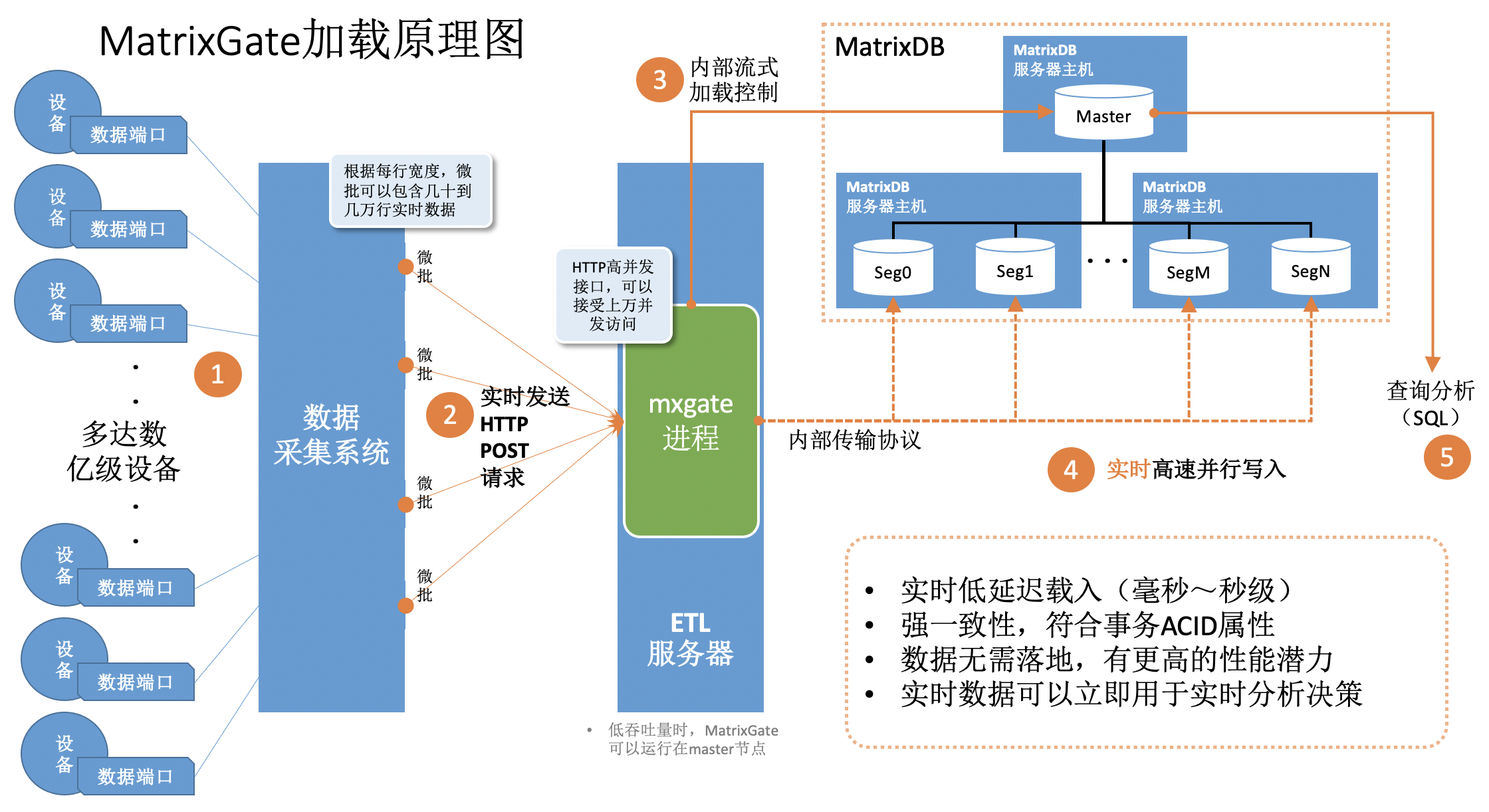
MatrixGate, abbreviated as mxgate, is a high-performance streaming data loading server located in the bin/mxgate directory of the MatrixDB installation. MatrixGate currently supports data ingestion via HTTP and STDIN interfaces, with support for TEXT and CSV data formats.
The data loading logic of MatrixGate is illustrated below:
mxgate config --db-database demo --target public.testtable --target public.testtable2 --allow-dynamic > mxgate.conf``
This command generates a configuration file named mxgate.conf. It allows users to customize data loading behavior for testtable and testtable2, while also supporting default global settings for loading into other tables.
