YMatrix provides a custom-built exporter that seamlessly integrates with the Prometheus monitoring ecosystem.
Note that the YMatrix exporter and its associated dashboards monitor only database-level metrics, not operating system metrics. OS-level monitoring requires additional exporters such as node_exporter. The module layout is shown below:

The YMatrix exporter is included in the YMatrix installation package and can be activated directly. After activation, install and deploy node_exporter, Grafana, and Prometheus.
createdb matrixmgr;psql -d matrixmgr
matrixmgr=# CREATE EXTENSION matrixts;
matrixmgr=# CREATE EXTENSION matrixmgr;
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_init_exporter();Upon success, a new schema named exporter appears in the matrixmgr database. This schema contains tables and views with cluster monitoring and configuration data. Do not modify the definitions or contents of these tables and views.
This command starts matrixdb_exporter on all cluster hosts.
Note!
If the cluster has the legacy monitoring system enabled, disable it first; otherwise, activation will fail.
To disable:SELECT mxmgr_remove_all('local');
node_exporter monitors operating system-level metrics. Download the latest version from the official site: node_exporter. The following example uses version 1.3.1 (run as root).
# Download node_exporter
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.3.1/node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
# Extract the package
tar -xvf node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
# Create a symbolic link
ln -s /usr/local/node_exporter-1.3.1.linux-amd64/ /usr/local/node_exporter
# Generate systemctl configuration
cat << EOF > /usr/lib/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
[Service]
User=root
Group=root
ExecStart=/usr/local/node_exporter/node_exporter
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Unit]
Description=node_exporter
After=network.target
EOF
# Start node_exporter
systemctl start node_exporter
systemctl status node_exporter
systemctl enable node_exporterNote!
node_exportermust be deployed on all cluster hosts. Repeat the above steps on each host.
Prepare a host that can access the exporter ports on all cluster nodes. This can be the Master, Standby Master, or a separate machine (Linux, macOS, Windows, etc.).
Install the latest version of Prometheus. Official download link: https://prometheus.io/download/.
The following commands use CentOS 7 as an example. For other operating systems, refer to their respective guides.
Note!
During installation, you may choose whether to include mxgate monitoring. The example below includes mxgate-related configuration. Remove that section if mxgate monitoring is not needed. See comments in the code.
# Download package
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.36.1/prometheus-2.36.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
# Extract to /usr/local and create symbolic link
tar -xf ./prometheus-2.36.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
ln -s /usr/local/prometheus-2.36.1.linux-amd64/ /usr/local/prometheus
# Create Prometheus user
useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M prometheus
# Create data directory
mkdir /data/prometheus -p
# Set ownership
chown -R prometheus:prometheus /usr/local/prometheus/
chown -R prometheus:prometheus /data/prometheus/
# Configure systemctl
cat << EOF > /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Documentation=https://prometheus.io/
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=prometheus
ExecStart=/usr/local/prometheus/prometheus --config.file=/usr/local/prometheus/prometheus.yml --storage.tsdb.path=/data/prometheus
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
# Edit Prometheus configuration
# Add matrixdb and node exporter IPs and ports in scrape_configs
# (matrixdb_exporter default port: 9273, node_exporter default port: 9100)
# Note: matrixdb and mxgate dashboards use the matrixdb_cluster label for cluster filtering.
# Add relabel_configs to replace job label with matrixdb_cluster.
# Set replacement to your cluster name.
# Example configuration:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "matrixdb_exporter"
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: ['job']
regex: .*
target_label: matrixdb_cluster
replacement: cluster1
action: replace
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9273"]
- job_name: "node_exporter"
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9100"]
# For multi-host clusters, list all host IPs and ports:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "matrixdb_exporter"
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: ['job']
regex: .*
target_label: matrixdb_cluster
replacement: cluster1
action: replace
static_configs:
- targets: ["192.168.0.1:9273", "192.168.0.2:9273", "192.168.0.3:9273"]
- job_name: "node_exporter"
static_configs:
- targets: ["192.168.0.1:9100", "192.168.0.2:9100", "192.168.0.3:9100"]
