MatrixGate is abbreviated as mxgate. It is a high-performance streaming data loading server located in bin/mxgate in the MatrixDB installation directory. MatrixGate currently provides HTTP and STDIN interfaces to load data, and the data format supports TEXT and CSV.
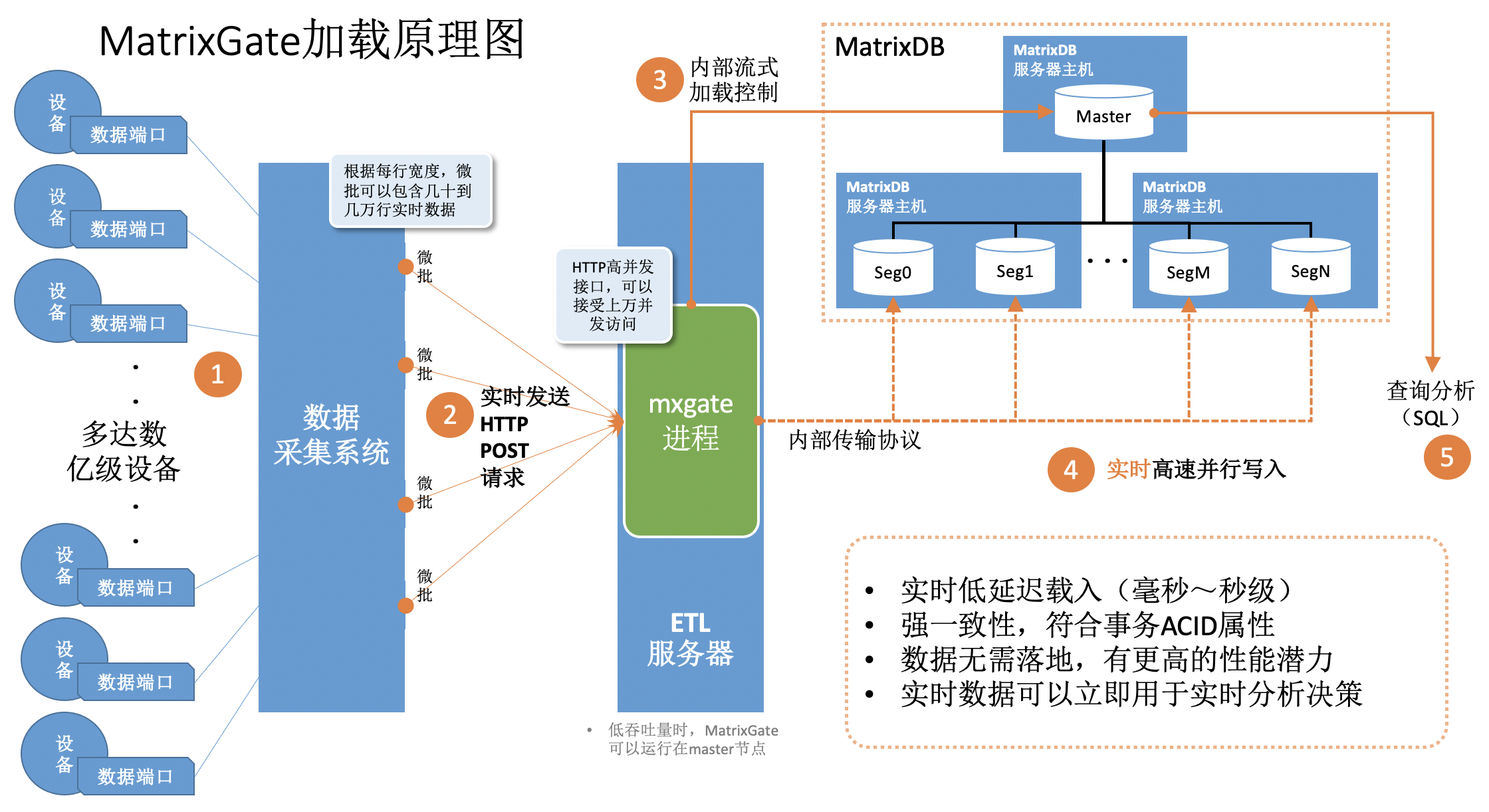
The logic of MatrixGate loading data is shown in the figure below, 1) The data acquisition system collects device data or receives data sent by the device 2) The acquisition system continuously sends data to MatrixGate's service process mxgate in a concurrent microbatch mode 3) The mxgate process and the MatrixDB master process communicate efficiently, communicate transactions and control information 4) The data is directly sent to the segment node and written in parallel at high speed.
