YMatrix
Quick Start
Connecting
Benchmarks
Deployment
Data Usage
Manage Clusters
Upgrade
Global Maintenance
Expansion
Monitoring
Security
Best Practice
Technical Principles
Data Type
Storage Engine
Execution Engine
Streaming Engine(Domino)
MARS3 Index
Extension
Advanced Features
Advanced Query
Resource Groups
Federal Query
Grafana
Backup and Restore
Disaster Recovery
Guide
Performance Tuning
Troubleshooting
Tools
Configuration Parameters
SQL Reference
YMatrix 6 introduces etcd to store cluster configuration and state information. etcd is critical: any abnormality may lead to database instability or even system crashes.
This document describes how to install and deploy etcd monitoring. We recommend installing this monitoring setup for all production clusters, as healthy etcd status is a prerequisite for stable database operation.
Visit the Prometheus official website and download the following:
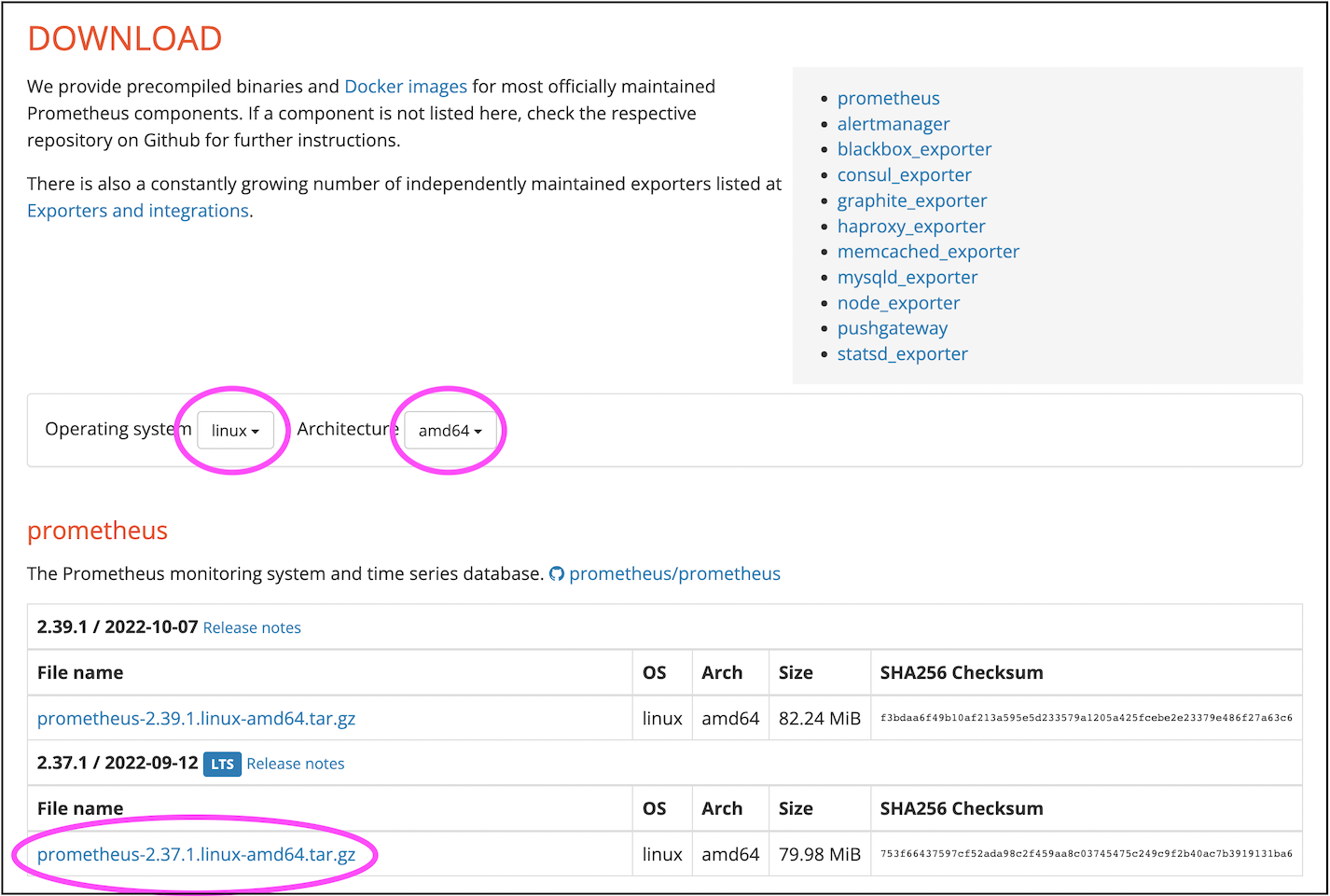
Upload the downloaded tar package to a Linux server. If possible, run Prometheus on a dedicated server. If resources are limited, you may temporarily place it on the standby or master host.