# Optional: Add the following block to enable mxgate monitoring, then restart Prometheus.
- job_name: "gate_exporter"
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: ['job']
regex: .*
target_label: matrixdb_cluster
replacement: cluster1
action: replace
static_configs:
- targets: ["192.168.0.1:9275"]
# Note: Pay attention to YAML indentation to avoid syntax errors.
# Start Prometheus
systemctl start prometheus
systemctl status prometheus
systemctl enable prometheusAfter startup, access the Prometheus Web UI to check the status: http://IP:9090/
In the Prometheus UI, go to Status → Targets:
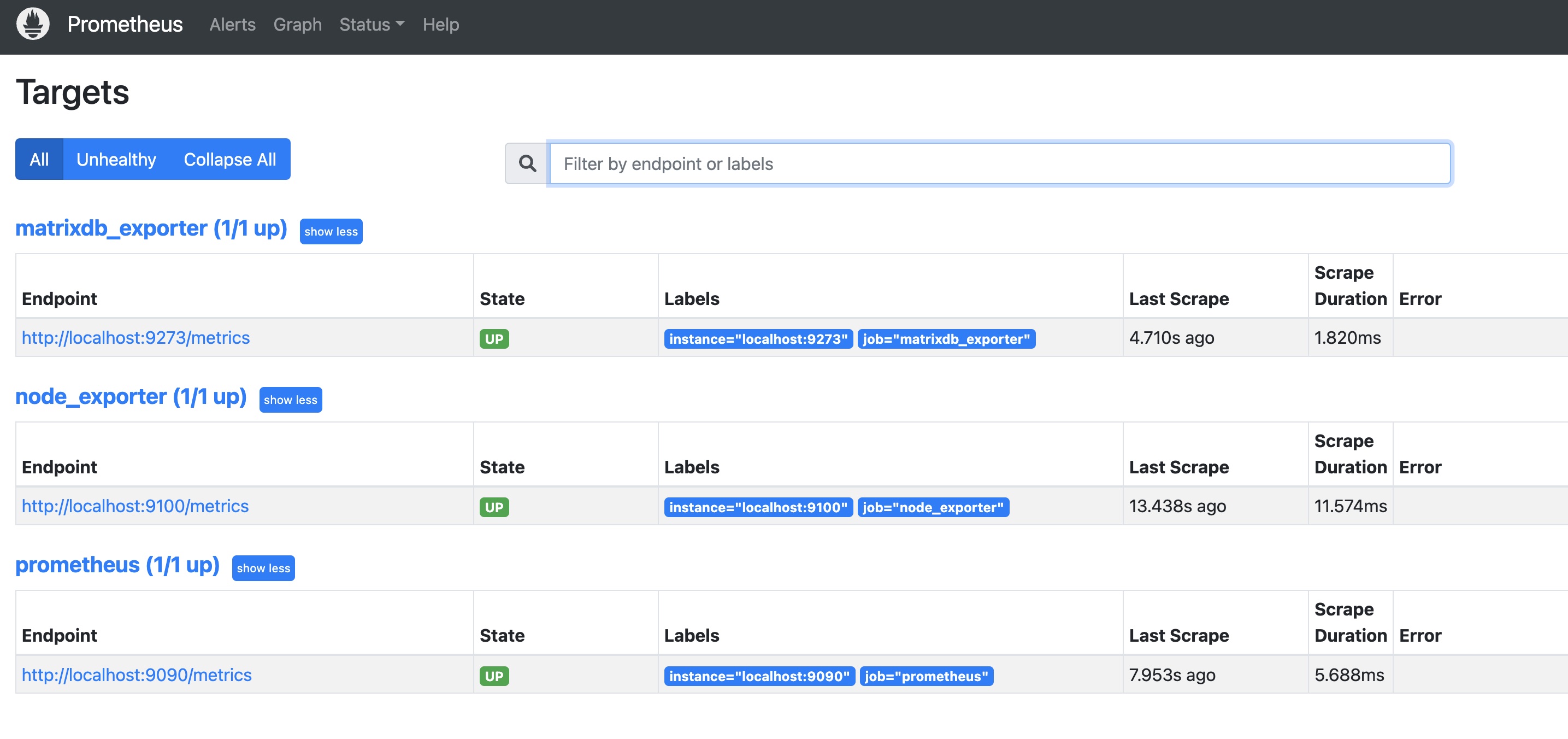
All configured exporters (matrixdb_exporter, node_exporter, and Prometheus itself) should show status UP, indicating successful deployment:
Prometheus stores monitoring data. Grafana retrieves and visualizes this data. Prepare a host that can access Prometheus (Grafana and Prometheus can be on the same host).