Specify the target database and target table to generate mxgate configuration file
mxgate config --db-database demo --target public.testtable --target public.testtable2 --allow-dynamic > mxgate.confThe above parameters will generate a configuration file mxgate.conf, allowing users to personalize the loading of testtable and testtable2, and can also use the global default settings to load data into other tables.
Modify mxgate configuration file as needed, such as configuration data separator, etc., and select the default configuration to ignore this step. You can see the settings corresponding to testtable and testtable2 in this configuration file as follows:
[[job.target]]
# delimiter = "|"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true
[[job.target]]
# delimiter = "|"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable2"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable2"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = trueIf the delimiter of testtable is @ and the delimiter of testtable2 is %, the above configuration can be modified to:
[[job.target]]
delimiter = "@"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = true
[[job.target]]
delimiter = "%"
# exclude-columns = []
# format = "text"
name = "job_text_to_public.testtable2"
# null-as = ""
table = "public.testtable2"
# time-format = "unix-second"
# use-auto-increment = truemxgate listens to port 8086 to receive data by default. You can see in mxgate.conf that the http-port sub-item under source.http is set to 8086. If necessary, you can change it to another port:
[source]
## Source plugin is the data entrance to MatrixGate
## Types restricted to: http
source = "http"
[source.http]
## Port of http push
# http-port = 8086
## Maximum request body size (after gzip)
## The server rejects requests with bodies exceeding this limit.
# max-body-bytes = 4194304
## The maximum number of concurrent HTTP connections to the server
## The server response with 503 after exceed this limit.
# max-concurrency = 40000Start mxgate, load configuration files, connect to demo database, and prepare to receive data loading requests
mxgate start --config mxgate.confCheck the backend service status
mxgate statusTerminate the background service
mxgate stopWhen encountering timeout or other problems, you need to force stop, you can do this:
mxgate stop --force| 参数名 | 参数值 | 参数含义 |
|---|---|---|
| [database]类别 | ||
| --db-database | 默认postgres | MatrixGate连接MatrixDB数据库名 |
| --db-master-host | 默认本机主机名 | MatrixGate连接MatrixDB主机名 |
| --db-master-port | 默认5432 | MatrixGate连接MatrixDB主机端口号 |
| --db-user | 默认当前系统用户名 | MatrixGate连接MatrixDB用户名 注意:该用户必须具有创建外部表的权限,如果使用的是非超级权限用户,请使用如下命令增加权限: alter user {username} CREATEEXTTABLE; |
| --db-password | 默认为空 | MatrixGate连接MatrixDB用户密码 |
| --db-max-conn | 默认10 | MatrixGate连接MatrixDB最大连接数 |
| [job]类别 | ||
| --allow-dynamic | 默认false | 当指定--allow-dynamic=true时,允许根据POST的数据内容(第一行),动态适配插入的目标表。此选项应仅用于MatrixGate启动时目标表名尚未确定的场景。如果固定插入某个已知的目标表,推荐用--target显式指定表名 |
| --delimiter | 默认为 | | 指定用于分隔文件每一行(行)中各列的字符 |
| --error-handling | 默认为'accurate' | 遇到格式错误行的处理方式 'accurate':错误数据不入库并记录错误日志,该批次其他数据不受影响 'legacy':该批次整体失败 |
| --exclude-columns | 默认为空 | 数据加载默认提供的列数量和列顺序需要与表定义一致,当数据加载仅提供部分列时,--exclude-columns用于标记排除的列名,其他列仍需要保证顺序与表定义一致。 提示:如果已经开启--use-auto-increment跳过自增字段,则不需要在此列出这些自增字段。这个参数只需要标记出其他还需要排除的列名即可 |
| --format | 默认 text | 指定源数据的数据格式text或csv。text速度最快,但不支持字符类型中出现换行。csv格式适用性更广,对字符类型的列必须用双引号。 |
| --null-as | 默认空字符串 | 指定表示空值的字符串。 默认值为无引号的空字符串。当数据表中的列约束为非空NOT NULL,且数据内容上该列给出了空值,将会导致加载报错。提示:如需要使用\N为空值,需要对反斜杠进行转义,如:--null-as \N |
