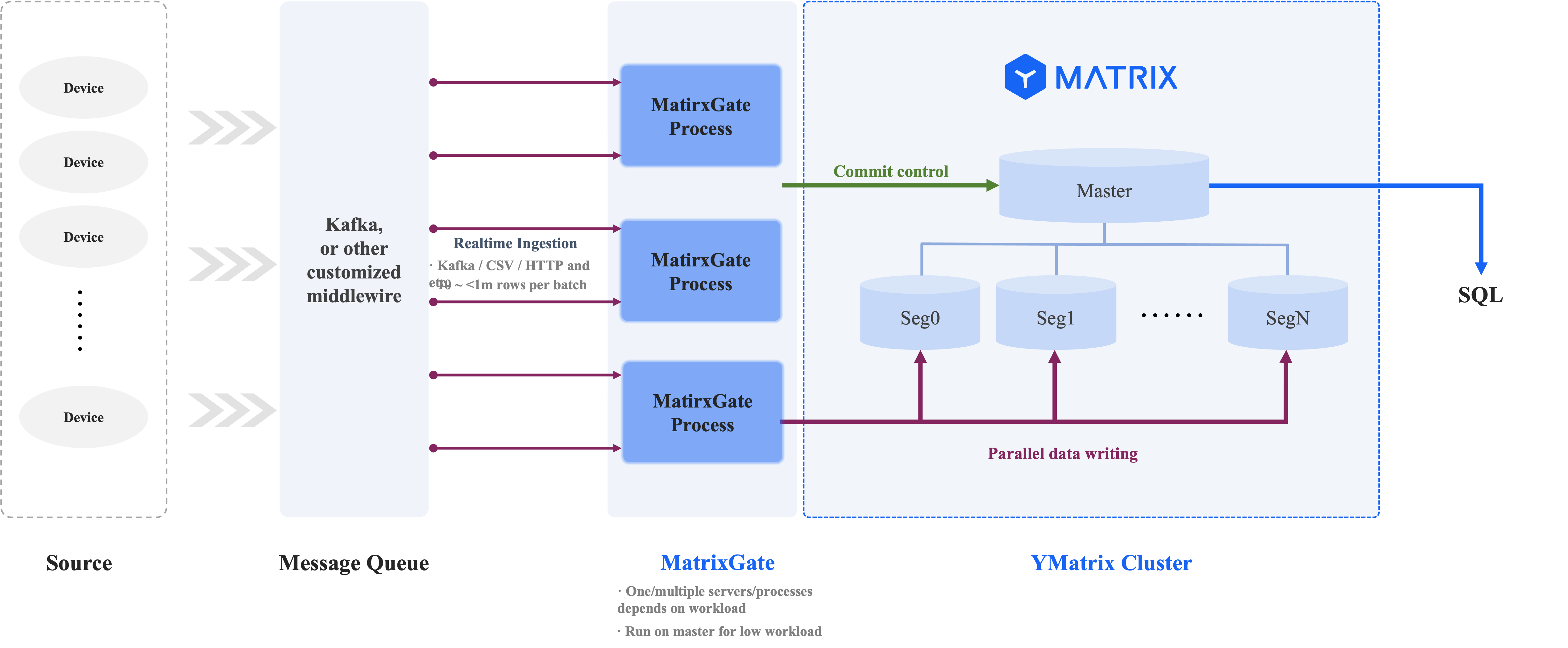
Comparison of INSERT with MatrixGate:
| Writing method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicable scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct INSERT | Simple interface | Low throughput performance | Low throughput performance, hundreds of thousands of data points/second |
| MatrixGate | High throughput performance Standard real-time |
Additional deployment is required, with operation and maintenance costs | High throughput performance, tens of millions of data points/second |
MatrixGate provides the following operating mode:
The following shows how to use these two modes to pour data into the data table. The schema of the data table dest is as follows:
=# CREATE TABLE dest(
time timestamp,
c1 int,
c2 text
)DISTRIBUTED BY(c1);The service mode has backend processes that are permanently resident, providing an HTTP interface to users and submitting time sequence data, which is a common way to use in production environments.
To use the service mode, you must first generate a configuration file and determine the database connection information, target table and other parameters.
$ mxgate config --db-database test \
--db-master-host localhost \
--db-master-port 5432 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--target public.dest \
--time-format raw \
--delimiter ',' \
> mxgate.confAs determined in the above command:
| Parameter name | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| --db-database | Database | test |
| --db-master-host | Database host | localhost |
| --db-master-port | Database Port | 5432 |
| --db-user | Database username | mxadmin |
| --target | Target Table | public.dest |
| --time-format | Time format | raw (plain text) |
| --delimiter | Delimiter | , |
Then, start MatrixGate and specify the configuration file you just generated in the startup parameters:
$ mxgate start --config mxgate.conf
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: 4.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2022-03-01; any
**********************************************************
Launching MatrixGate daemon...