Grafana version must be at least 8.0.0. Use the latest version if possible. Download link: https://grafana.com/grafana/download.
The following commands use CentOS 7 as an example. For other systems, refer to their guides (run as root).
wget https://dl.grafana.com/enterprise/release/grafana-enterprise-8.5.5-1.x86_64.rpm
yum install grafana-enterprise-8.5.5-1.x86_64.rpmsudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
sudo systemctl enable grafana-serverAfter installation, access port 3000 on the host:
http://<IP_or_hostname>:3000Log in with the default credentials: admin / admin. Change the password for security.
After deploying the exporter, Prometheus, and Grafana, load the dashboard to visualize metrics.
Each dashboard requires a data source. First, add the data source:
Click the gear icon in Grafana and select Data Sources:
Click Add data source:

Select Prometheus under Databases:
Name the data source (e.g., MatrixDB-Prometheus) and enter the Prometheus server IP and port in URL:
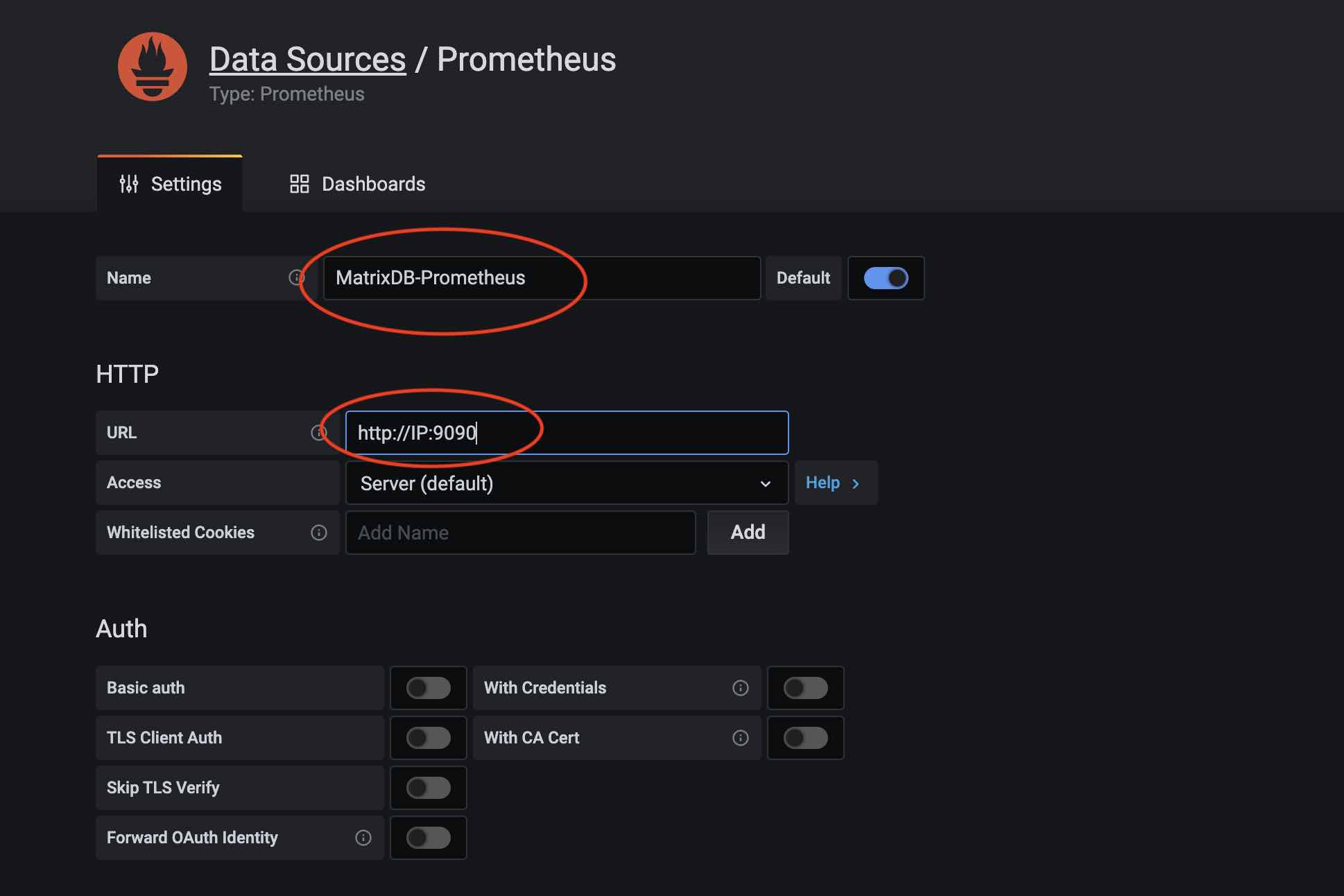
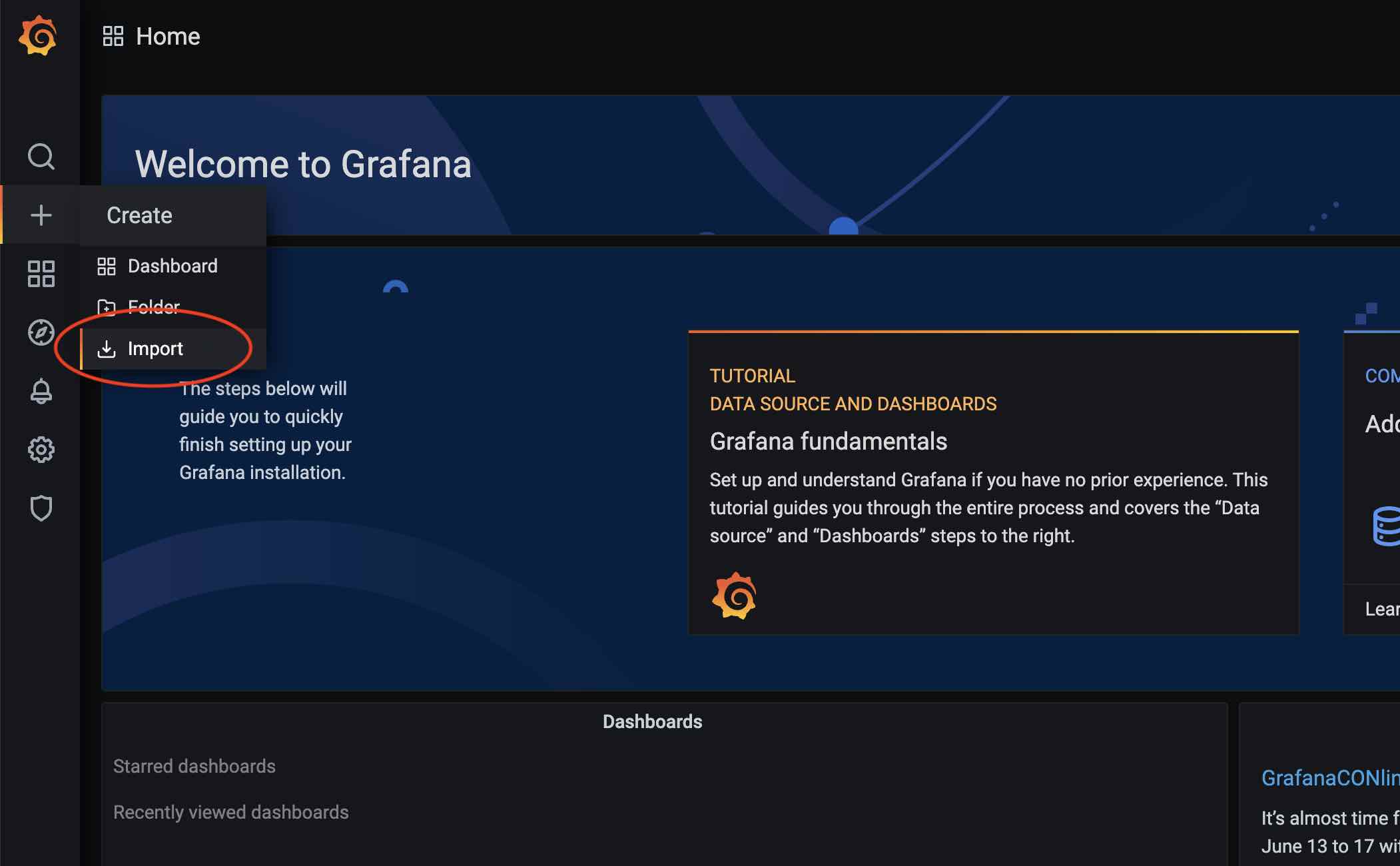
After adding the data source, import the dashboard. Click the + icon and select Import:
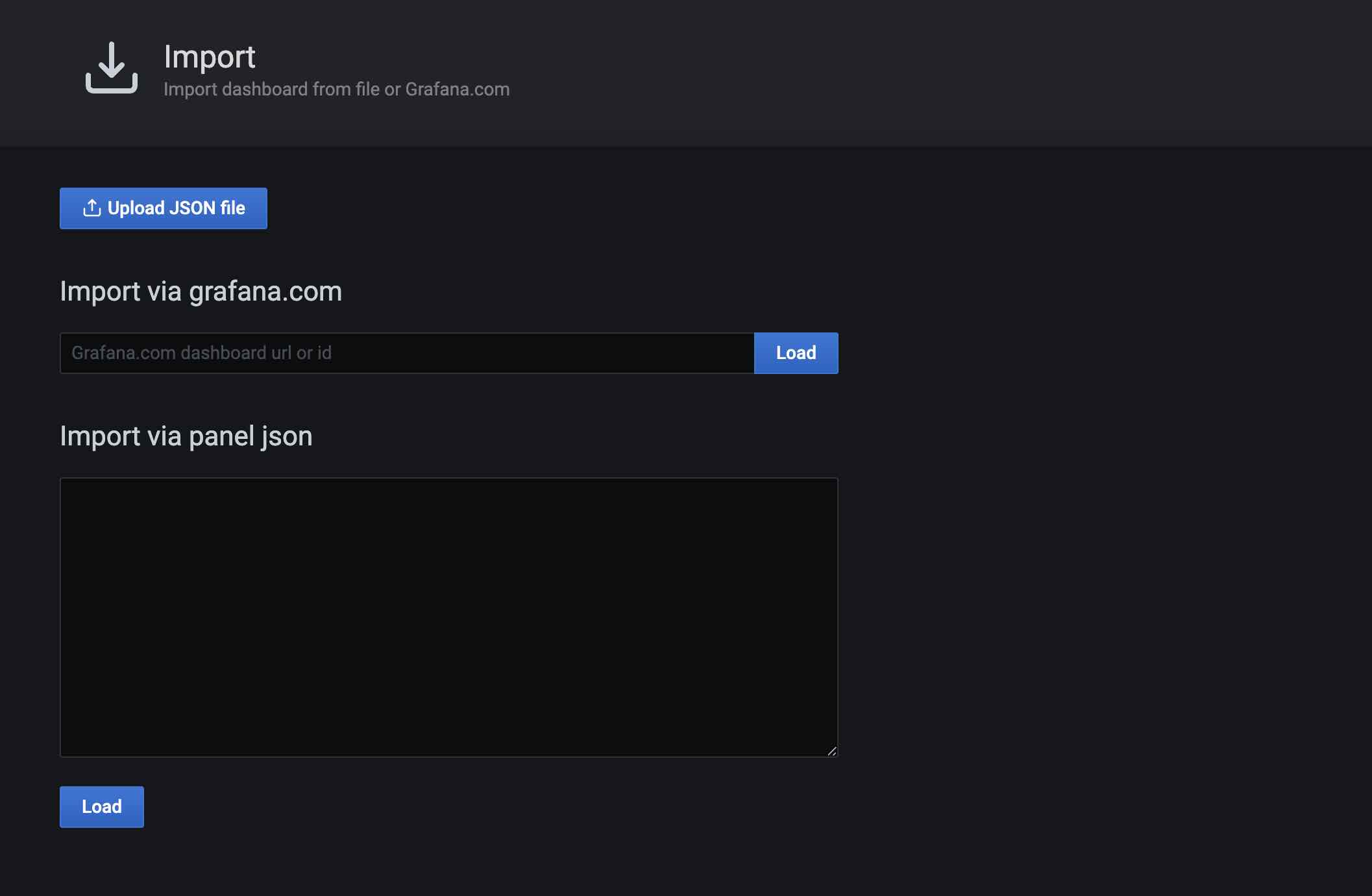
Import options: use official URL/ID, paste JSON, or upload a file. Here, upload from file. The YMatrix Prometheus dashboard is located at $GPHOME/share/doc/postgresql/extension/PrometheusDashboard.json in the installation directory:
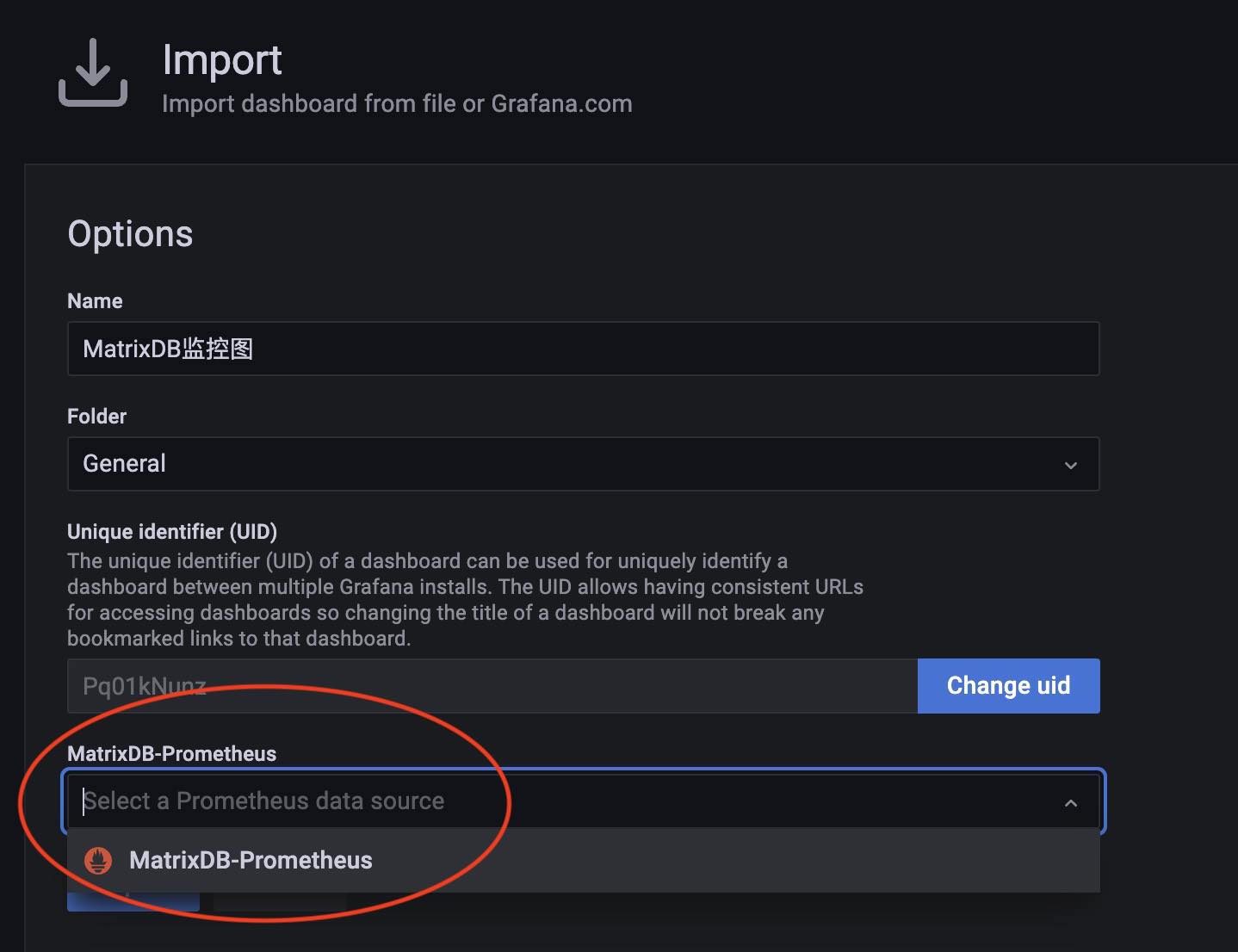
During import, select the Prometheus data source created earlier:
The imported dashboard now appears in the dashboard list.
For detailed interpretation of dashboard metrics, see YMatrix Monitoring Parameter Guide
The previous steps show how to add the YMatrix dashboard. Now, add the node_exporter dashboard.