| --time-format | 默认unix-second | 指定时间戳单位:unix-second|unix-ms|unix-nano|raw。\n MatrixGate默认将每行数据的第一列当作时间戳的Unix表示,自动将其转化为数据库时间格式。如果时间戳不在第一列,或者用户已经自行转换为数据库格式,则应使用raw,这样MatrixGate不会做时间类型转换。 |
| --upsert-key | 默认为空 | 进行upsert的键名,可以指定多个。 需要做upsert的表,必须建立UNIQUE约束,且参数中要指定所有约束键。 |
| --deduplicate-key | 默认为空 | 用法和upsert类似,区别是只更新空值,如果旧值非空,新值丢弃。 和--upsert-key参数互斥,只能选一种。 |
| --use-auto-increment | 默认true | 当target表中含有自增字段时,是否在加载数据中跳过自增字段赋值而使用系统默认自增值 |
| --target | schemaName.tableName | 指定目标的表名,schemaName可以省略,默认为public。允许指定多个目标表,使用方法是 "--target 表1 --target 表2 …"。当不提供此参数时,可以额外指定--allow-dynamic参数来允许动态适配表名。 |
| [misc]类别 | ||
| --log-archive-hours | 默认为72 | 日志目录下,超过一定时间未发生改变的matrixgate日志文件,被自动压缩 |
| --log-compress | 默认为true | 是否开启log自动压缩的全局开关 |
| --log-dir | 默认为/home/mxadmin/gpAdminLogs | 日志目录 |
| --log-max-archive-files | 默认为0 | 最多保留多少个压缩的log文件,超过这个数量,则最老的日志文件会被删除。0为不删除 |
| --log-remove-after-days | 默认为0 | 被压缩后的log文件,再经过多少天被自动删除。0为不删除 |
| --log-rotate-size-mb | 默认为100 | 当前log文件超过一定大小则自动切换到一个新文件,旧文件则立即压缩 |
| [source]类别 | ||
| --source | 默认http | MatrixGate数据来源,支持http、stdin、kafka、transfer |
| [source]类别 | [http] | |
| --http-port | 默认8086 | MatrixGate用户提交数据的HTTP接口 |
| --max-body-bytes | 默认4194304 | 每个HTTP包体大小上限 |
| --max-concurrency | 默认40000 | HTTP最大并发连接数 |
| --request-timeout | 默认0 | 请求超时时间,默认0,无限等待。当设置大于0的值,会在等待毫秒单位的设置时间后超时并返回HTTP408。 |
| --disable-keep-alive | 默认false | MatrixGate在每次HTTP请求后强制断开连接 |
| --http-debug | 默认false | 输出附加HTTP诊断信息 |
| [source]类别 | [transfer] | |
| --src-host | 源库master的ip地址 | |
| --src-port | 源库master的端口号 | |
| --src-user | 连接源库的用户名(建议使用superuser) | |
| --src-password | 连接密码 | |
| --src-schema | 源表的schema名 | |
| --src-table | 源表的表名 | |
| --src-sql | 进行迁移数据过滤的SQL | |
| --compress | 源数据库segment主机到本数据的传输方法: 空白字符串“”,代表不压缩,明文传输 gzip:使用gzip压缩,需要源数据库的segment主机上必须安装有gzip这个linux命令 lz4:使用lz4压缩,需要源数据库的segment主机上必须安装有lz4这个linux命令 推荐 lz4 > gzip > 不压缩 |
|
| --port-base | 传输中会占用一批端口,端口的范围为9129~ | |
| --local-ip | 必须用源库可以连接到本机的IP地址 | |
| [writer]类别 | ||
| --interval | 默认100毫秒 | MatrixGate执行批量数据加载时间周期 |
| --stream-prepared | 默认10 | 插入工作进程并行度 |
| --use-gzip | 默认'auto' | MatrixGate向segment发送数据时是否开启压缩,可配置参数为auto/yes/no |
| --max-seg-conn | 默认128 | 外部表从MatrixGate拉取数据时启动的segment数量,调大该参数会增加网络连接资源 |
| --timing | 默认false | 开启该参数后,MatrixGate在记录日志时会为每条INSERT增加耗时信息 |
| --insert-timeout | 默认0 | MatrixGate执行INSERT语句超时时间,默认为0,无限等待。 设置大于0的值后会在等待毫秒单位配置时间后超时。 |
| 其他 | ||
| --help | 显示用法和参数列表 |
MatrixGate对外提供HTTP API,支持各种编程语言通过HTTP接口将数据导入到MatrixDB数据库中。MatrixGate HTTP protocol format| Protocol Type | Protocol Format | Usage and Examples |
| --- | --- |
| URL | http://mxgate-host:port | Specify mxgate connection address |
| PATH | / | Currently supported /, ignore / after any PATH |
| HTTP Method | POST | Currently supports POST method to load data |
| HTTP Header | Content-Encoding: gzip | Currently supports gzip for HTTP Body content compression |
| | Content-Type: text/plain | Currently supported text/plain |
| HTTP Body | SchemaName.TableName
Timestamp|ID]|C1|C2|..|Cn | The first behavior of the Body format is the target table loaded by data. SchemeName can be omitted. The default is Public. TableName is a required item. The second row starts with a time-series data row. Each row corresponds to a row of the target table. The | separator is used between columns and the \n separator is used between rows. The first field of each line is a timestamp, and the format is UNIX timestamp is accurate to seconds, see the description of --time-format. The second field of each row is TagID, integer. The third field to the last field of each row is the column corresponding to the target table. It is recommended that the DDL definition of the target table also follows the column order of (Timestamp, TagID, C1, C2,…, Cn) |
