MatrixGate is abbreviated as mxgate. It is a high-performance streaming data loading server located in bin/mxgate in the MatrixDB installation directory. MatrixGate currently provides HTTP and STDIN interfaces to load data, and the data format supports TEXT and CSV.
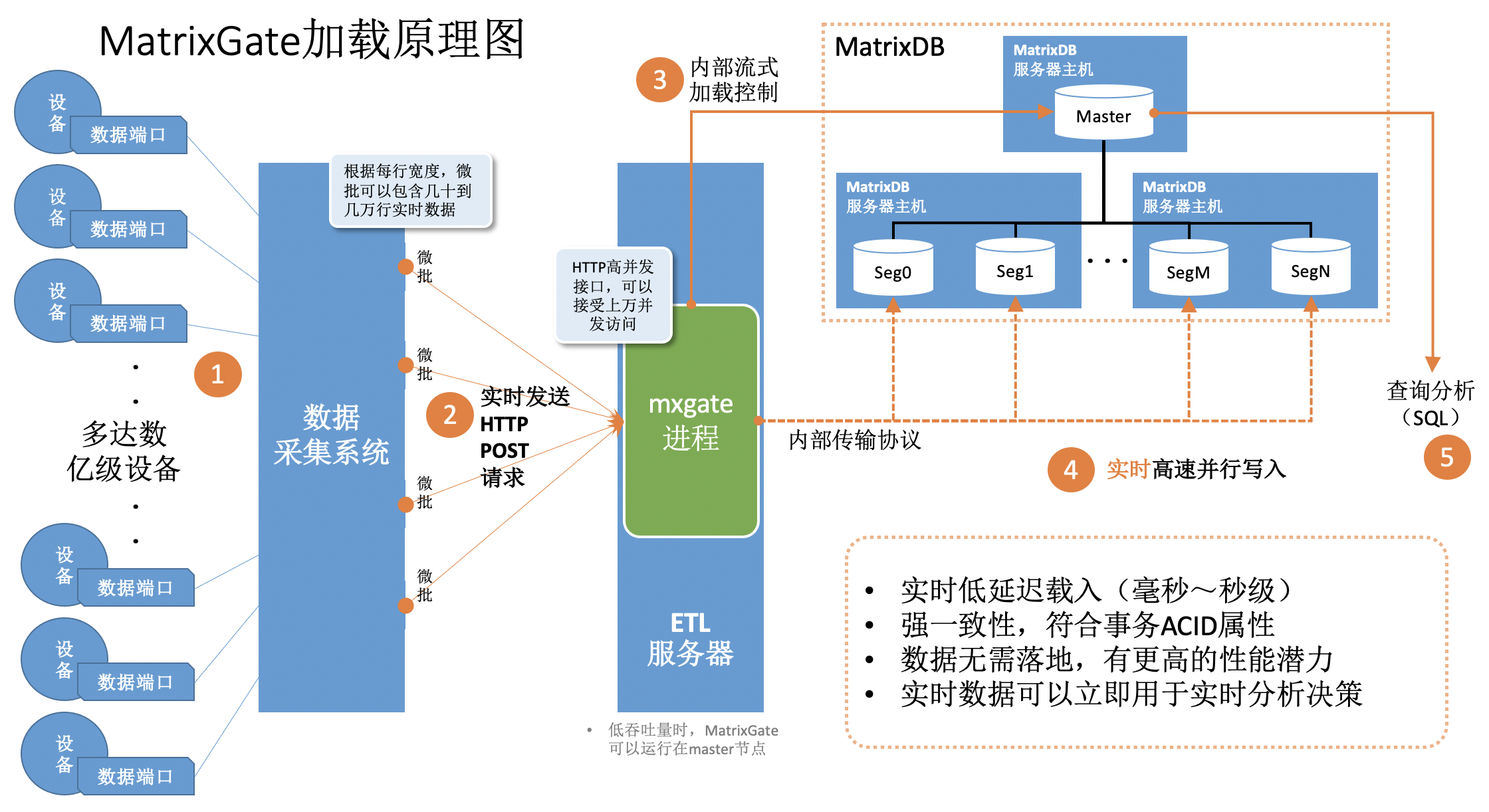
The logic of MatrixGate loading data is shown in the figure below, 1) The data acquisition system collects device data or receives data sent by the device 2) The acquisition system continuously sends data to MatrixGate's service process mxgate in a concurrent microbatch mode 3) The mxgate process and the MatrixDB master process communicate efficiently, communicate transactions and control information 4) The data is directly sent to the segment node and written in parallel at high speed.