mxgate.conf file as needed (e.g., set field delimiters). Skip this step if using defaults. The generated configuration includes entries like:``
[[job.target]]
# delimiter = "|"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true
[[job.target]]
# delimiter = "|"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable2"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable2"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true``
If testtable uses @ as delimiter and testtable2 uses %, update the config accordingly:
``
[[job.target]]
delimiter = "@"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true
[[job.target]]
delimiter = "%"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable2"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable2"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true``
By default, mxgate listens on port 8086. This can be seen in the mxgate.conf under source.http.http-port. You may change it if necessary:
``
[source]
## Source plugin is the data entrance to MatrixGate
## Types restricted to: http
source = "http"
[source.http]
## Port of http push
# http-port = 8086
## Maximum request body size (after gzip)
## The server rejects requests with bodies exceeding this limit.
# max-body-bytes = 4194304
## The maximum number of concurrent HTTP connections to the server
## The server response with 503 after exceed this limit.
# max-concurrency = 40000``
demo database, and prepare to receive data:``
mxgate start --config mxgate.conf``
``
mxgate status``
``
mxgate stop``
To force stop in case of timeout or other issues:
``
mxgate stop --force``
| Parameter | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
--db-database |
postgres | Database name that MatrixGate connects to in MatrixDB |
--db-master-host |
localhost | Hostname of the MatrixDB master node |
--db-master-port |
5432 | Port number of the MatrixDB master node |
--db-user |
current OS user | Username used by MatrixGate to connect to MatrixDB Note: This user must have permission to create external tables. For non-superusers, grant privileges using: alter user {username} CREATEEXTTABLE; |
--db-password |
empty | Password for the MatrixDB user |
--db-max-conn |
10 | Maximum number of connections from MatrixGate to MatrixDB |
--interval |
100 ms | Interval (in milliseconds) for batch data loading execution |
--source |
http | Data source type; supports http and stdin |
--target |
schemaName.tableName | Target table name. Schema name is optional and defaults to public. Multiple tables can be specified using multiple --target options. If not provided, use --allow-dynamic to enable dynamic table resolution |
--allow-dynamic |
false | When set to true, enables dynamic mapping of POST data to target tables based on the first line of input. Use only when target tables are not known at startup. For fixed targets, explicitly specify with --target |
--format |
text | Input data format: text or csv. text is faster but does not allow newlines in fields. csv is more flexible; string fields must be enclosed in double quotes |
--delimiter |
| | Field delimiter character within each row |
--null-as |
empty string | String representation of NULL values. Default is an unquoted empty string. For \N, escape the backslash: --null-as \\N |
--time-format |
unix-second | Timestamp unit: unix-second, unix-ms, unix-nano, or raw. MatrixGate treats the first column as a Unix timestamp by default. Use raw if the timestamp is not in the first column or already in DB format |
--use-auto-increment |
true | Whether to skip auto-increment columns during load and use system-generated values |
--exclude-columns |
empty | List of column names to exclude during load. Remaining columns must match table definition order. Auto-increment columns skipped via --use-auto-increment do not need to be listed here |
--help |
— | Display usage and parameter list |
MatrixGate provides an HTTP API, allowing data ingestion into MatrixDB from any programming language via HTTP.
| Protocol Element | Format | Usage and Example |
|---|---|---|
| URL | http://mxgate-host:port |
Address to connect to mxgate |
| PATH | / |
Only root path / is supported; any suffix is ignored |
| HTTP Method | POST | Only POST method is supported for data loading |
| HTTP Header | Content-Encoding: gzip |
Supports gzip compression of request body |
Content-Type: text/plain |
Only text/plain content type is supported |
|
| HTTP Body | SchemaName.TableNameTimestamp\|ID\|C1\|C2\|...\|Cn |
First line specifies the target table (SchemaName is optional, defaults to public). Subsequent lines contain time-series data. Each line corresponds to one row in the target table. Columns are separated by |, rows by \n. The first field is a Unix timestamp (see --time-format). Second field is TagID (integer). Remaining fields map to table columns. It is recommended that the target table DDL follows (Timestamp, TagID, C1, C2, ..., Cn) column order |
| Code | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 204 | StatusNoContent | Data successfully loaded into MatrixGate |
| 400 | StatusBadRequest | Bad request: e.g., malformed POST body, table not found, content encoding mismatch |
| 405 | StatusMethodNotAllowed | Non-POST HTTP method used |
| 500 | StatusInternalServerError | Database-side error; load failed. Response body contains detailed error message |
| 503 | StatusServiceUnavailable | Request rejected: e.g., max connections exceeded, or MatrixGate is shutting down |
testtable in the demo database:``
CREATE TABLE testtable (time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, tagid INT, c1 INT, c2 INT, c3 INT)
DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid);``
data.txt:``
public.testtable
1603777821|1|101|201|301
1603777822|2|102|202|302
1603777823|3|103|203|303``
``
mxgate --config mxgate.conf``
``
curl http://localhost:8086/ -X POST -H 'Content-Type: text/plain' --data-binary "@data.txt"``
``
demo=# SELECT * FROM testtable ;
time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3
------------------------+-------+-----+-----+-----
2020-10-27 05:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303
2020-10-27 05:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302
2020-10-27 05:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301