MatrixGate HTTP response code
| Response Code | Response Code Meaning | Remarks |
| --- | --- |
| 200 | StatusOK | Some data format is wrong, and the response Body will contain the wrong line with error message, such as: At line: 2missing data for column "c3" |
| 204 | StatusNoContent | Data loaded successfully to MatrixGate |
| 400 | StatusBadRequest | Data request errors, such as POST BODY format error, target table does not exist, data compression format does not match the HTTP request header, etc. |
| 405 | StatusMethodNotAllowed | HTTP Non-POST Request |
| 408 | StatusTimeout | Request timeout |
| 500 | StatusIntervalServerError | Database error, data loading failed, response Body contains detailed error information |
| 503 | StatusServiceUnavailable | MatrixGate rejects requests, such as exceeding the maximum number of connections, or MatrixGate is closing, etc |
CREATE TABLE testtable (time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, tagid INT, c1 INT, c2 INT, c3 INT)
DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid);public.testtable
1603777821|1|101|201|301
1603777822|2|102|202|302
1603777823|3|103|203|303mxgate --config mxgate.confcurl http://localhost:8086/ -X POST -H 'Content-Type: text/plain' --data-binary "@data.txt"demo=# SELECT extract(epoch FROM "time"), * FROM testtable;
date_part | time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1603777821 | 2020-10-27 13:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301
1603777822 | 2020-10-27 13:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302
1603777823 | 2020-10-27 13:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303
(3 rows)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;public class MxgateExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { MxgateExample http = new MxgateExample(); http.sendingPostRequest(); }
// HTTP Post request
private void sendingPostRequest() throws Exception {
// mxgate listens on port 8086 of localhost
String url = "http://localhost:8086/";
URL obj = new URL(url);
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) obj.openConnection();
// Setting basic post request
con.setRequestMethod("POST");
con.setRequestProperty("Content-Type","text/plain");
String postJsonData = "public.testtable\n1603777821|1|101|201|301\n1603777822|2|102|202|302\n1603777823|3|103|203|303";
con.setDoOutput(true);
DataOutputStream wr = new DataOutputStream(con.getOutputStream());
// When the data is in Chinese, it can be encoded by postJsonData.getBytes("UTF-8")
wr.write(postJsonData.toString().getBytes("UTF-8"));
wr.flush();
wr.close();
int responseCode = con.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("Sending 'POST' request to URL : " + url);
System.out.println("Post Data : " + postJsonData);
System.out.println("Response Code : " + responseCode);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream()));
String output;
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();
while ((output = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(output);
}
in.close();
System.out.println(response.toString());
}}
<a name="python"><br/></a>
### 6.2 MatrixGate HTTP API Python Exampleimport http.client
class MxgateExample(object): def init(self):
self.url = "localhost:8086"
self.postData = "public.testtable\n/" \
"1603777821|1|101|201|301\n/" \
"1603777822|2|102|202|302\n/" \
"1603777823|3|103|203|303"
self.headers = {"Content-Type": "text/plain"}
# HTTP Post request
def sending_post_request(self):
conn = http.client.HTTPConnection(self.url)
conn.request("POST", "/", self.postData, self.headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
