Please refer to MatrixDB Installation and Deployment for the teaching video of this course.
MatrixDB can be installed on Redhat 7, CentOS 7, Galaxy Kirin V10 operating system + ARM platform support and CentOS-compatible operating systems. This document describes the steps to quickly deploy MatrixDB on a single node. (If the host cannot connect to the external network, please refer to MatrixDB 4 offline cluster deployment).
Before installation, please first Download MatrixDB installation file.
The server installation process includes two steps: installation preparation and database deployment. The optional post-installation settings and basic database management commands are also discussed later.
All preparation operations need to be performed under the root user.
MatrixDB requires Python 3.6. Please use the following command to install and set Python 3.6 as the default version:
yum install centos-release-scl
yum install rh-python36
scl enable rh-python36 bashInstall parquet dependencies
yum install -y epel-release || yum install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-$(cut -d: -f5 /etc/system-release-cpe | cut -d. -f1).noarch.rpm
yum install -y https://apache.jfrog.io/artifactory/arrow/centos/$(cut -d: -f5 /etc/system-release-cpe | cut -d. -f1)/apache-arrow-release-latest.rpm
yum install -y arrow-libs-3.0.0 parquet-libs-3.0.0Turn off the firewall:
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl disable firewalld.serviceTurn off SELINUX, edit /etc/selinux/config, and set the value of SELINUX to disabled:
sed s/^SELINUX=.*$/SELINUX=disabled/ -i /etc/selinux/config
setenforce 0Make sure there is a persistent host name on the installation node. If it does not exist, please use the following command to set the host name:
hostnamectl set-hostname mdwModify the /etc/hosts file and map the host name to a local network card address:
192.168.100.10 mdwNotes!
Do not add the aboveentry repeatedly in /etc/hosts, otherwise an error will appear "Inter-host network connection test failed" when MXUI is initialized.
When using the root user to execute the following yum command to install the database RPM package, the system dependency library will be automatically installed. By default, it will be installed in the /usr/local/matrixdb directory:
yum install matrixdb-4.0.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpmNote: During the actual installation process, please replace the file name with the latest downloaded rpm package name
After the installation is successful, the supervisor, cylinder, and mxui processes will be automatically started. These background processes are used to provide graphic operation interfaces, manage and control clusters, etc.
Please use the root user to execute the following command to install the python package that MatrixDB depends on. Please note that source greenplum_path.sh must be executed so that the correct version of the dependency package can be installed:
source /usr/local/matrixdb/greenplum_path.sh
yum install gcc python3-devel
pip3 install --upgrade setuptools
pip3 install argparse psutil pygresql pyyaml MatrixDB provides a simple and easy-to-use database deployment method, including graphic deployment and command line deployment, and it is recommended to use graphic deployment. Remote graphic deployment requires server ports 8240 and 4617 to access. The graphic UI service is provided by the mxui process.
Use your browser to access the following graphic installation wizard URL, which is the server IP as described in step 1.1:
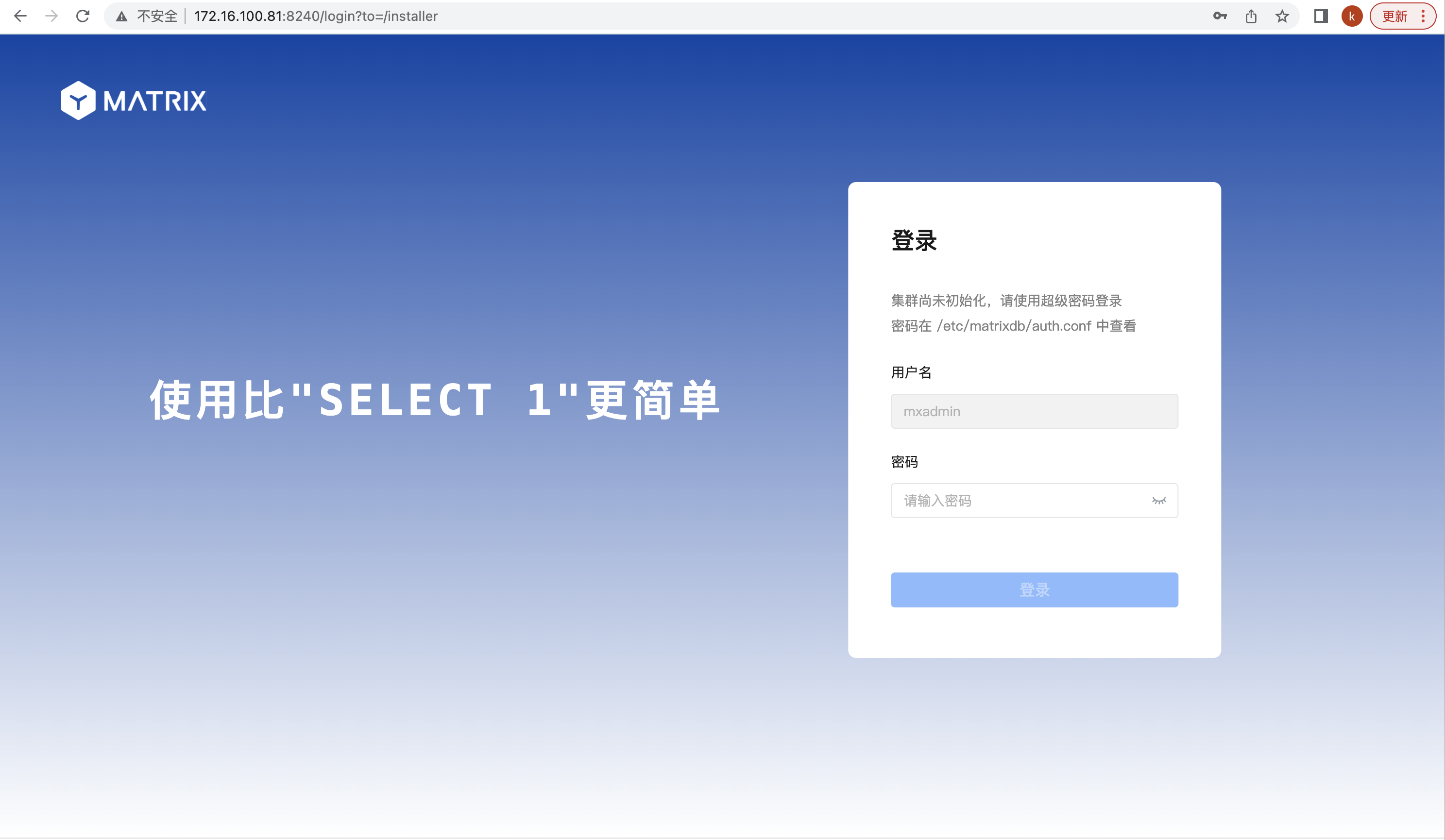
http://<IP>:8240/On the first page of the installation wizard, you need to fill in the superuser password, which can be found in /etc/matrixdb/auth.conf:
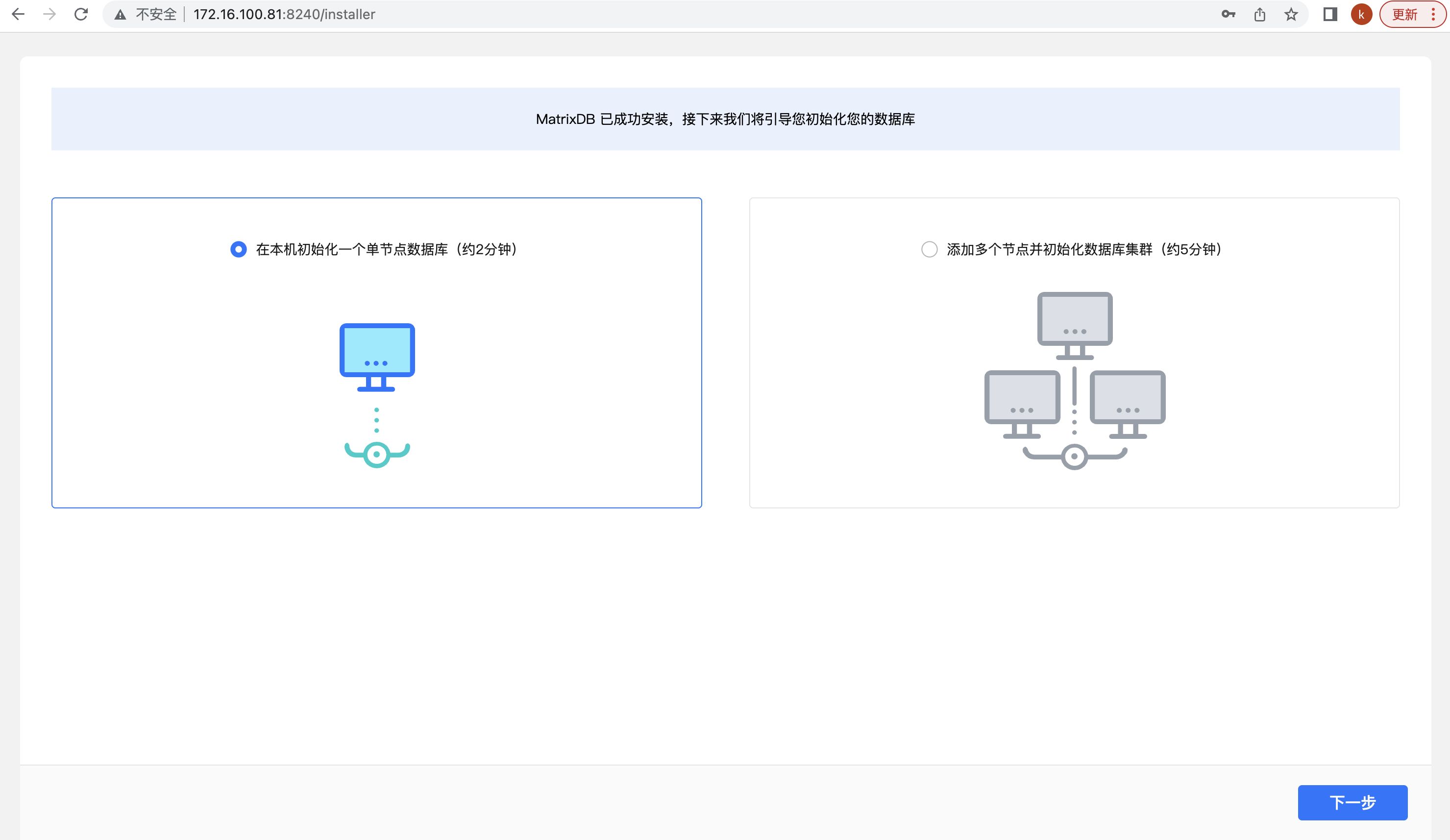
The second page automatically selects "Initialize a single node database on the local machine", please click Next:
Next, start the five-step operation of stand-alone deployment.
The first step is to automatically collect system information. Please check the number of cores and memory size of the system and click Next:
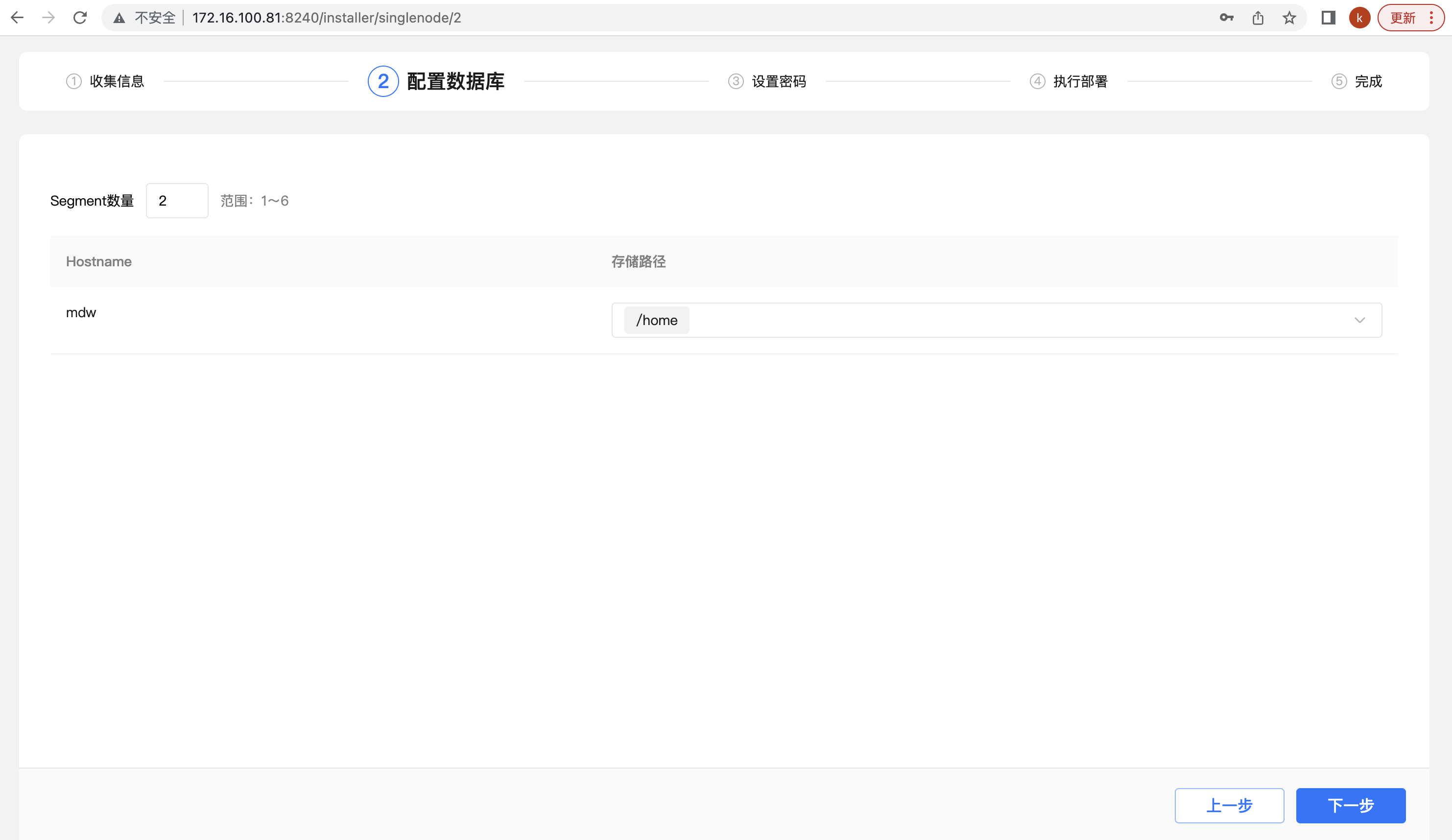
The second step is to select the database directory storage path and the number of segments. The system automatically recommends the largest disk space and the number of segments matching the system resources. You can adjust it according to the specific usage scenario. After confirming, click Next:
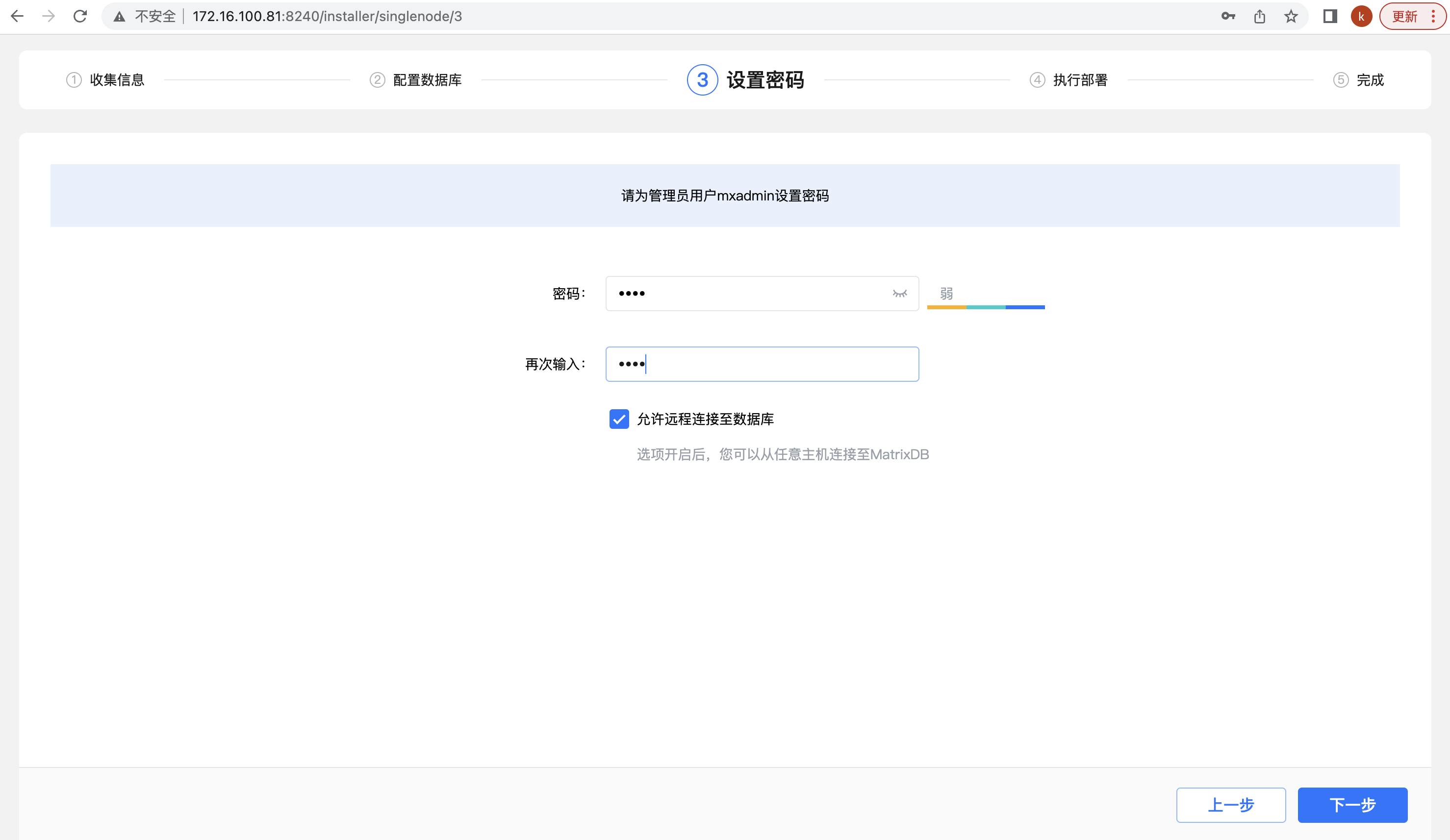