$ tar xvfz prometheus-*.tar.gzYou can move the extracted prometheus-* directory to /usr/local/.
Edit the configuration file:
$ cd prometheus-*
sudo vi prometheus.ymlAppend the following content to the end of the file:
- job_name: "etcd"
static_configs:
- targets: ["172.31.33.128:4679", "172.31.45.253:4679", "172.31.35.134:4679"]The targets array must be replaced with the addresses of all etcd nodes in your cluster.
You can find this information in the /etc/matrixdb6/physical_cluster.toml file on the Master host:
$ cat physical_cluster.toml
cluster_id = '79LhQxjuwmXgSWZCjcdigF'
supervisord_grpc_port = 4617
deployer_port = 4627
etcd_endpoints = ['http://10.0.159.1:4679', 'http://10.0.172.185:4679', 'http://10.0.170.90:4679', 'http://10.0.146.2:4679', 'http://10.0.146.195:4679', 'http://10.0.150.110:4679', 'http://10.0.169.149:4679']Note!
If the/etc/matrixdb6/physical_cluster.tomlfile does not exist and no etcd process is found, your cluster was not deployed using the 6.x architecture and does not require etcd monitoring.
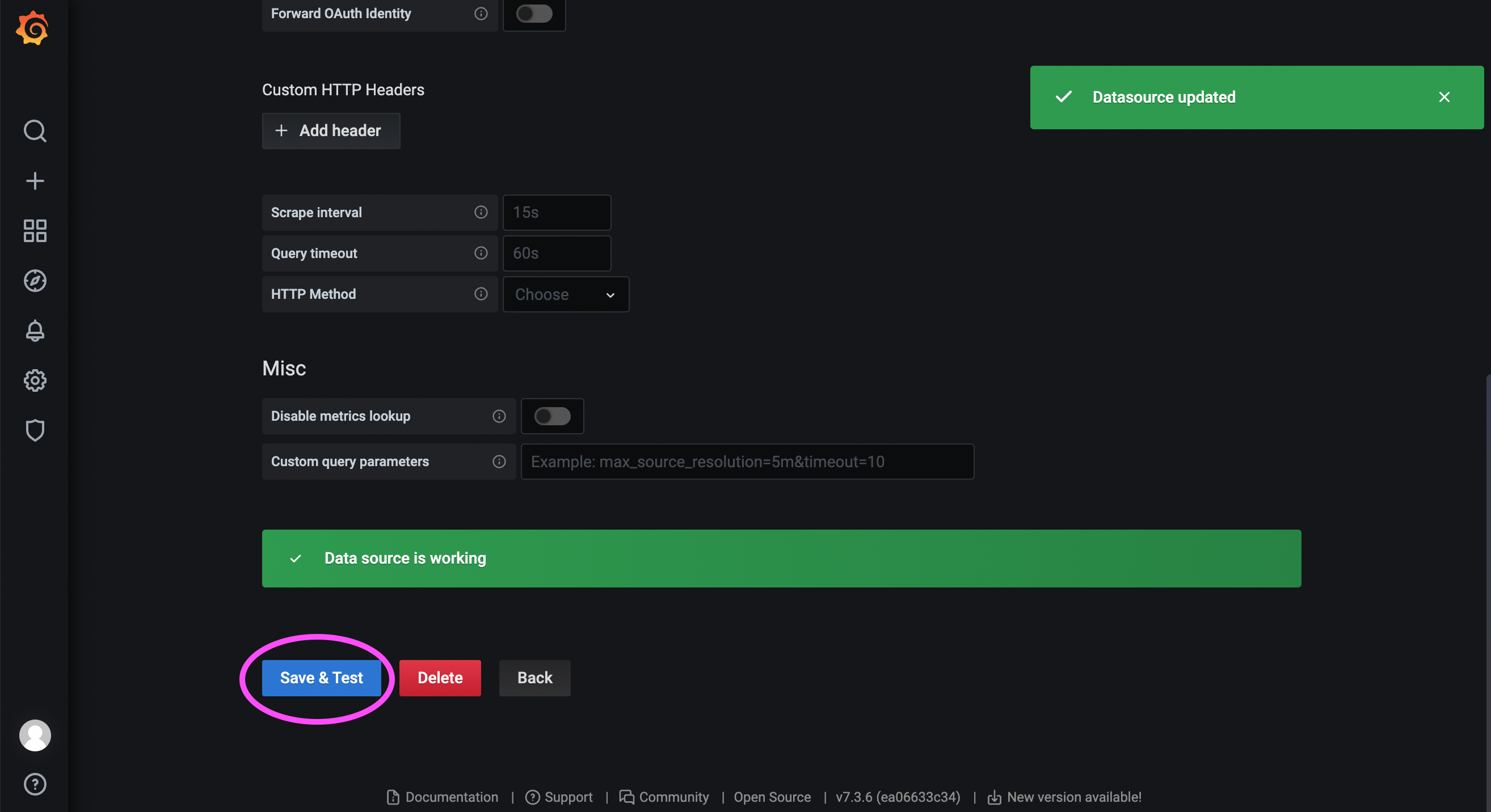
./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.ymlNote!