response_code = response.getcode()
print(f"Sending 'POST' request to URL : {self.url}")
print(f"Post Data : {self.postData}")
print(f"Response Code : {response_code}")
output = response.read()
print(output)if name == 'main': gate_post = MxgateExample() gate_post.sending_post_request()
<a name="C#"><br/></a>
### 6.3 MatrixGate HTTP API C# Example
> It is recommended to use the C# Core development environment for developing codeusing System; using System.IO; using System.Net; using System.Text;
namespace HttpPostTest { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var url = "http://10.13.2.177:8086/"; var txt = "public.dest\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,1,a1\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,2,a2\n2021-01-01 00:00:00,3,a3";
HttpPost(url,txt);
}public static string HttpPost(string url, string content){ string result = ""; HttpWebRequest req = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url); req.Method = "POST"; req.ContentType = "text/plain";
#region Add Post parameters
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(content);
req.ContentLength = data.Length;
using (Stream reqStream = req.GetRequestStream()){
reqStream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
reqStream.Close();
}
#endregion
HttpWebResponse resp = (HttpWebResponse)req.GetResponse();
Stream stream = resp.GetResponseStream();
//Get the response content
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream, Encoding.UTF8)){
result = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
return result;
}} }
> If you encounter the problem of error when serving connection ***** body size exceeds the given limit, increase the max-body-bytes under mxgate.conf
### 6.4 MatrixGate HTTP API Golang Examplepackage main
import ( "bytes" "net/http" )
func PostDataToServer(URL string) error {
data := public.testtable 1603777821|1|101|201|301 1603777822|2|102|202|302 1603777823|3|103|203|303
resp, err := http.Post(URL, "application/text", bytes.NewBuffer([]byte(data)))
if err != nil {
return err
}
if resp.StatusCode != 200 {
// Deal with the response body.
return nil
}
// Deal with the response body.
return nil}
func main() { err := PostDataToServer("http://127.0.0.1:8086") if err != nil{ panic(err) }
}
## 7 MatrixGate Loading Special Types
### 7.1 MatrixGate loading CSV file example
- Create table csvtable in demo databaseCREATE TABLE csvtable (time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, tagid INT, c1 INT, c2 INT, c3 INT) DISTRIBUTED BY (tagid);
- Edit the data load file data.csv, the content is as follows1603777821|1|101|201|301 1603777822|2|102|202|302 1603777823|3|103|203|303
- Start mxgate, specify the source parameter to stdin, the target table is an existing csvtable, and the loading parallelism is 2mxgate \ --source stdin \ --db-database demo \ --db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \ --db-master-port 5432 \ --db-user mxadmin \ --time-format unix-second \ --delimiter "|" \ --target csvtable \ --parallel 2 < data.csv
- Connect to the database to query whether the data is loaded successfullydemo=# SELECT * FROM csvtable ; time | tagid | c1 | c2 | c3 -----------------------+-------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2020-10-27 05:50:23+08 | 3 | 103 | 203 | 303 2020-10-27 05:50:22+08 | 2 | 102 | 202 | 302 2020-10-27 05:50:21+08 | 1 | 101 | 201 | 301
(3 rows)
### 7.2 MatrixGate loading json field example
### 7.2.1 json
- Create tablecreate table json_test(id int, j json);
- Create data files
`~/json.csv`1|"{""a"":10, ""b"":""xyz""}"
- load
Here we use the stdin mode as an example, and the other modes are the same.