The node_exporter dashboard is available on Grafana's website: Dashboard. Import it by entering the dashboard ID:
During import, select the previously added MatrixDB-Prometheus data source. If node_exporter uses a separate Prometheus instance, add a dedicated data source.

After enabling cluster metric collection, each host runs a collection service. Logs are stored in /var/log/matrixdb.
If you restart YMatrix or reboot and restart YMatrix, the matrixdb_exporter automatically starts without manual intervention.
To stop the matrixdb_exporter service, connect to the matrixmgr database and run:
psql -d matrixmgr
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_remove_exporter();To re-enable data collection, run:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_deploy_exporter();Note!
mxmgr_remove_exporterstops onlymatrixdb_exporter. You must stopnode_exporter, Grafana, and Prometheus separately.
Upgrade from the legacy monitoring system to the new Prometheus-based monitoring.
First, install and deploy Prometheus, and upgrade Grafana to the latest version:
# Disable legacy monitoring
psql -d matrixmgr
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_remove_all('local');
# Initialize and start new monitoring
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_init_exporter();Note!
Both monitoring systems can coexist. You can run the new system without disabling the old one, though this results in redundancy.
MatrixGate, a high-performance data ingestion component, also supports the Prometheus monitoring ecosystem. Typically, MatrixDB and MatrixGate metrics are stored in the same Prometheus instance. The following steps assume this setup.
Like the YMatrix exporter, deploying gate_exporter requires the matrixmgr database and the matrixts and matrixmgr extensions. Assume these are already created.
Call mxmgr_init_gate_exporter to initialize and start:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_init_gate_exporter();Upon success, a new schema named gate_exporter appears in the matrixmgr database. This schema contains tables and views for gate monitoring and configuration. Do not modify them.
This command starts gate_exporter on the Master host.
To stop gate_exporter, run mxmgr_init_gate_exporter:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_remove_gate_exporter();To restart, run mxmgr_remove_gate_exporter:
matrixmgr=# SELECT mxmgr_deploy_gate_exporter();Similar to the YMatrix dashboard, the MatrixGate dashboard file is located at $GPHOME/share/doc/postgresql/extension/MxgateDashboard.json. Import this file to load the dashboard.
For detailed metric interpretation, see MatrixGate Monitoring Parameter Guide