Specify the target database and target table to generate mxgate configuration file
mxgate config --db-database demo --target public.testtable --target public.testtable2 --allow-dynamic > mxgate.confThe above parameters will generate a configuration file mxgate.conf, allowing users to personalize the loading of testtable and testtable2, and can also use the global default settings to load data into other tables.
Modify mxgate configuration file as needed, such as configuration data separator, etc., and select the default configuration to ignore this step. You can see the settings corresponding to testtable and testtable2 in this configuration file as follows:
[[job.target]]
# delimiter = "|"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true
[[job.target]]
# delimiter = "|"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable2"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable2"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = trueIf the delimiter of testtable is @ and the delimiter of testtable2 is %, the above configuration can be modified to:
[[job.target]]
delimiter = "@"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true
[[job.target]]
delimiter = "%"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable2"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable2"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = truemxgate listens to port 8086 to receive data by default. You can see in mxgate.conf that the http-port sub-item under source.http is set to 8086. If necessary, you can change it to another port:
[source]
## Source plugin is the data entrance to MatrixGate
## Types restricted to: http
source = "http"
[source.http]
## Port of http push
# http-port = 8086
## Maximum request body size (after gzip)
## The server rejects requests with bodies exceeding this limit.
# max-body-bytes = 4194304
## The maximum number of concurrent HTTP connections to the server
## The server response with 503 after exceed this limit.
# max-concurrency = 40000Start mxgate, load configuration files, connect to demo database, and prepare to receive data loading requests
mxgate start --config mxgate.confCheck the backend service status
mxgate statusTerminate the background service
mxgate stopWhen encountering timeout or other problems, you need to force stop, you can do this:
mxgate stop --force| Parameter name | Parameter value | Parameter meaning |
| --- | --- |
| --db-database | Default postgres | MatrixGate connection MatrixDB database name |
| --db-master-host | Default native host name | MatrixGate connection MatrixDB host name |
| --db-master-port | Default 5432 | MatrixGate connection MatrixDB host port number |
| --db-user | Default current system user name | MatrixGate connection to MatrixDB user name
Note: This user must have permission to create external tables. If you are using a non-super permission user, please use the following command to increase permissions: alter user {username} CREATEEXTTABLE; |
| --db-password | Default is empty | MatrixGate connection to MatrixDB user password |
| --db-max-conn | Default 10 | MatrixGate connection MatrixDB maximum number of connections |
| --interval | Default 100ms | MatrixGate execution batch data loading time period |
| --source | Default http | MatrixGate data source, supports http and stdin |
| --target | schemaName.tableName | Specify the table name of the target. schemaName can be omitted, and the default is public. Multiple target tables are allowed to be specified, using "--target Table 1 --target Table 2...". When this parameter is not provided, the --allow-dynamic parameter can be specified to allow dynamic adaptation of table names. |
| --allow-dynamic | Default false | When --allow-dynamic=true is specified, the inserted target table is allowed to dynamically adapt to the data content (first row) of the POST. This option should only be used in scenarios where the target table name is not yet determined when MatrixGate is started. If you insert a known target table in a fixed manner, it is recommended to use --target to explicitly specify the table name |
| --format | Default text | Specify the data format text or csv for the source data. Text has the fastest speed, but does not support newlines in character types. The csv format is more applicable and must be double quoted for character-type columns. |
| --delimiter | Default is | | Specifies the characters used to separate columns in each row (row) of the file |
| --null-as | Default empty string | Specifies a string representing an empty value. The default value is an empty string without quotes. When the column in the data table is constrained to non-empty NOT NULL, and the column on the data content gives an empty value, it will cause a loading error. Tip: If you need to use \N as a null value, you need to escape the backslash, such as: --null-as \N |
| --time-format | Default unix-second | Specify the time stamp unit: unix-second|unix-ms|unix-nano|raw. \n MatrixGate defaults to the first column of each row of data as a Unix representation of a timestamp, and automatically converts it into a database time format. If the timestamp is not in the first column, or the user has converted it to the database format itself, you should use raw so that MatrixGate will not perform time-type conversion. |
| --use-auto-increment | Default true | When the target table contains a self-increment field, whether to skip the self-increment field assignment in the load data and use the system default self-increment |
| --exclude-columns | Default is empty | The number of columns and column order provided by data loading by default need to be consistent with the table definition. When only partial columns are provided by data loading, --exclude-columns is used to mark the excluded column names, and other columns still need to ensure that the order is consistent with the table definition. Tip: If --use-auto-increment is enabled, you do not need to list these self-increment fields here. This parameter only needs to mark other column names that need to be excluded |
| --help | | Display usage and parameter list |
MatrixGate provides an HTTP API to the outside world, supporting various programming languages to import data into MatrixDB databases through the HTTP interface.