The key is `--format csv`mxgated \ --source stdin \ --db-database postgres \ --db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \ --db-master-port 7000 \ --db-user mxadmin \ --time-format raw \ --format csv \ --delimiter "|" \ --target json_test < ~/json.csv
- View loading datapostgres=# select * from json_test; id | j ----+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | {"a":10, "b":"xyz"} (1 row)
### 7.2.2 json array
- Create tablecreate table json_array_test(id int, j _json);
- Create data files
`~/json_array.csv`1|"{""{\""a\"":10, \""b\"":\""xyz\""}"",""{\""c\"": 10}""}"
- loadmxgate \ --source stdin \ --db-database postgres \ --db-master-host 127.0.0.1 \ --db-master-port 7000 \ --db-user mxadmin \ --time-format raw \ --format csv \ --delimiter "|" \ --target json_array_test < ~/json_array.csv
- verifypostgres=# select * from json_array_test ; id | j ----+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | {"{\"a\":10, \"b\":\"xyz\"}","{\"c\": 10}"} (1 row)
> Note: Because the json column contains special characters such as quotes, the --format parameter of mxgate must be csv
## 8 Observe mxgate operation indicators:
watch is a subcommand of mxgate, which uses a series of indicators to describe the operation of mxgate daemon.
There are two modes of watch:
- Real-time observation mode, print gate's indicators every 3 seconds in a sar-like format.
- Historical Observation Mode, you can specify any time period, any time period (such as every hour yesterday, every day last month, every month last year) to statistically import speed.
### 8.1 Real-time observationmxgate watch
The mxgate run indicators will be collected every three seconds, and the output results are as follows Time WCount ICount WSpeed/s ISpeed/s WBandWidth MB/S BlocakItems2022-04-28 15:20:58 14478858 14527011 2598081 2627887 2395 0 2022-04-28 15:21:01 22231035 22633254 2584059 2702081 2222 0 2022-04-28 15:21:04 30494310 30500874 2754425 2622540 3551 0 2022-04-28 15:21:07 38004210 38032956 2503300 2510694 2862 0 2022-04-28 15:21:10 46188696 46298223 2728162 2755089 2227 0 ...
The description of the above indicators can be obtained through the --info parametermxgate watch --info
By default, only speed indicators will be output. The time indicator can be observed through the --watch-lateency parameter to analyze problems.mxgate watch --watch-latency
### 8.2 Historical data observationmxgate watch --history
The average speed of each hour from the current time -24 hours to the current time will be calculated. The output result is as follows TIME RANGE | SPEED/S | BANDWIDTH MB/S | BLOCK ITEMS2022-04-28 16:00:00-2022-04-28 17:00:00 | 2208010 | 1254.48 | 0 2022-04-28 17:00:00-2022-04-28 18:00:00 | 1157920 | 1327.00 | 0 2022-04-28 18:00:00-2022-04-28 19:00:00 | 2228666 | 2162.32 | 0 2022-04-28 19:00:00-2022-04-28 20:00:00 | 1371092 | 2881.30 | 0 2022-04-28 20:00:00-2022-04-28 21:00:00 | 1575320 | 2608.20 | 0
Among them, SPEED/S, BANDWIDTH MB/S represents the speed and import bandwidth of the imported entry (MB/s in units),
BLOCK ITEMS represents the amount of data blocking in mxgate. This value will rise when the database consumption speed cannot keep up with the production speed of data sources (http, kafka, etc.).
You can add `--watch-start`, `--watch-end`, `--watch-duration` parameters to control the time interval and period of observation historical data.
For examplemxgate watch --history --watch-start '2022-03-27 00:00:00' --watch-end '2022-04-27 00:00:00' --watch-duration '168h'
Average import speeds per week (every 168h) from March 27 to April 27
Among them, `--watch-duration` supports three units: `h``` `m``