MatrixGate daemon started successfullyAfter the startup is successful, use the curl tool to send an HTTP request to submit the data.
Notes!
In production environments, data is submitted using HTTP libraries supported by programming languages
The test data file rows_header.csv has been prepared, with the following content:
$ cat rows_header.csv
public.dest
2021-01-01 00:00:00,1,a1
2021-01-01 00:00:00,2,a2
2021-01-01 00:00:00,3,a3When submitting data, the first row must specify the target table name, because the MatrixGate service may have multiple target tables.
Submit data:
curl http://localhost:8086/ -X POST -H 'Content-Type: text/plain' --data-binary "@rows_header.csv"MatrixGate binds to port 8086 by default, which can be modified through configuration files.
Query the injected data:
=# SELECT * FROM dest;
time | c1 | c2
--------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2021-01-01 00:00:00 | 11 | a11
2021-01-01 00:00:00 | 12 | a12
2021-01-01 00:00:00 | 13 | a13
(3 rows)For more detailed API parameters, please refer to Document.
MatrixGate also provides other operation and maintenance commands for operation and maintenance management.
View Status
$ mxgate status
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: 4.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2022-03-01; any
**********************************************************
PID 15146 alive
Launched At 2021-09-01 14:59:03
Up For 26 seconds
Binary /usr/local/matrixdb-4.2.0.community/bin/mxgated
Log /home/mxadmin/gpAdminLogs/matrixgate.2021-09-01_145904.log
Config /home/mxadmin/mxgate.confYou can see the service program running status, configuration files and log paths, which are used to track down problems.
Stop service
$ mxgate stop
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: 4.2.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2022-03-01; any
**********************************************************
PID 15146 stoppedmxgate stop can stop the service.
Observation Service
You can use the mxgate watch subcommand to observe the service in real time
$ mxgate watch
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: 4.5.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2022-05-14; any
**********************************************************
watch cmd will run forever until killed, you can use watch -T n to change the duration to n seconds;and you can use mxgate watch --info to get info of columns;
Time WCount ICount WSpeed/s ISpeed/s WBandWidth MB/S BlocakItems
2022-04-28 15:20:58 14478858 14527011 2598081 2627887 2395 0
2022-04-28 15:21:01 22231035 22633254 2584059 2702081 2222 0
2022-04-28 15:21:04 30494310 30500874 2754425 2622540 3551 0
2022-04-28 15:21:07 38004210 38032956 2503300 2510694 2862 0
2022-04-28 15:21:10 46188696 46298223 2728162 2755089 2227 0
...Or use mxgate watch --history to observe historical data
$ mxgate watch --history
**********************************************************
__ __ _ _ ____ _
| \/ | __ _| |_ _ __(_)_ __/ ___| __ _| |_ ___
| |\/| |/ _` | __| '__| \ \/ / | _ / _` | __/ _ \
| | | | (_| | |_| | | |> <| |_| | (_| | || __/
|_| |_|\__,_|\__|_| |_/_/\_\\____|\__,_|\__\___|
Version: 4.5.0
Your Copy is Licensed to: yMatrix.cn; 2022-05-14; any
**********************************************************
TIME RANGE | SPEED/S | BANDWIDTH MB/S | BLOCK ITEMS
2022-04-28 16:00:00-2022-04-28 17:00:00 | 2208010 | 1254.48 | 0
2022-04-28 17:00:00-2022-04-28 18:00:00 | 1157920 | 1327.00 | 0
2022-04-28 18:00:00-2022-04-28 19:00:00 | 2228666 | 2162.32 | 0
2022-04-28 19:00:00-2022-04-28 20:00:00 | 1371092 | 2881.30 | 0
2022-04-28 20:00:00-2022-04-28 21:00:00 | 1575320 | 2608.20 | 0Command line mode is used to pour data files into one go, and the process exits after the end.
It's still the data file just now. Remove the first row of the target table, only keep the data rows, and execute the following command:
$ cat rows.csv | mxgate --source stdin --db-database test --db-master-host localhost --db-master-port 5432 --db-user mxadmin --time-format raw --target public.dest --parallel 2 --delimiter ',' For more methods of file access, please refer to File Access
The migration mode of mxgate is mainly used for high-speed data migration of single-table, and supports migration of data tables of other Greenplum 5, Greenplum 6, and YMatrix clusters to the current YMatrix cluster. Currently, there are three main usages:
Notes!
For the specific usage of the migration mode, please refer to Single Table Migration Tool - mxgate, and for the full library migration method, please refer to Full Library Migration Tool - mxshift.
Notes!
For a complete introduction to the MatrixGate tool, please see MatrixGate.