MatrixGate HTTP protocol format
| Protocol Type | Protocol Format | Usage and Examples |
| --- | --- |
| URL | http://mxgate-host:port | Specify mxgate connection address |
| PATH | / | Currently supported /, ignore / after any PATH |
| HTTP Method | POST | Currently supports POST method to load data |
| HTTP Header | Content-Encoding: gzip | Currently supports gzip for HTTP Body content compression |
| | Content-Type: text/plain | Currently supported text/plain |
| HTTP Body | SchemaName.TableName
Timestamp|ID]|C1|C2|..|Cn | The first behavior of the Body format is the target table loaded by data. SchemeName can be omitted. The default is Public. TableName is a required item. The second row starts with a time-series data row. Each row corresponds to a row of the target table. The | separator is used between columns and the \n separator is used between rows. The first field of each line is a timestamp, and the format is UNIX timestamp is accurate to seconds, see the description of --time-format. The second field of each row is TagID, integer. The third field to the last field of each row is the column corresponding to the target table. It is recommended that the DDL definition of the target table also follows the column order of (Timestamp, TagID, C1, C2,…, Cn) |
MatrixGate HTTP response code
| Response Code | Response Code Meaning | Remarks | | --- | --- | | 204 | StatusNoContent | Data loaded successfully to MatrixGate | | 400 | StatusBadRequest | Data request errors, such as POST BODY format error, target table does not exist, data compression format does not match the HTTP request header, etc. | | 405 | StatusMethodNotAllowed | HTTP Non-POST Request | | 500 | StatusIntervalServerError | Database error, data loading failed, response Body contains detailed error information | | 503 | StatusServiceUnavailable | MatrixGate rejects requests, such as exceeding the maximum number of connections, or MatrixGate is closing, etc |
CREATE TABLE testtable (time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, tagid INT, c1 INT, c2 INT, c3 INT)
DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid);public.testtable
1603777821|1|101|201|301
1603777822|2|102|202|302
1603777823|3|103|203|303mxgate --config mxgate.confcurl http://localhost:8086/ -X POST -H 'Content-Type: text/plain' --data-binary "@data.txt"
demo=# SELECT * FROM testtable ;
time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3
-----------------------+-------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2020-10-27 05:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303
2020-10-27 05:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302
2020-10-27 05:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301(3 rows)
## 6 Programming Language Connection MatrixGate
<a name="java"><br/></a>
### 6.1 MatrixGate HTTP API Java Exampleimport java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.URL;
public class MxgateExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { MxgateExample http = new MxgateExample(); http.sendingPostRequest(); }
// HTTP Post request
private void sendingPostRequest() throws Exception {
// mxgate listens on port 8086 of localhost
String url = "http://localhost:8086/";
URL obj = new URL(url);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
// Setting basic post request
con.setRequestMethod("POST");
con.setRequestProperty("Content-Type","text/plain");
String postJsonData = "public.testtable\n1603777821|1|101|201|301\n1603777822|2|102|202|302\n1603777823|3|103|203|303";
con.setDoOutput(true);
DataOutputStream wr = new DataOutputStream(con.getOutputStream());
// When the data is in Chinese, it can be encoded by postJsonData.getBytes("UTF-8")
wr.write(postJsonData.toString().getBytes("UTF-8"));
wr.flush();
wr.close();
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("Sending 'POST' request to URL : " + url);
System.out.println("Post Data : " + postJsonData);
System.out.println("Response Code : " + responseCode);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String output;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((output = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(output);
}
in.close();
System.out.println(response.toString());
}}
<a name="python"><br/></a>
### 6.2 MatrixGate HTTP API Python Exampleimport http.client
class MxgateExample(object): def init(self):
self.url = "localhost:8086"
self.postData = "public.testtable\n/" \
"1603777821|1|101|201|301\n/" \
"1603777822|2|102|202|302\n/" \
"1603777823|3|103|203|303"
self.headers = {"Content-Type": "text/plain"}
# HTTP Post request
def sending_post_request(self):
conn = http.client.HTTPConnection(self.url)
conn.request("POST", "/", self.postData, self.headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
response_code = response.getcode()
print(f"Sending 'POST' request to URL : {self.url}")