Typically, you should run Prometheus as a background system service by configuring it as a systemd service.
Refer to the official documentation for installing Grafana.
Note!
Grafana version 8.2.5 or higher is required.
First, log in to the Grafana web interface. The default URL is:
http://<IP_or_domain_of_the_host>:3000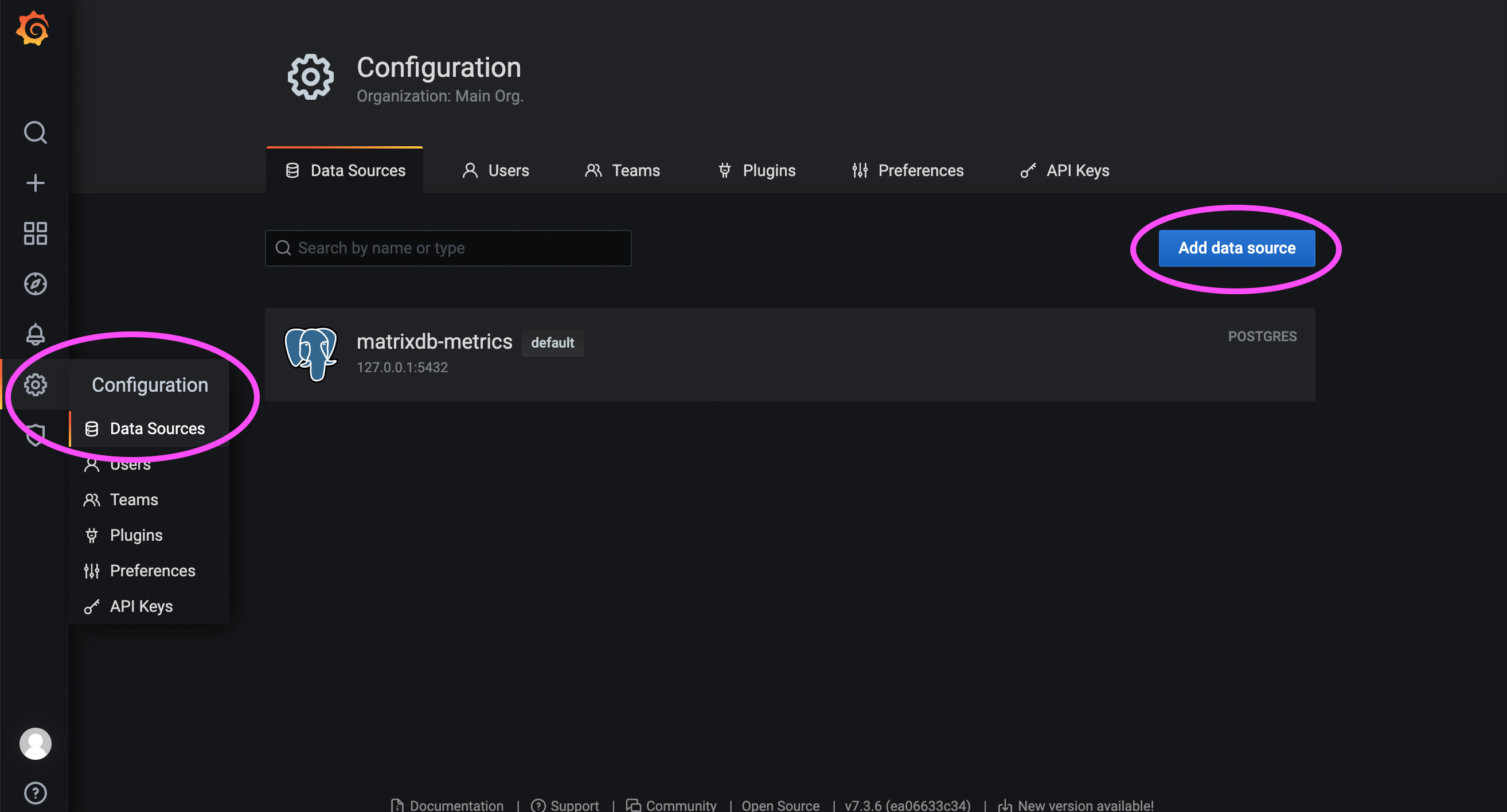
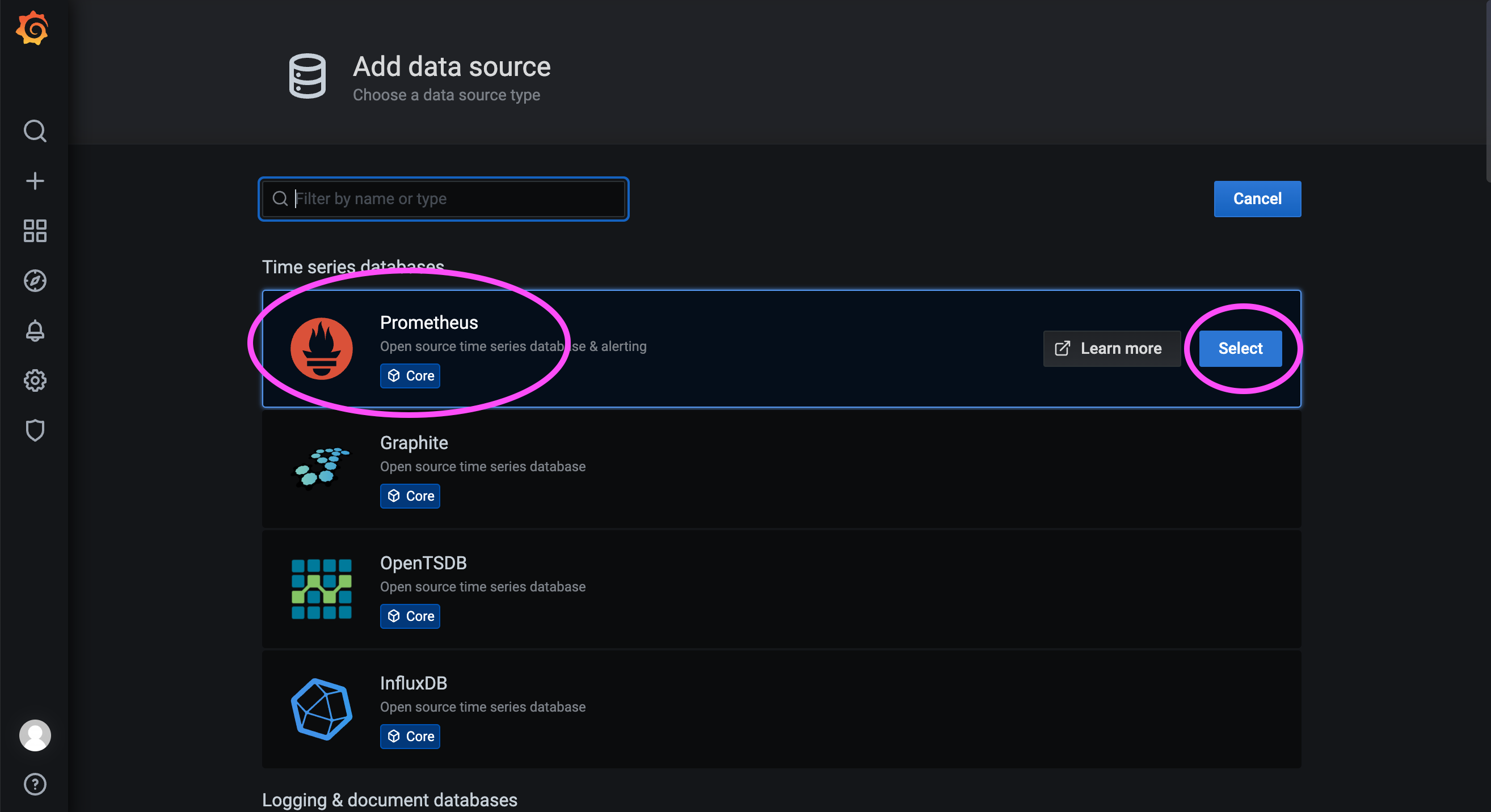

172.31.23.21:9090 is the service port of the Prometheus instance deployed in the previous step.