Step 3: Set the password. MatrixDB will create an mxadmin database administrator account and serve as a super account. In this link, set the password of the mxadmin account and click "Next" (the password of the database account is set here, not the password of the operating system account). In addition, there is another option that is "Allow remote connection to the database", which is checked by default:
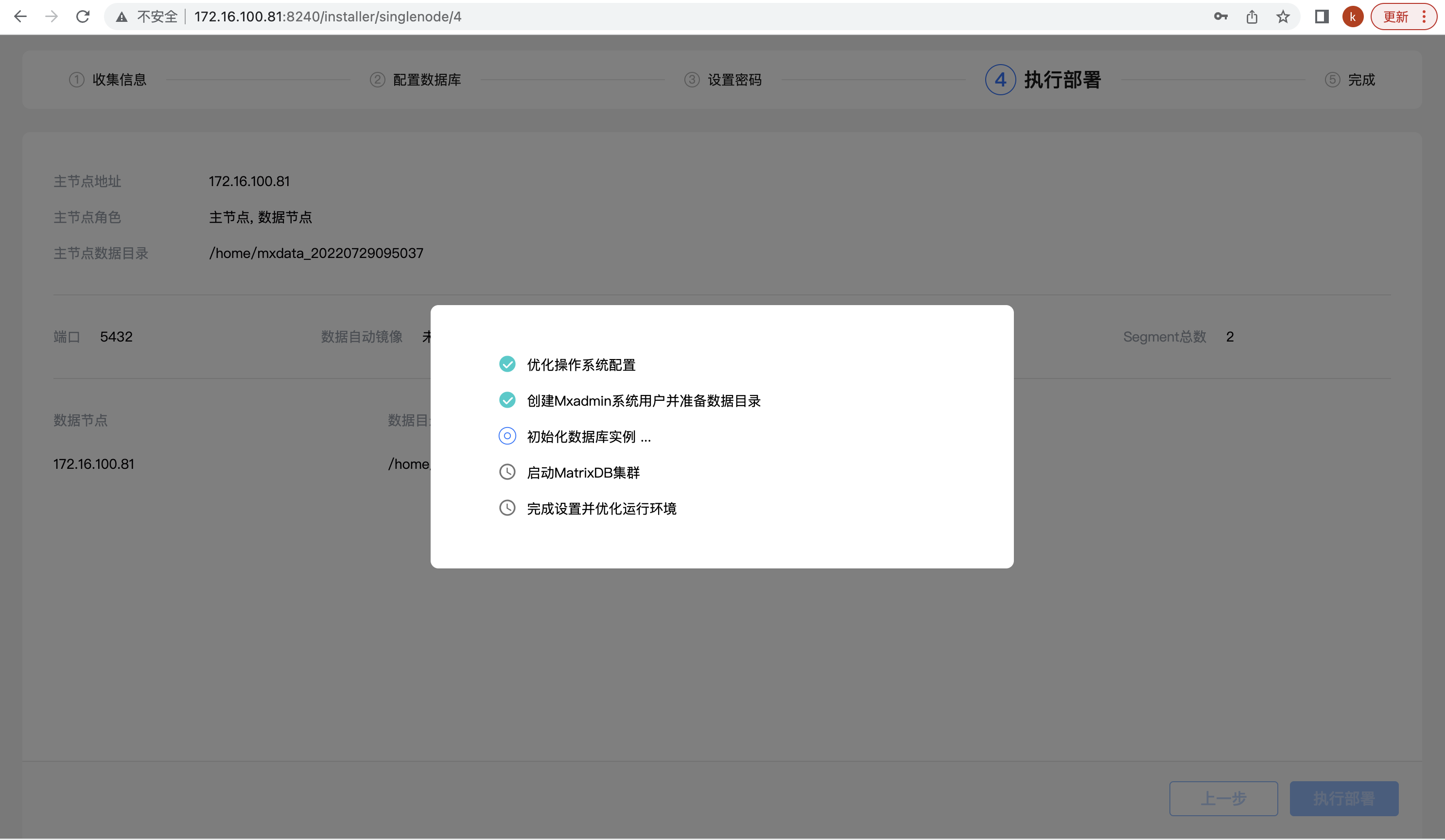
Step 4: Start deploying the database. The page displays tasks for background operations, including system settings, creating users and directories, initializing databases, starting databases, and cleaning and optimization. After clicking "Execute Deployment", start the deployment operation and display the progress of task completion in real time: 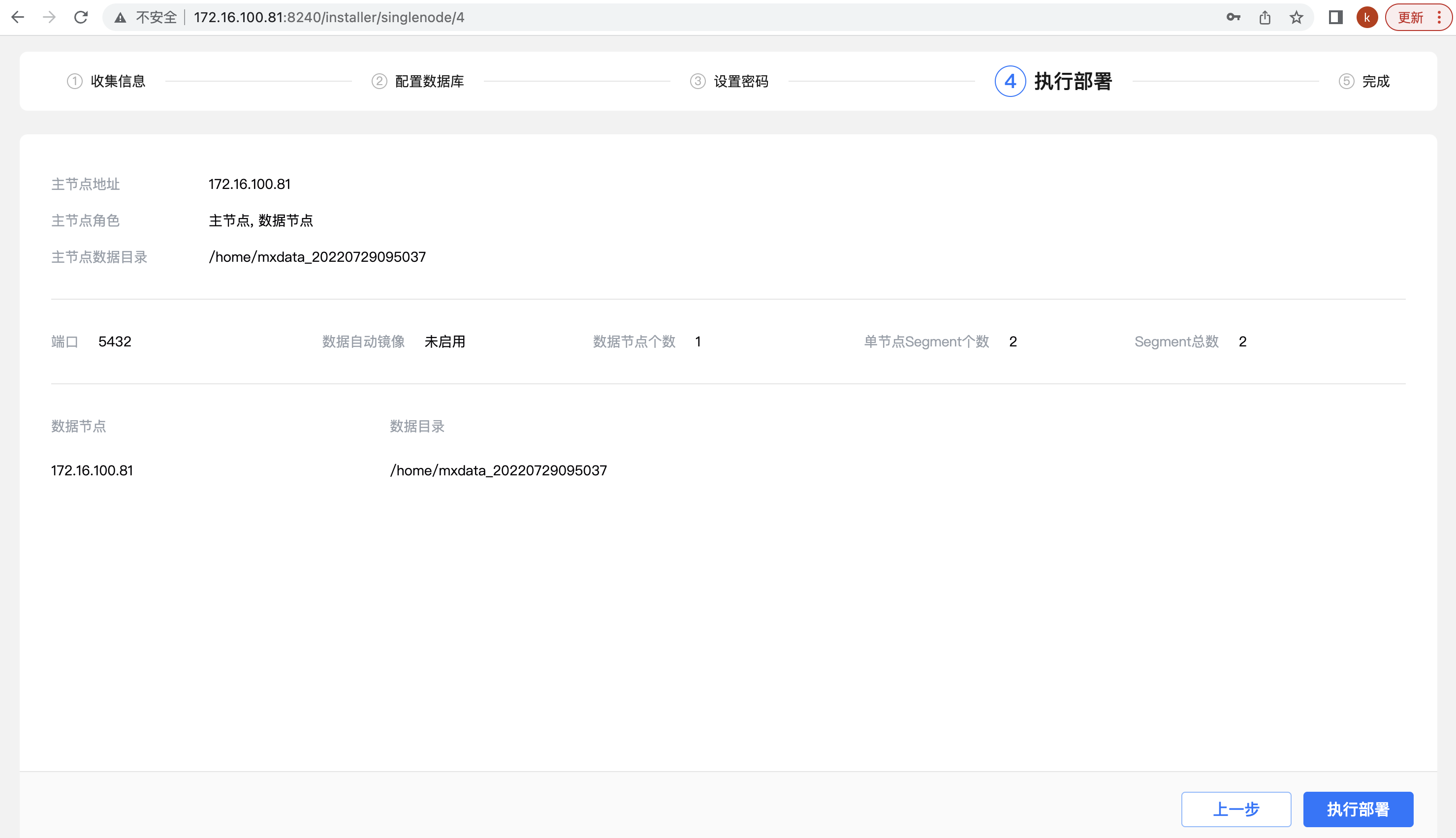
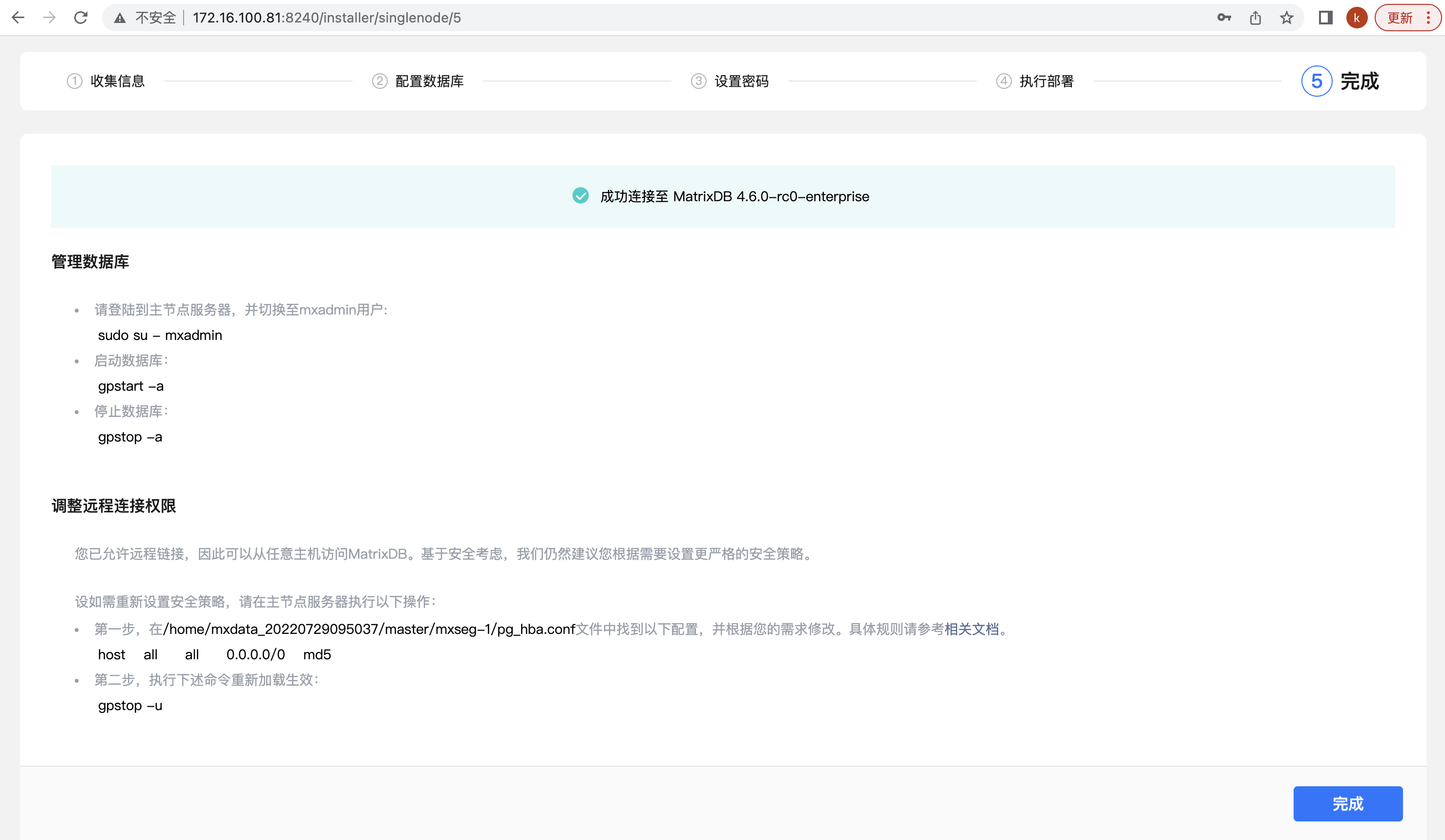
Step 5, complete. After the deployment operation is completed, you can click the "Finish" button to display the test connection and some subsequent optional configurations, including allowing remote connections, installing a graphic client, etc. Click Test Connection to automatically test whether the connection can be successfully connected.