print(f"Post Data : {self.postData}")
print(f"Response Code : {response_code}")
output = response.read()
print(output)if name == 'main': gate_post = MxgateExample() gate_post.sending_post_request()
<a name="C#"><br/></a>
### 6.3 MatrixGate HTTP API C# Example
> It is recommended to use the C# Core development environment for developing codeusing System; using System.IO; using System.Net; using System.Text;
namespace HttpPostTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var url = "http://10.13.2.177:8086/"; var txt = "public.dest\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,1,a1\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,2,a2\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,3,a3";
HttpPost(url,txt);
}public static string HttpPost(string url, string content){ string result = ""; HttpWebRequest req = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url); req.Method = "POST"; req.ContentType = "text/plain";
#region Add Post parameters
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(content);
req.ContentLength = data.Length;
using (Stream reqStream = req.GetRequestStream()){
reqStream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
reqStream.Close();
}
#endregion
HttpWebResponse resp = (HttpWebResponse)req.GetResponse();
Stream stream = resp.GetResponseStream();
//Get the response content
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream, Encoding.UTF8)){
result = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
return result;
}} }
> If you encounter the problem of error when serving connection ***** body size exceeds the given limit, increase the max-body-bytes under mxgate.conf
### 6.4 MatrixGate HTTP API Golang Examplepackage main
import ( "bytes" "net/http" )
func PostDataToServer(URL string) error {
data := public.testtable 1603777821|1|101|201|301 1603777822|2|102|202|302 1603777823|3|103|203|303
resp, err := http.Post(URL, "application/text", bytes.NewBuffer([]byte(data)))
if err != nil {
return err
}
if resp.StatusCode != 200 {
// Deal with the response body.
return nil
}
// Deal with the response body.
return nil}
func main() { err := PostDataToServer("http://127.0.0.1:8086") if err != nil{ panic(err) }
}
## 7 MatrixGate Loading Special Types
### 7.1 MatrixGate loading CSV file example
- Create table csvtable in demo databaseCREATE TABLE csvtable (time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, tagid INT, c1 INT, c2 INT, c3 INT) DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid);
- Edit the data load file data.csv, the content is as follows1603777821|1|101|201|301 1603777822|2|102|202|302 1603777823|3|103|203|303
- Start mxgate, specify the source parameter to stdin, the target table is an existing csvtable, and the loading parallelism is 2mxgate \ --source stdin \ --db-database demo \ --db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \ --db-master-port 5432 \ --db-user mxadmin \ --time-format unix-second \ --delimiter "|" \ --target csvtable \ --parallel 2 < data.csv
- Connect to the database to query whether the data is loaded successfullydemo=# SELECT * FROM csvtable ; time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3 -----------------------+-------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2020-10-27 05:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303 2020-10-27 05:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302 2020-10-27 05:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301
(3 rows)
### 7.2 MatrixGate loading json field example
### 7.2.1 json
- Create tablecreate table json_test(id int, j json);
- Create data files
`~/json.csv`1|"{""a"":10, ""b"":""xyz""}"
- load
Here we use the stdin mode as an example, and the other modes are the same.
The key is `--format csv`mxgated \ --source stdin \ --db-database postgres \ --db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \ --db-master-port 7000 \ --db-user mxadmin \ --time-format raw \ --format csv \ --delimiter "|" \ --target json_test < ~/json.csv
- View loading datapostgres=# select * from json_test; id | j ----+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | {"a":10, "b":"xyz"} (1 row)
### 7.2.2 json array
- Create tablecreate table json_array_test(id int, j _json);
- Create data files
`~/json_array.csv`1|"{""{\""a\"":10, \""b\"":\""xyz\""}"",""{\""c\"": 10}""}"
- loadmxgate \ --source stdin \ --db-database postgres \ --db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \ --db-master-port 7000 \ --db-user mxadmin \ --time-format raw \ --format csv \ --delimiter "|" \ --target json_array_test < ~/json_array.csv
- verifypostgres=# select * from json_array_test ; id | j ----+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | {"{\"a\":10, \"b\":\"xyz\"}","{\"c\": 10}"} (1 row)
> Note: Because the json column contains special characters such as quotes, the --format parameter of mxgate must be csv