Visit the Grafana community:
https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/?search=Etcd+Cluster+Overview
The above link shows community-provided dashboards:
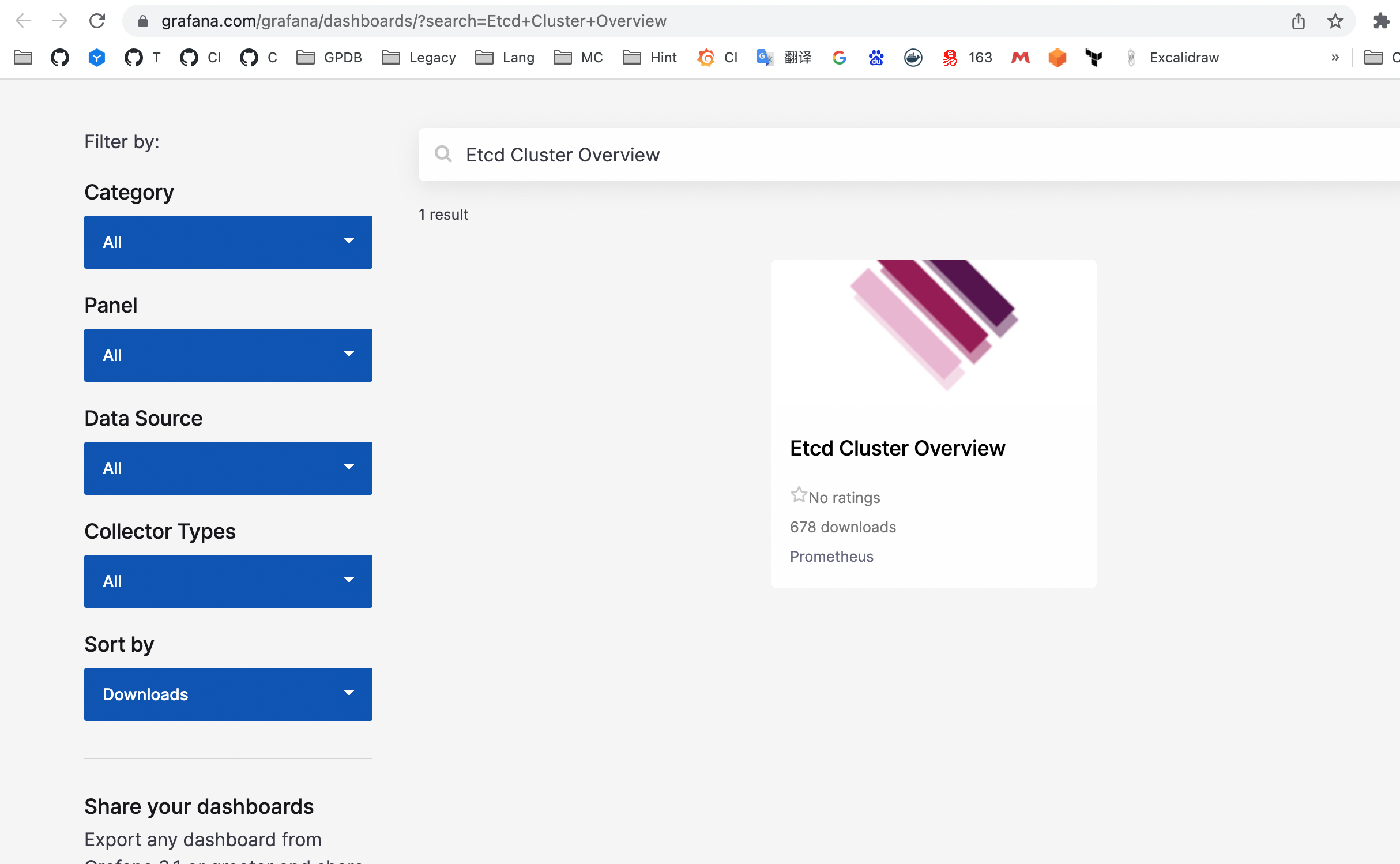
Click into the desired dashboard to obtain its ID:
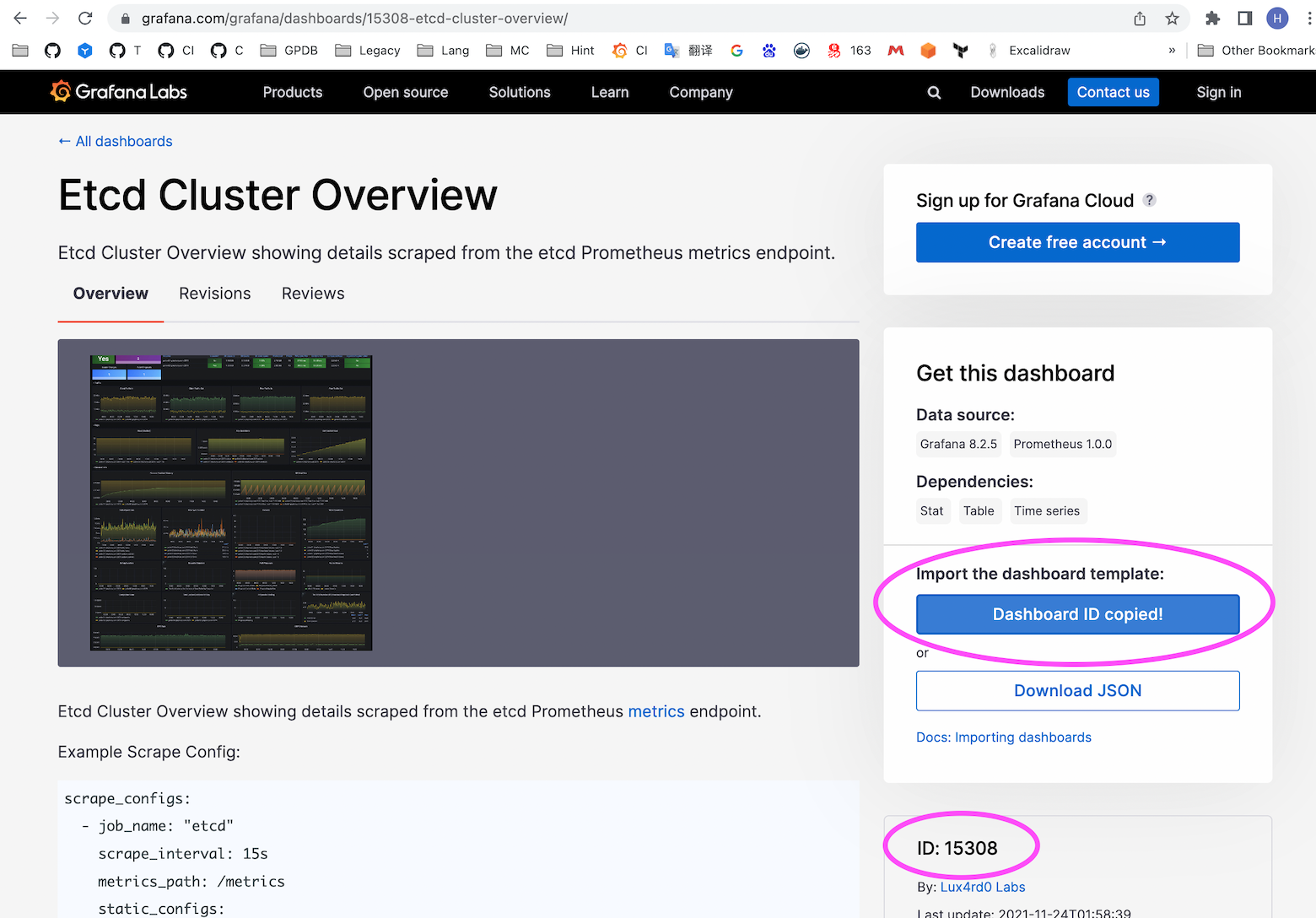