(3 rows)``
``
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class MxgateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MxgateExample http = new MxgateExample();
http.sendingPostRequest();
}
// HTTP Post request
private void sendingPostRequest() throws Exception {
// mxgate listens on port 8086 of localhost
String url = "http://localhost:8086/";
URL obj = new URL(url);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
// Setting basic post request
con.setRequestMethod("POST");
con.setRequestProperty("Content-Type","text/plain");
String postJsonData = "public.testtable\n1603777821|1|101|201|301\n1603777822|2|102|202|302\n1603777823|3|103|203|303";
con.setDoOutput(true);
DataOutputStream wr = new DataOutputStream(con.getOutputStream());
// Encode using UTF-8 if data contains Chinese characters
wr.write(postJsonData.toString().getBytes("UTF-8"));
wr.flush();
wr.close();
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("Sending 'POST' request to URL : " + url);
System.out.println("Post Data : " + postJsonData);
System.out.println("Response Code : " + responseCode);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String output;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((output = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(output);
}
in.close();
System.out.println(response.toString());
}
}``
``
import http.client
class MxgateExample(object):
def __init__(self):
# mxgate listens on port 8086 of localhost
self.url = "localhost:8086"
self.postData = "public.testtable\n/" \
"1603777821|1|101|201|301\n/" \
"1603777822|2|102|202|302\n/" \
"1603777823|3|103|203|303"
self.headers = {"Content-Type": "text/plain"}
# HTTP Post request
def sending_post_request(self):
conn = http.client.HTTPConnection(self.url)
conn.request("POST", "/", self.postData, self.headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
response_code = response.getcode()
print(f"Sending 'POST' request to URL : {self.url}")
print(f"Post Data : {self.postData}")
print(f"Response Code : {response_code}")
output = response.read()
print(output)
if __name__ == '__main__':
gate_post = MxgateExample()
gate_post.sending_post_request()``
Recommended to develop using C# Core environment
``
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
namespace HttpPostTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var url = "http://10.13.2.177:8086/";
var txt = "public.dest\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,1,a1\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,2,a2\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,3,a3";
HttpPost(url,txt);
}
public static string HttpPost(string url, string content){
string result = "";
HttpWebRequest req = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);
req.Method = "POST";
req.ContentType = "text/plain";
#region Add Post Parameters
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(content);
req.ContentLength = data.Length;
using (Stream reqStream = req.GetRequestStream()){
reqStream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
reqStream.Close();
}
#endregion
HttpWebResponse resp = (HttpWebResponse)req.GetResponse();
Stream stream = resp.GetResponseStream();
// Get response content
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream, Encoding.UTF8)){
result = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
return result;
}
}
}``
If you encounter the error "error when serving connection ***** body size exceeds the given limit", increase the
max-body-bytesvalue inmxgate.conf.
``
package main
import (
"bytes"
"net/http"
)
func PostDataToServer(URL string) error {
data := `public.testtable
1603777821|1|101|201|301
1603777822|2|102|202|302
1603777823|3|103|203|303
`
resp, err := http.Post(URL, "application/text", bytes.NewBuffer([]byte(data)))
if err != nil {
return err
}
if resp.StatusCode != 200 {
// Handle response body
return nil
}
// Handle response body
return nil
}
func main() {
err := PostDataToServer("http://127.0.0.1:8086")
if err != nil{
panic(err)
}
}``
csvtable in the demo database:``
CREATE TABLE csvtable (time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, tagid INT, c1 INT, c2 INT, c3 INT)
DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid);``
data.csv:``
1603777821|1|101|201|301
1603777822|2|102|202|302
1603777823|3|103|203|303``
stdin source, targeting existing csvtable, with parallelism level 2:``
mxgate \
--source stdin \
--db-database demo \
--db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \
--db-master-port 5432 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--time-format unix-second \
--delimiter "|" \
--target csvtable \
--parallel 2 < data.csv``
``
demo=# SELECT * FROM csvtable ;
time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3
------------------------+-------+-----+-----+-----
2020-10-27 05:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303
2020-10-27 05:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302
2020-10-27 05:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301
(3 rows)``
``
create table json_test(id int, j json);``
~/json.csv
``
1|"{""a"":10, ""b"":""xyz""}"``
stdin mode; other modes are similar):--format csv due to special characters in JSON.--format csv
``
mxgated \
--source stdin \
--db-database postgres \
--db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \
--db-master-port 7000 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--time-format raw \
--format csv \
--delimiter "|" \
--target json_test < ~/json.csv``
``
postgres=# select * from json_test;
id | j
----+-----------------------
1 | {"a":10, "b":"xyz"}
(1 row)``
``
create table json_array_test(id int, j _json);``
~/json_array.csv
``
1|"{""{\""a\"":10, \""b\"":\""xyz\""}"",""{\""c\"": 10}""}"``
``
mxgate \
--source stdin \
--db-database postgres \
--db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \
--db-master-port 7000 \
--db-user mxadmin \
--time-format raw \
--format csv \
--delimiter "|" \
--target json_array_test < ~/json_array.csv``
``
postgres=# select * from json_array_test ;
id | j
----+---------------------------------------------
1 | {"{\"a\":10, \"b\":\"xyz\"}","{\"c\": 10}"}
(1 row)``
Note: Because JSON fields contain quotes and other special characters, the
--formatparameter must be set tocsv.