MatrixGate 4.3 has added a migration mode, which can quickly migrate table data from other Greenplum5, Greenplum6 and other MatrixDB clusters to the current MatrixDB cluster.
High-speed migration allows data to bypass the master node, read directly from the source cluster segment, forwarded through mxgate, and sent to the target cluster segment. There is no master single-node bottleneck, and the number of segments in the source cluster and the target cluster may be inconsistent.
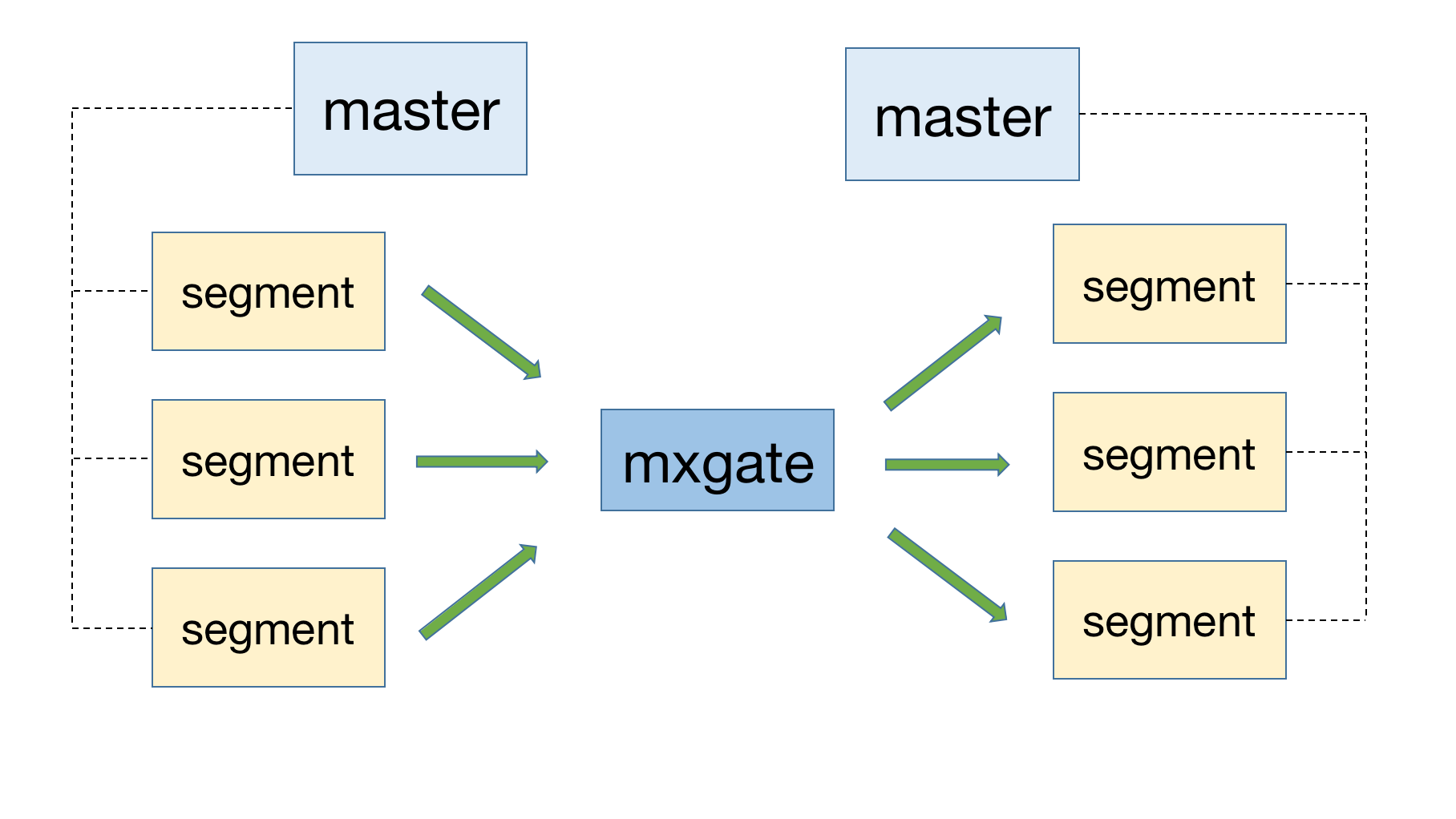
Full table migration is used to migrate full table data, and the usage is as follows:
mxgate --source transfer \
--src-host 172.31.41.7 \
--src-port 5432 \
--src-db postgres \
--src-user ec2-user \
--src-password abc \
--src-schema public \
--src-table trans_ao \
--compress "gzip" \
--port-base 9129 \
--local-ip 172.31.33.128 \
--db-database ttt \
--target public.trans_ao \
--format text \
--time-format raw \
--use-auto-increment=falsein:
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
| --source | Function portal, 'transfer' must be specified |
| --src-host | IP address of source library master |
| --src-port | Port number of source library master |
| --src-user | Username for connecting to the source library (superuser is recommended) |
| --src-password | Connection Password |
| --src-schema | schema name of the source table |
| --src-table | Table name of the source table |
| --compress | Transfer method from the source database segment host to this data: The blank string "" means non-compression, plain text transmission gzip: Using gzip compression, the linux command gzip that requires the source database must be installed on the segment host lz4: Using lz4 compression, the linux command lz4 that requires the source database must be installed on the segment host recommended lz4 > gzip > non-compression |
| --port-base | A batch of ports will be occupied during transmission, and the port range is 9129~ |
| --local-ip | The IP address that must be connected to the local machine using the source library |
| --db-database | The database name where the migration target table is located |
| --target | The migration target table name can be in the form of \<schema>.\<table>. If the schema name is not written, the default is public |
| --format | text or csv, CSV is required only if there are complex strings (including newlines, quotes, and separators) in the migrated data. When both text/csv are available in other cases, text mode is preferred |
| --time-format | must be raw in transfer mode |
| --use-auto-increment | When the target table includes a self-increment field of serial type, the fields of this type will be skipped by default in mxgate. This option is added to close the logic of skipping mxgate |
Another usage of migration mode is to quickly export data to a file:
mxgate --source transfer \
--src-host 172.31.41.7 \
--src-port 5432 \
--src-db postgres \
--src-user ec2-user \
--src-schema public \
--src-table trans_ao_1 \
--compress "lz4" \
--port-base 9129 \
--local-ip 172.31.33.128 \
--save-to-dir /tmp/receive/ \
--db-database ttt \
--transform nil \
--writer nil \
--target trans_aoUse the --save-to-dir parameter to specify the file storage path.
Note that even if exported to a file, the --db-database and --target parameters need to be given to specify the target library and table, and the target library and table must exist
Filtering migration can be specified by SQL to filter data that needs to be synchronized by using the --src-sql parameter. It can be used in table-to-table migration and table-to-file migration:
mxgate --source transfer \
--src-host 172.31.41.7 \
--src-port 5432 \
--src-db postgres \
--src-user ec2-user \
--src-sql "select * from demo where c1 = 'xxxx'" \
--compress "lz4" \
--port-base 9129 \
--local-ip 172.31.33.128 \
--save-to-dir /tmp/receive/ \
--db-database ttt \
--transform nil \
--writer nil \
--target trans_aoFor detailed parameters related to migration tools, please refer to mxbackup and mxrestore