Note!
The dashboard associated with this ID may change over time. Currently, the ID is 15308; users should verify based on their own search results.
As shown below, import dashboard ID 15308:
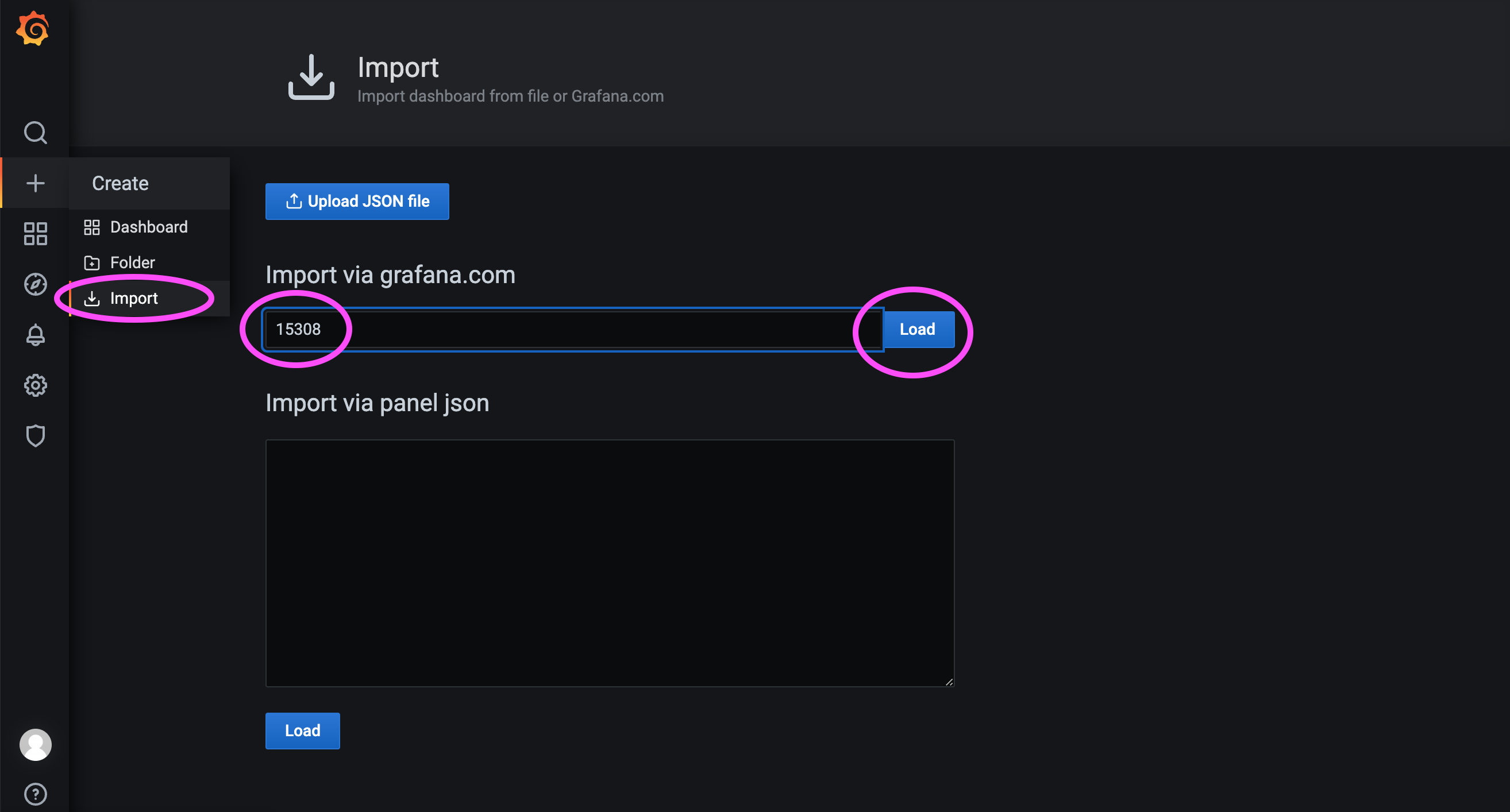
Then select the data source configured earlier and load the dashboard:
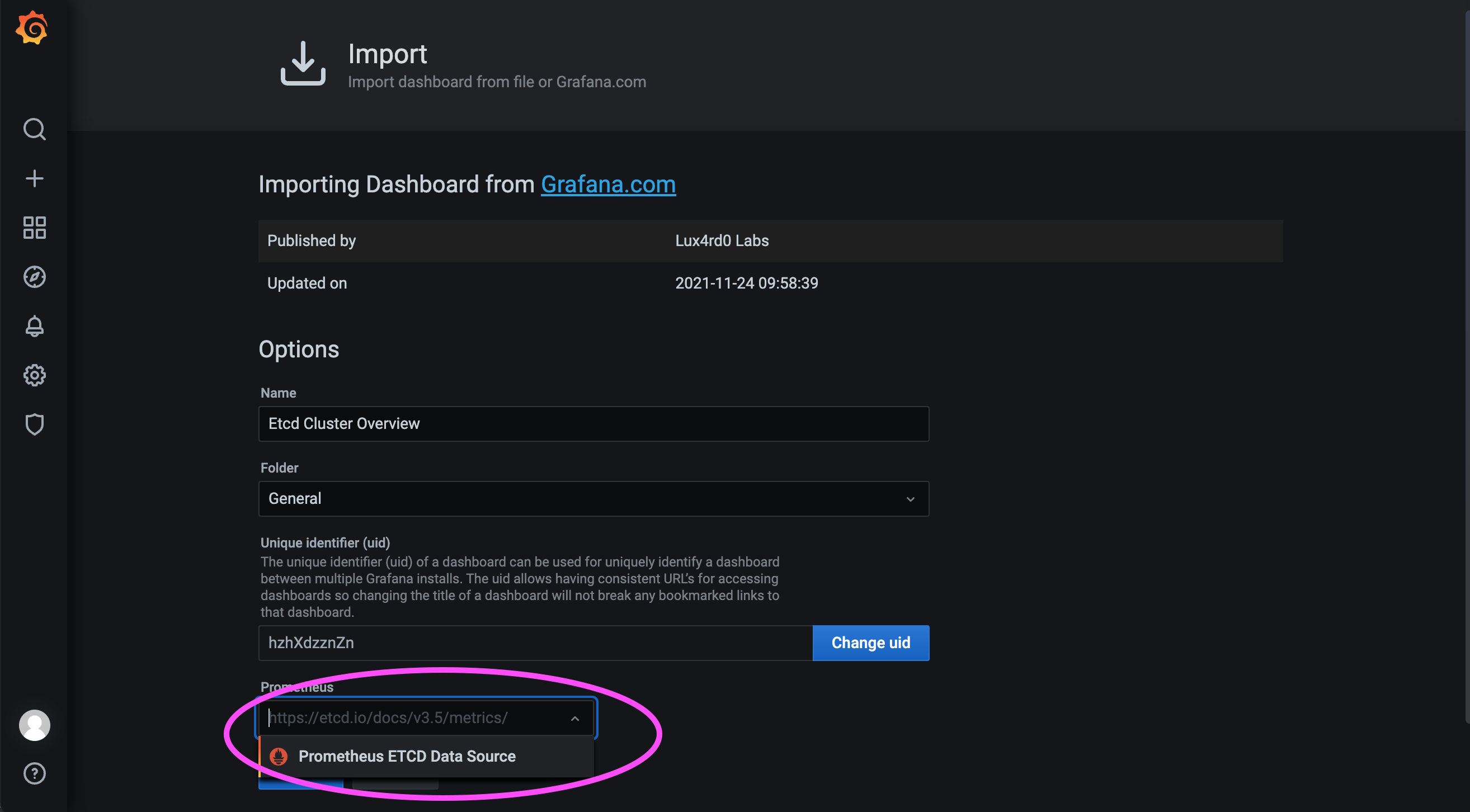
If the server is in an internal network, importing by ID 15308 may fail. In that case, download the JSON file of the dashboard from an internet-connected machine and import it manually:
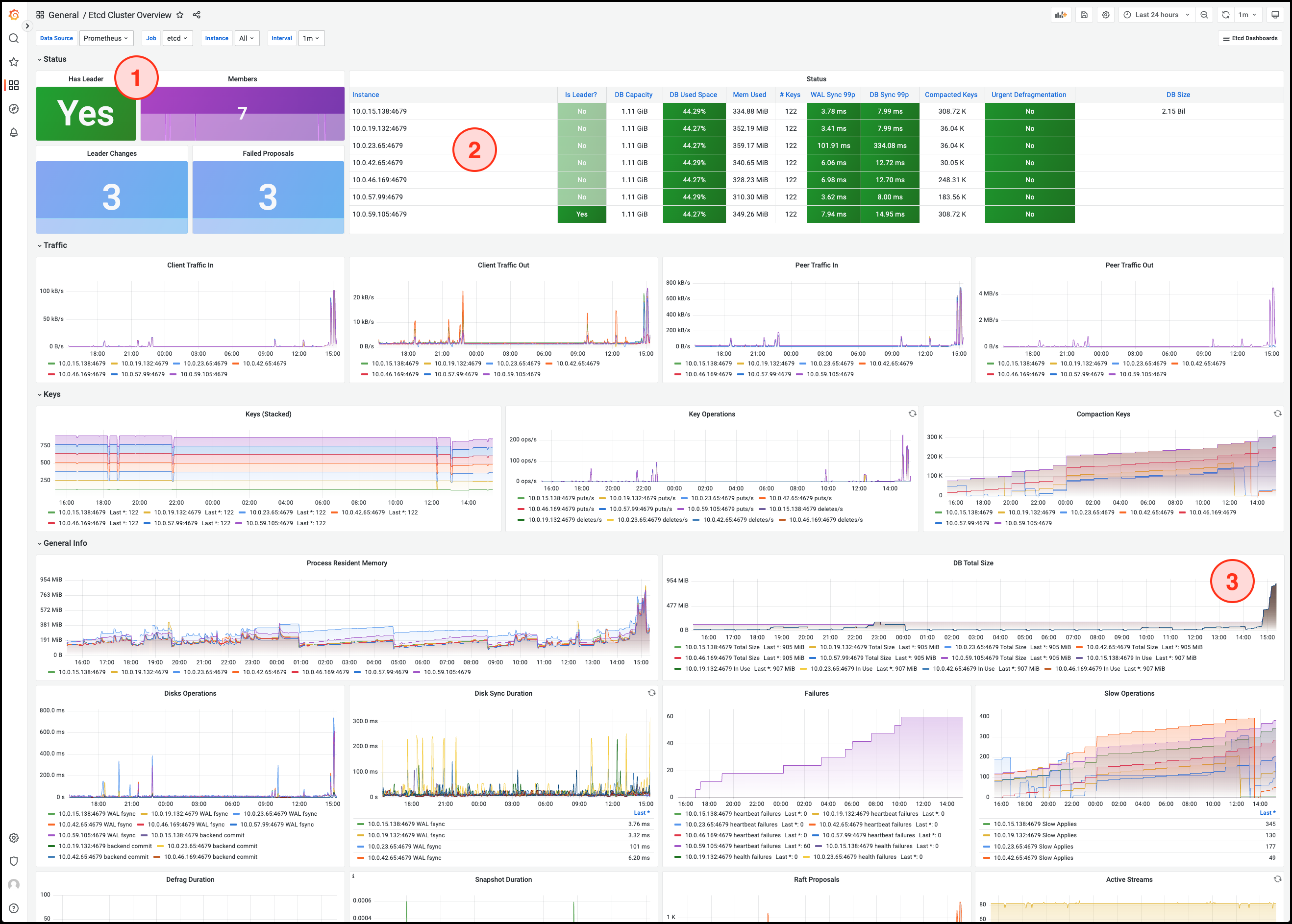
etcd Service Status and Member Count
Quorum Member List and Process Status
DB Total Size displays the growth of etcd data over time. An abnormal increase may lead to the database reaching its size limit.
Note!
For more metrics and detailed explanations, refer to the etcd official documentation.