MatrixDB also provides a one-click stand-alone command line deployment. The command is as follows. After execution, the database can be automatically started and used immediately:
source /usr/local/matrixdb/greenplum_path.sh
sudo env "PATH=$PATH" mxsetupSSH logs in to the server and switches to MatrixDB administrator user mxadmin:
sudo su - mxadminMatrixDB default installation supports remote connection. If "Allow remote connection to database" is not checked during the installation process, please manually modify the $MASTER_DATA_DIRECTORY/pg_hba.conf file to add a line like this, indicating that users from any IP who access all databases are allowed to connect through password authentication. The IP range or database name can be limited according to actual needs to be used to reduce security risks:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5To facilitate remote connections, and also test whether the database is initialized normally, please execute the following command to set the password for the database administrator user mxadmin (please replace mxpass with your password):
psql -c "alter role mxadmin with password 'mxpass'" -h localhost -p 5432 mxdbAfter completing these modifications, you need to execute the following command to reload the new settings of pg_hba.conf in the database:
gpstop -uSSH logs in to the server and switches to MatrixDB administrator user mxadmin:
sudo su - mxadminMatrixDB start, stop, restart and status viewing can be completed separately through the following commands. More command parameters can be viewed through --help:
gpstart -a
gpstop -af
gpstop -arf
gpstateMatrixDB can be installed on low-end devices, as follows:
| Minimum configuration |
|---|
| 1GHZ Dual-Core Processor |
| 2GB memory |
| 2GB disk space |
| RAID 1 (mirror) |
If installed on a memory device below 2G, you can add swaps according to the following commands before installation to ensure that the device has no less than 2G swap space.
Create and enable a 2G SWAP area:
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/opt/swapfile count=2048 bs=1MiB
sudo chmod 600 /opt/swapfile
sudo mkswap /opt/swapfile
sudo swapon /opt/swapfile
swapon -s
free -mEdit /etc/fstab to add the following line to persist the swap area:
/opt/swapfile swap swap sw 0 0MatrixDB is compatible with PostgreSQL 12 protocol. Many commercial and open source client tools that support PostgreSQL 12 can be used with MatrixDB, making it easier for you to remotely access MatrixDB from your laptop and other personal computers.
Taking open source DBeaver as an example, select to download the corresponding operating system installation package at https://dbeaver.io/download/. After installation, when connecting to the MatrixDB database, select PostgreSQL as the database type. DBeaver will automatically detect whether there is a correct JDBC driver in your system, or prompt to download it.

MatrixDB's command line tool psql can also be used remotely on Windows or Mac systems. Mac users can directly use brew to install:
brew install libpq
brew link --force libpq ailWindows users, please download and install it from here: https://www.postgresql.org/download/windows/
After psql is installed, you can connect to the MatrixDB server by specifying the host name and -p port by specifying the port. Other common parameters of psql are as follows:
psql -h [hostname or IP] -p [port] -U [username] -W -d [database name]For example:
psql -h 127.0.0.1 -p 5432 -U mxadmin -W -d mxdb